The low frequency oscillator gives rhythm to the passage from one sequence to another. The speed can be statically set with the “frequency” knob and dynamically with the modulation input situated on the first section. The “synchronization” interrupter synchronizes this generator on the tempo of the host application. In this case, the “frequency” knob selects multiples and
The passage from one step to the next can also be done by the means of a trigger signal (from the keyboard for example) connected to the “next trigger” input.
The two “On” and “Off” button start and stop this generator. When it starts, it resets the sequence manager on the first step.
The starting and stopping can be done dynamically with the associated trigger inputs. The “length” knob sets the trigger signal width coming from the sequencer.
The “backward” interrupter allows a
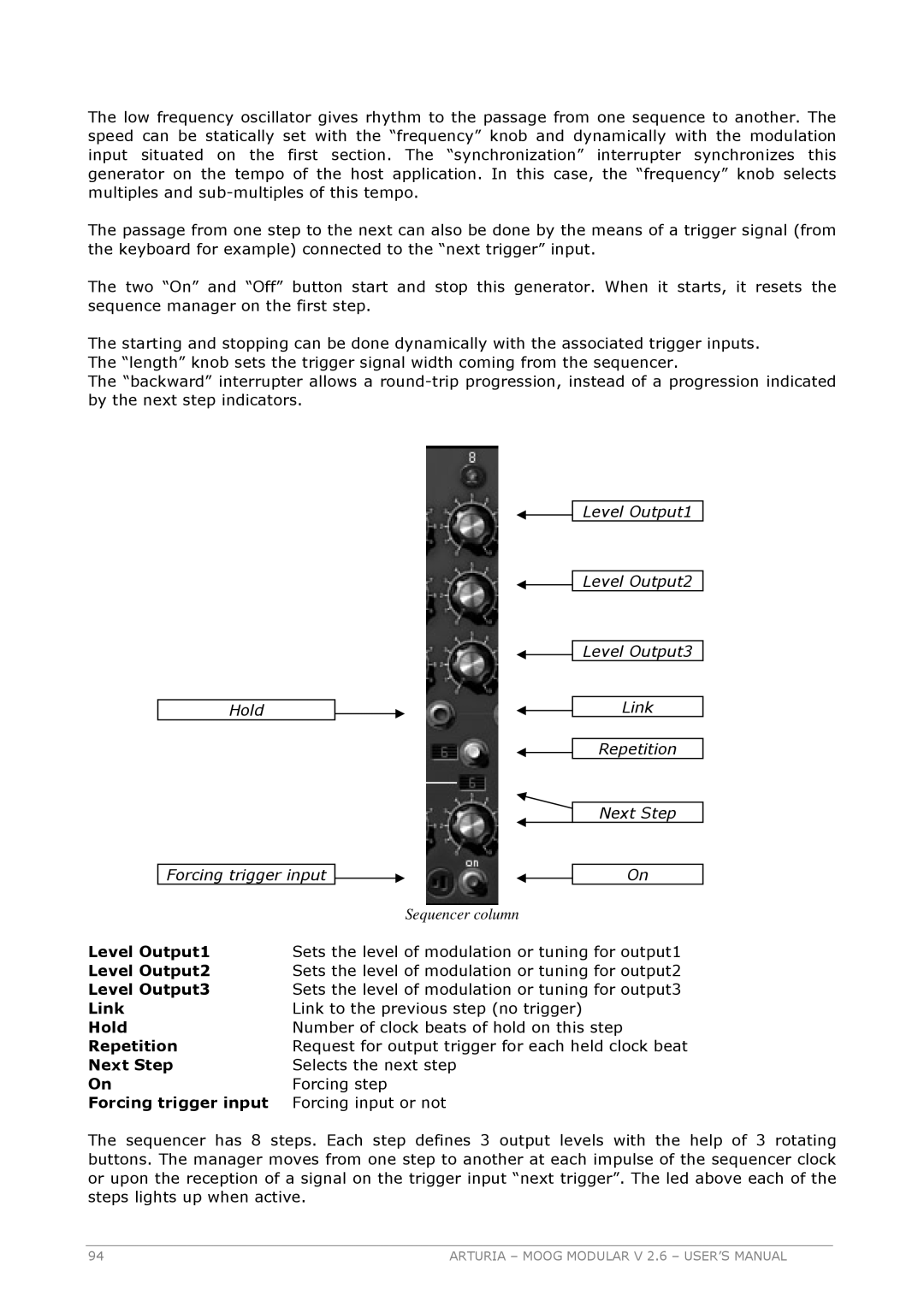
Hold
![]() Level Output1
Level Output1
![]() Level Output2
Level Output2
![]() Level Output3
Level Output3
Link
Repetition
Next Step
Forcing trigger input ![]()
On
| Sequencer column |
Level Output1 | Sets the level of modulation or tuning for output1 |
Level Output2 | Sets the level of modulation or tuning for output2 |
Level Output3 | Sets the level of modulation or tuning for output3 |
Link | Link to the previous step (no trigger) |
Hold | Number of clock beats of hold on this step |
Repetition | Request for output trigger for each held clock beat |
Next Step | Selects the next step |
On | Forcing step |
Forcing trigger input | Forcing input or not |
The sequencer has 8 steps. Each step defines 3 output levels with the help of 3 rotating buttons. The manager moves from one step to another at each impulse of the sequencer clock or upon the reception of a signal on the trigger input “next trigger”. The led above each of the steps lights up when active.
94 | ARTURIA – MOOG MODULAR V 2.6 – USER’S MANUAL |