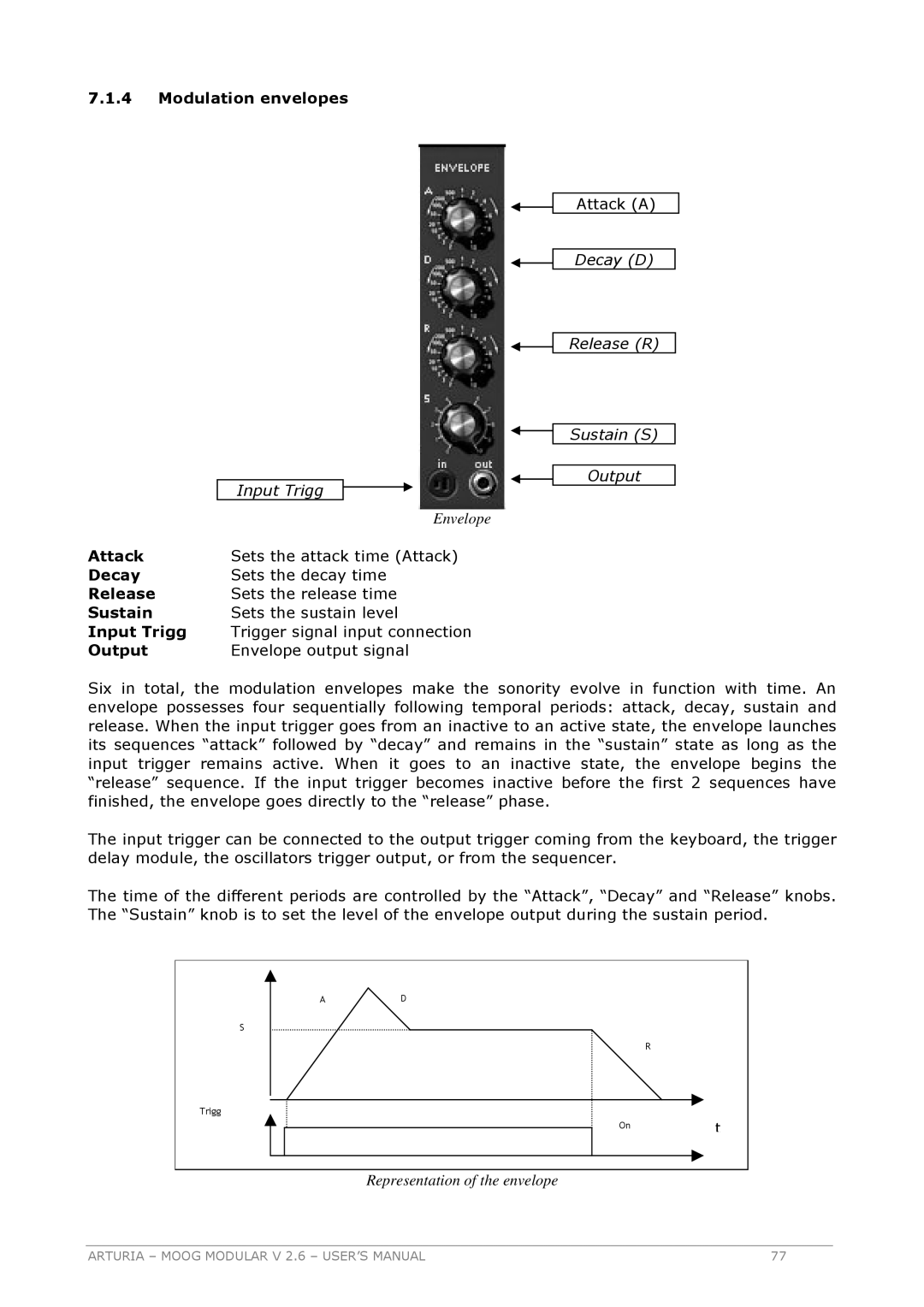
7.1.4Modulation envelopes
Input Trigg
Envelope
Attack (A)
Decay (D)
Release (R)
Sustain (S)
Output
Attack | Sets the attack time (Attack) |
Decay | Sets the decay time |
Release | Sets the release time |
Sustain | Sets the sustain level |
Input Trigg | Trigger signal input connection |
Output | Envelope output signal |
Six in total, the modulation envelopes make the sonority evolve in function with time. An envelope possesses four sequentially following temporal periods: attack, decay, sustain and release. When the input trigger goes from an inactive to an active state, the envelope launches its sequences “attack” followed by “decay” and remains in the “sustain” state as long as the input trigger remains active. When it goes to an inactive state, the envelope begins the “release” sequence. If the input trigger becomes inactive before the first 2 sequences have finished, the envelope goes directly to the “release” phase.
The input trigger can be connected to the output trigger coming from the keyboard, the trigger delay module, the oscillators trigger output, or from the sequencer.
The time of the different periods are controlled by the “Attack”, “Decay” and “Release” knobs. The “Sustain” knob is to set the level of the envelope output during the sustain period.
A | D |
|
S |
|
|
|
| R |
Trigg |
|
|
| On | t |
|
|
Representation of the envelope
ARTURIA – MOOG MODULAR V 2.6 – USER’S MANUAL | 77 |