|
|
|
|
| 192.168.14.4 |
| |
|
|
|
|
| 255.255.255.128 |
| |
|
|
| GRF 400 | GRF 1600 | SP Switch |
|
|
| Switch |
|
|
| Adapter | Switch |
|
node 1 | SP Switch | HIPPI | HIPPI |
| node 6 | ||
| SP | Adapter |
|
|
| SP |
|
|
|
|
| SP Switch |
| ||
192.168.13.1 |
|
|
|
|
| 192.168.14.6 | |
|
|
|
| Adapter |
| ||
255.255.255.0 |
|
|
|
|
| 255.255.255.0 | |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
| 192.168.14.129 |
| |
|
|
|
|
| 255.255.255.128 |
| |
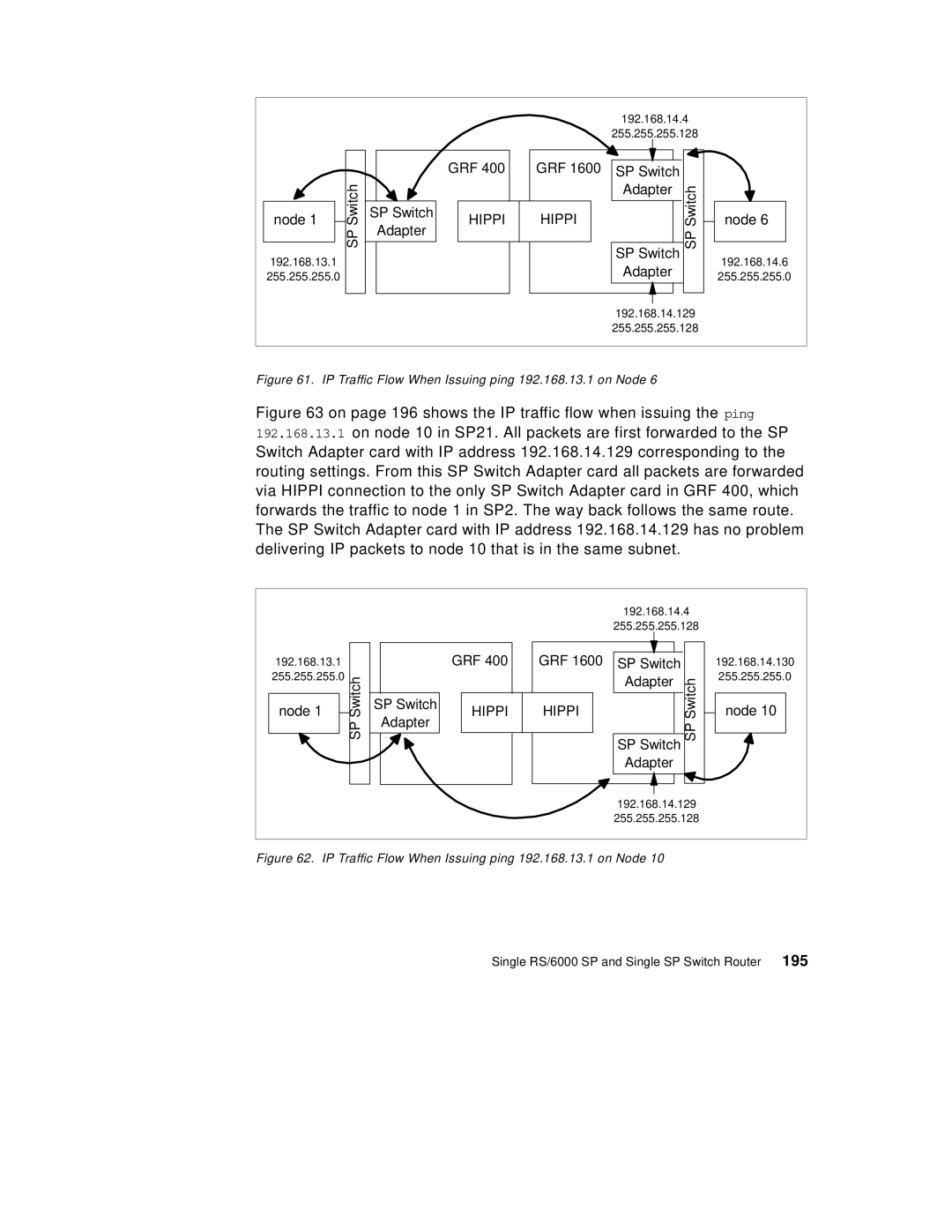
Figure 61. IP Traffic Flow When Issuing ping 192.168.13.1 on Node 6
Figure 63 on page 196 shows the IP traffic flow when issuing the ping 192.168.13.1 on node 10 in SP21. All packets are first forwarded to the SP Switch Adapter card with IP address 192.168.14.129 corresponding to the routing settings. From this SP Switch Adapter card all packets are forwarded via HIPPI connection to the only SP Switch Adapter card in GRF 400, which forwards the traffic to node 1 in SP2. The way back follows the same route. The SP Switch Adapter card with IP address 192.168.14.129 has no problem delivering IP packets to node 10 that is in the same subnet.
|
|
|
|
| 192.168.14.4 |
| |
|
|
|
|
| 255.255.255.128 |
| |
192.168.13.1 |
|
| GRF 400 | GRF 1600 | SP Switch |
| 192.168.14.130 |
255.255.255.0 | Switch |
|
|
| Adapter | Switch | 255.255.255.0 |
|
|
|
|
| |||
node 1 | SP Switch | HIPPI | HIPPI |
| node 10 | ||
| SP | Adapter |
|
|
| SP |
|
|
|
|
| SP Switch |
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| Adapter |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 192.168.14.129 |
| |
|
|
|
|
| 255.255.255.128 |
| |