|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| $ 53,000 |
|
|
|
|
| ||||
|
| HIPPI Adapter | 13,500 |
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| 66,500 | $ 53,000 |
|
|
|
| |
|
| 135 MHz | Wide Node |
|
| 48,000 |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| 19,000 |
|
|
|
| |||
|
| 64 MB memory |
|
| 3,200 |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| 72,000 |
| $ 53,000 |
|
| |||
|
| 4.5 GB Disk |
|
| 1,950 |
|
|
| |||
|
|
| 595 | 48,000 |
|
|
| ||||
|
| Ethernet |
|
|
| 20,000 |
|
| |||
|
| SP Switch Adapter |
|
| 10,000 | 3,200 |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
| 73,000 |
|
| ||||||
|
| HIPPI Adapter |
|
| 17,500 | 1,950 |
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||
|
|
|
| 595 |
| 48,000 |
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
| 81,245 |
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
| 10,000 |
| 3,200 |
|
| |
|
|
| 4 FDDI |
|
| 15,980 |
| 1,950 |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 75,730 |
| 595 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 10,000 |
|
| |
|
|
|
| 2 ATM 155 Adapters * |
|
|
|
| 5,390 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 69,135 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
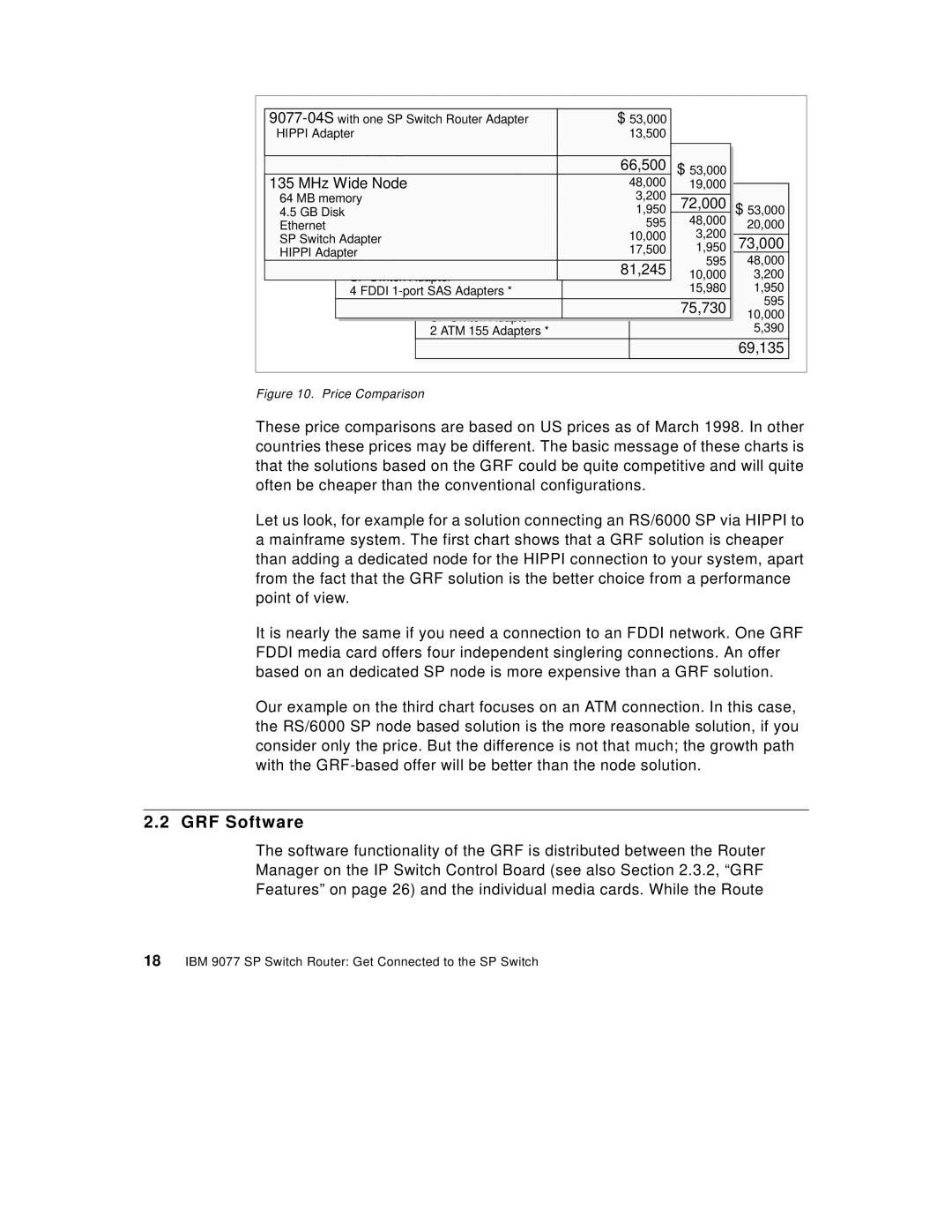
Figure 10. Price Comparison
These price comparisons are based on US prices as of March 1998. In other countries these prices may be different. The basic message of these charts is that the solutions based on the GRF could be quite competitive and will quite often be cheaper than the conventional configurations.
Let us look, for example for a solution connecting an RS/6000 SP via HIPPI to a mainframe system. The first chart shows that a GRF solution is cheaper than adding a dedicated node for the HIPPI connection to your system, apart from the fact that the GRF solution is the better choice from a performance point of view.
It is nearly the same if you need a connection to an FDDI network. One GRF FDDI media card offers four independent singlering connections. An offer based on an dedicated SP node is more expensive than a GRF solution.
Our example on the third chart focuses on an ATM connection. In this case, the RS/6000 SP node based solution is the more reasonable solution, if you consider only the price. But the difference is not that much; the growth path with the
2.2 GRF Software
The software functionality of the GRF is distributed between the Router Manager on the IP Switch Control Board (see also Section 2.3.2, “GRF Features” on page 26) and the individual media cards. While the Route