Release
G10 Cmts Hardware Guide
Table of Contents
Chapter
Initial Installation
Part
Appendixes
Index
Viii JUNOSg 3.0 G10 Cmts Hardware Guide
List of Figures
List of Figures
Front Fan Tray Replacement 164
List of Figures
List of Tables
List of Tables
List of Tables
Objectives
Document Organization
Audience
Audience
Documentation Conventions
Documentation Conventions
Documentation Feedback
Contact Juniper Networks
Contact Juniper Networks
Part
JUNOSg 3.0 G10 Cmts Hardware Guide
System Overview
System Description
System Description
Typical Cmts Location
Headend Architecture
Field-Replaceable Units FRUs
Field-Replaceable Units FRUs
G10 Cmts Features and Functions
G10 Cmts Features and Functions
Functional Overview
Broadband Cable Processor Asic
G10 Cmts Components
G10 Cmts Components
G10 Cmts
G10 Cmts Hardware Overview
G10 Cmts Management
G10 Cmts Management
Front View of Fully Configured Chassis
G10 Cmts Hardware Overview
Front View of Partially Configured Chassis
Rear View of Fully Configured Chassis
Air Management Panel
Rear
JUNOSg 3.0 G10 Cmts Hardware Guide
G10 Cmts Hardware Overview
G10 Cmts Hardware Overview
Hardware Component Overview
Chassis
Physical Characteristics
Chassis Physical Specifications
Specification Value
Chassis
Card Cage and Midplane Specifications
Chassis Environmental Specifications
Card Cage and Midplane
Signals carried by the connectors are described in Table
Midplane P1 P5 Connectors
Front View
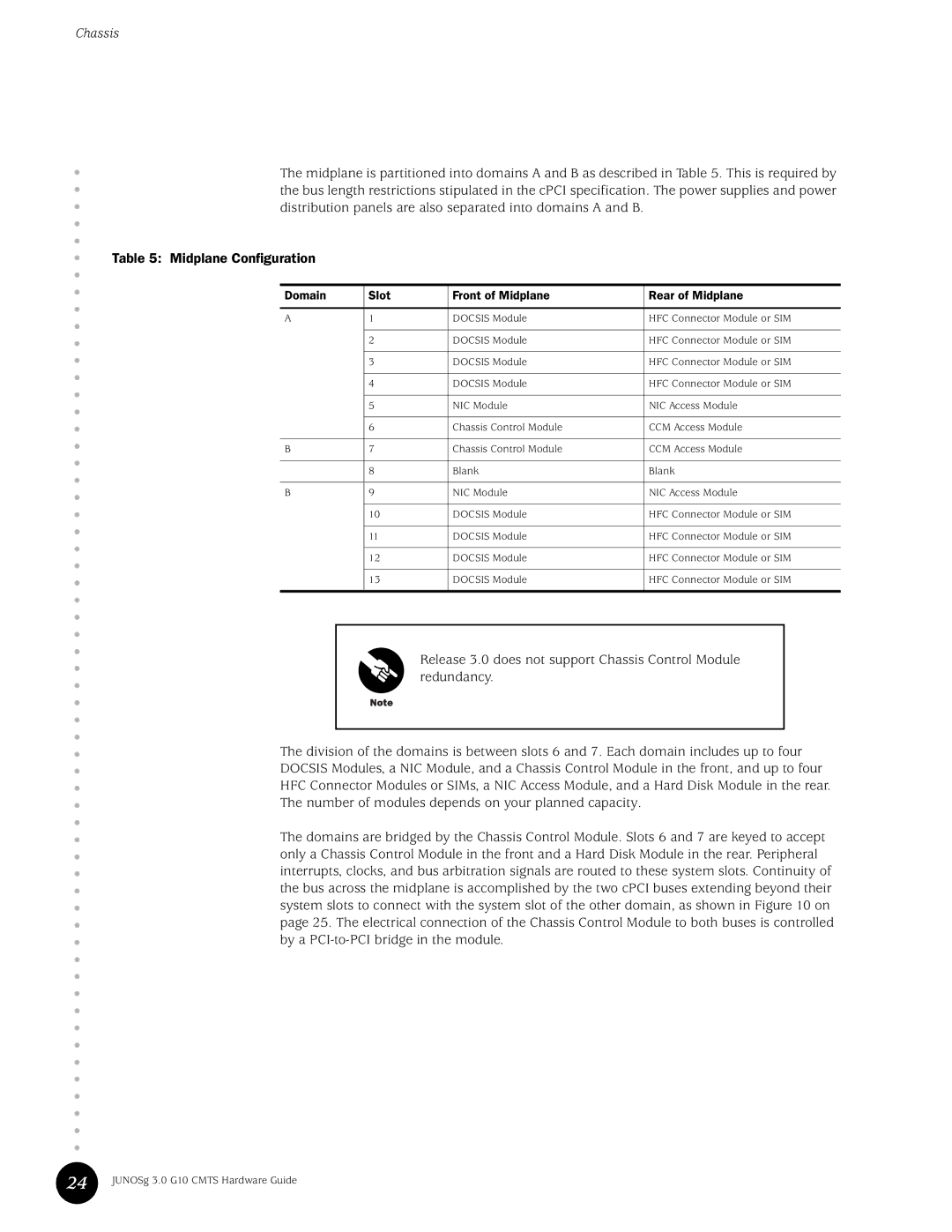
Distribution panels are also separated into domains a and B
Chassis Versions
Midplane Domains
Power Supplies
Power Supply LEDs
Cmts
Power Transition Modules
Cooling and Fans
Docsis Module
Docsis Module Front Panel
Functional Characteristics
Data Packet Processing
Higher Layer Functions
MAC Layer Functions
Modem Management
Physical and Electrical Characteristics
Docsis Module Physical Dimensions
Docsis Module Operational Characteristics
Docsis Module LEDs
Chassis Control Module
Chassis Control Module
Through the Chassis Control Module
Chassis Control Module Front Panel
Configuration, State, and Alarm Data
Chassis Control Module Physical Dimensions
Chassis Control Module Connectors
Chassis Control Module Switches
Chassis Control Module LEDs
NIC Module
NIC Module
NIC Module Front Panel
NIC Module Physical Dimensions
NIC Module Connectors
Single-Mode, Midrange Gbic Specifications
Single-Mode, Long-Range Gbic Specifications
Parameter Value
Multimode Gbic Specifications
1000BT Gbic Specifications
NIC Module LEDs
Color Function
NIC Access Module
NIC Access Module LEDs
Chassis Rear Modules
Chassis Rear Modules
NIC Access Module Front Panel
HFC Connector Module
HFC Connector Module Fast Ethernet LEDs
HFC Connector Module Rear Panel
G10 Cmts Data Flow
Switched I/O Module
SIM Fast Ethernet Port LEDs
SIM Rear Panel
Hard Disk Module
Hard Disk Module Rear Panel
System Architecture Overview
JUNOSg Internet Software Overview
Routing Engine Software Components
JUNOSg Internet Software Overview
Routing and Forwarding Tables
Interface Process
Software Installation and Upgrade Procedures
Tools for Accessing and Controlling the Software
Software Monitoring Tools
Downstream Data Path
Data Path Processing
Data Path Processing
Upstream Data Path
G10 Cmts Data Flow
Part
JUNOSg 3.0 G10 Cmts Hardware Guide
Prepare the Site
Safety Precautions
Safety Precautions
Safety Precautions
JUNOSg 3.0 G10 Cmts Hardware Guide
AC Power
Power
Power
DC Power
G10 Cmts Environmental Specifications
Environment
Environment
Mounting
Mounting
Tools and Equipment Required for Installation
Tools and Equipment Required for Installation
Characterization of Installation Site
Coaxial Cable Requirements
Coaxial Cable Requirements
Coaxial Cable Requirements
Characterization of Installation Site
RF Plant/HFC Environment Characterization
Existing Docsis Service Characterization
Upstream Cmts Parameter Characterization
Upstream Parameters Port
Characterization of Installation Site
Downstream Cmts Parameter Characterization
Downstream Parameters Port
Upstream Frequency Spectrum Utilization
Frequency Description of Utilization
Summary Checklist
Summary Checklist
Average Noise Spectrum Analyzer Settings
Setting Value
Noise Measurement Methodology
Average Upstream Noise Measurement
Peak Noise Spectrum Analyzer Setup
Average Upstream Noise Measurement Example
Additional Characterization Tables
Additional Characterization Tables
Docsis Service
Upstream Cmts Parameter Characterization
Additional Characterization Tables
Verification of Shipping Cartons
Verification of Shipping Cartons
G10 Cmts Installation Checklist
G10 Cmts Installation Checklist
Step Number Completion Status
Connect to Power Sources
Install the Cmts
Ground the Chassis
Ground the Chassis
Rack Mounting
Air Flow Through Chassis
17.3 in 439.4 mm 18.6 in 472.6 mm Front
Lifting the Chassis
Rack-Mounted Chassis
100
Rack Fully Populated with Three G10 Cmts Chassis
Install Power Supplies
Install Power Supplies
101
Power Supply Installation
102
Install a Docsis Module
Install a Docsis Module
104
Air Management Module Removal
Install an HFC Connector Module or SIM
Install an HFC Connector Module or SIM
106
HFC Connector Module Installation
107
Install a Chassis Control Module
Install a Hard Disk Module
Install a NIC Access Module
Install a Chassis Control Module
Cable an HFC Connector Module or SIM
Cable an HFC Connector Module or SIM
110
On page 54 for port labeling
111
112
Rear Coaxial Cable Connections
113
Cable a Chassis Control Module
114
Cable a NIC Module
Cable a NIC Access Module
Cable a NIC Access Module
115
116
NIC Access Module Cable Connections
117
NIC Access Module in Slot
NIC Access Module Wiring Plan
118
Connect to Power Sources
Attach a PC to the Chassis Control Module
119
Attach a PC to the Chassis Control Module
Connect to Power Sources
AC Power Cord and Retainer Clip
Terminal block. The guard will be reinstalled in step
DC Power Transition Module
Power On the G10 Cmts
Connect the Power and Perform Initial Configuration
123
Power On the G10 Cmts
Power Fault
Docsis Module LED Status
125
Status Meaning
Chassis Control Module LED Status
NIC Module LED Status
Power On and Configure the PC
Power On and Configure the PC
NIC Access Module LED Status
127
Perform Initial Software Configuration
Perform Initial Software Configuration
129
Root@host-name#commit
Troubleshooting and Maintenance
131
JUNOSg 3.0 G10 Cmts Hardware Guide
RF Measurements
Downstream RF Measurement in Catv Mode
Downstream RF Measurement in Catv Mode
Downstream RF Measurement in Spectrum Analyzer Mode
Downstream RF Measurement in Spectrum Analyzer Mode
Rf-power rf-power
Cable-options downstream hierarchy level
Press the Span key and enter 6 MHz
Upstream RF Measurement
Upstream RF Measurement
Cable-options upstream
Preamble
Multiple Upstream Bursts
Upstream RF Measurement
Troubleshooting
Features for Troubleshooting
Cable modem flaps command
Features for Troubleshooting
Flap List
Flap List Association to Potential Issues
Output Field Value Potential Issues
To establish an operational baseline
Local Event Log
Local Event Log Headings Displayed
User@host show log cable
Output Field Object Meaning
Operational Commands
PBC-CMTS-MIB MIB
ServiceGuard Management System
Cmts Is Not Powering Up
Cmts Power and Booting Issues
Cmts Power and Booting Issues
Cmts Powers Down
Ideal HFC Plant Configuration Issues
Ideal HFC Plant Configuration Issues
Cable Modem Cannot Successfully Range
Cable Modem Cannot Establish IP Connectivity
Cable Modem Cannot Successfully Register
User@host show cable modem
Cable Modem Throughput is Slow
User@host show cable qos-profile
Ideal HFC Plant Configuration Issues
User@host show cable modem summary total interface
Ideal HFC Plant Configuration Issues
HFC Plant Related Issues
HFC Plant Related Issues
Cable Modem is Dropped
Cable Modem Cannot Successfully Range
CMTS, which reduces the cable modem throughput
Replacement Procedures
Remove Power Supplies
Power Supplies
Power Supply Removal
Replace a Fan Tray
Fan Trays
Fan Trays
Front Fan Trays
Front Fan Tray Replacement
Rear Fan Tray Replacement
Remove a Docsis Module
Module Removal
Module Removal
Docsis Module Removal
Remove an HFC Connector Module or SIM
Remove a Chassis Control Module
User@host request system halt
Remove a NIC Access Module
Remove a Hard Disk Module
Remove a NIC Module
170
171
JUNOSg 3.0 G10 Cmts Hardware Guide
Safety
Agency Certifications
Immunity
Agency Certifications
Radio Frequency RF Specifications
175
Radio Frequency RF Specifications
Downstream RF Channel Transmission Characteristics
Upstream RF Channel Transmission Characteristics
177
Downstream RF Signal Output Characteristics
Docsis Downstream Channel Rates and Spacing
Symbol Rate Channel Width Bit-rate/sec Ksym/sec KHz1
179
Docsis Maximum Upstream Channel Rates and Widths
16QAM
Radio Frequency RF Specifications
EIA Channel Plan
EIA Channel Plans
Channel
EIA Channel Plans
AAA
EIA Channel Plans
STD IRC HRC
EIA Channel Plans
187
JUNOSg 3.0 G10 Cmts Hardware Guide
Index
Index
Docsis
LED
10, 16, 68, 89, 124, 149
Index
Index