Solaris SFS Driver
Last Updated June 14
Removing the Utilities Using the emlxuremove Script
Downloading and Installing the Driver for Solaris 8 or
Starting the HBAnyware Utility from the Command Line
Using the HBAnyware Utility Command-Line Interface
Page
104
Introduction 131 Situations That Involve HBAnyware
Using the emlxdrv Utility 124
Introduction 161
Console and Log Messages 139
Use Cases 161
HBA Compatibility
Compatibility
Procedure
Known Issues
Method 1 Using the Installit Script recommended
Downloading and Installing the Driver for Solaris 8 or
Method 2 Using Individual Patches
To obtain and install individual patches
Page
Unpacking the Utility Files
Installing the FCA Utilities
Emlxuinstall script is available
To install the utilities kit using the emlxuinstall script
Prerequisites
Enter y. The following message is displayed
Known Issues
Installing the HBAnyware Utility
JRE and instructions for installation can be found at
Unzip the HBAnyware package file. Type
To install HBAnyware with Web Launch Log on as ‘root’
Installing the HBAnyware Utility with Web Launch
Run the install script. Type
Installing or Updating the Utilities Package Manually
Installing the HBAnyware Utility Security Configurator
Compatibility
Unzip the HBAnywareSSC package file
Removing the Utilities Using the emlxuremove Script
To remove the emlxu utilities package
Removing the Utilities Package Manually
Configuration
Driver Parameters
Solaris SFS and lpfc Driver Parameter Cross-Reference
Solaris SFS and lpfc Driver Parameter Cross-Reference Table
Solaris SFS and lpfc Driver Parameter Cross-Reference
Solaris SFS and lpfc Driver Parameter Cross-Reference
Solaris SFS and lpfc Driver Parameter Cross-Reference
Procedure
Starting the HBAnyware Security Configurator
Starting the HBAnyware Utility
Starting HBAnyware with Web Launch
Starting the HBAnyware Utility from the Command Line
Changing Management Mode
Enter desired management mode Press Enter Click OK
Examples of Modifications
Menu Bar
HBAnyware Utility Window Element Definitions
Toolbar
Discovery-Tree
Toolbar Buttons
Sort Toolbar Buttons
Property Tabs
Using the HBAnyware Utility Command-Line Interface
Status Bar
Discovery-Tree Icons
Out-of-Band Access
Using the CLI Client
Syntax Rules
SaveConfig
CLI Client Command Reference Version
ListHBAs
Sample response
PortAttrib
HBAAttrib
ServerAttrib
PortStat
Parameters
TargetMapping
Reset
Download
DriverConfig
AllNodeInfo
Sample response for a successful download
DriverParamsGlobal
DriverParams
Sample abbreviated response
SetDriverParam
PciData
SetBootBios
LoopMap
Wakeup
GetBeacon
Below is a sample response
PostTest
SetBeacon
EchoTest
Dump
Loopback
DeleteDumpFiles
SetPersistentBinding
PersistentBinding
RemovePersistentBinding
RemoveAllPersistentBinding
Sample response would be
BindingSupport
BindingCapabilities
SetBindingSupport
HBAnyware Utility, Discovery Information
Discovering HBAs
HBAnyware Utility, HBA Discovery Settings Dialog Box
Configuring Discovery Settings
Sorting Local HBAs Only
Sorting HBAs
Sorting by Host Name
Sorting by Fabric Address
Viewing Discovery Information
Viewing HBA Information
Discovery Information Field Definitions
Host Information Tab
Viewing Host Information
Host Information Field Definitions
Driver Parameter Tab Field Definitions
Host Driver Parameters Tab
Driver Parameter Tab Buttons
Adapter Summary Field Definitions
Viewing General HBA Attributes
Adapter Status Area Field Definitions
Adapter Details Field Definitions
Viewing Detailed HBA Information
Port Attributes Field Definitions
Loop Map Table Definitions
Viewing Fabric Information
Discovery Information Field Definitions
Viewing Target Information
Target Information Field Definitions
LUN Information Field Definitions
Viewing LUN Information
HBAnyware Utility, Statistics Tab
Viewing Port Statistics
Port Statistics Field Definitions
Viewing Firmware Information
Enable/Disable Click to enable or disable the boot code
Firmware Field Definitions
Firmware Area
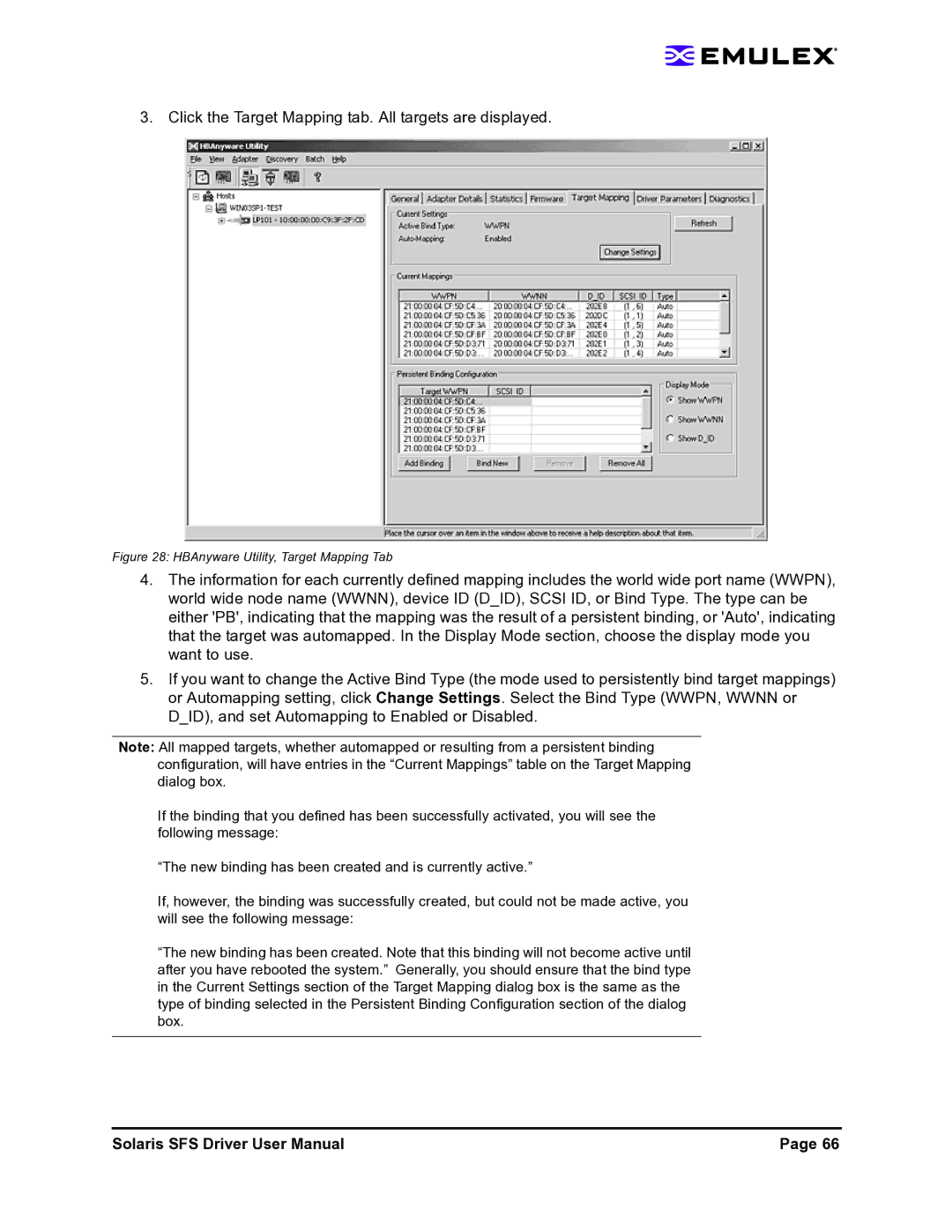
Target Mapping Field Definitions
Viewing Target Mapping
Resetting HBAs
Following warning screen appears
Updating Firmware
HBAnyware Utility, Firmware Download Dialog Box
Click Start Download
Click Browse. The Firmware File Selection dialog box appears
HBAnyware Utility, Batch Firmware Download Dialog Box
Updating Firmware Batch Mode
Solaris SFS driver is installed properly
Enabling or Disabling the Bios
HBAnyware Utility, Firmware Tab with Bios Disabled
Setting Driver Parameters
HBAnyware Utility, HBA Selected Driver Parameters Tab
Setting Driver Parameters for an HBA
Resetting All Default Values
Setting Driver Parameters for a Host
Restoring All Parameters to Their Earlier Values
Restoring All Parameters to Their Earlier Values
Assigning Batch Mode Parameters to HBAs
Creating the Batch Mode Driver Parameters File
HBAnyware Utility, Batch Driver Parameters Update Dialog Box
Setting Up Persistent Binding
Click the Target Mapping tab. All targets are displayed
HBAnyware Utility, Add Persistent Binding Dialog Box
Changing Parameters or Bindings for Solaris 8, 9
Adding New Targets Using sd.conf for Solaris 8, 9
Save the file and exit
No-Reboot Firmware Updates
Setting Up Target/LUN Blocking Using sd.conf
Loading or Unloading the Driver Without Rebooting
Running a Quick Test
Performing Diagnostic Tests
Running a Post Test
Using Beaconing
Click OK. a Post Test window shows Post test information
Displaying PCI Registers and Wakeup Information
Creating Diagnostic Dumps
Click Start Dump
HBAnyware Utility, Advanced Diagnostics Dialog Box
Running Advanced Diagnostic Tests
Running Loopback Tests
HBAnyware Utility, Advanced Diagnostic Tests Warning
Running End-to-End Echo Tests
Click Start. The following warning window appears
Saving the Log File
An example of a saved log file appears below
Out-of-Band SAN Management
HBAnyware Utility, Add Remote Host Dialog Box
Adding a Single Host
HBAnyware Utility, Add Remote Hosts Window
Adding a Range of Hosts
Removing Hosts
HBAnyware Security
Introduction
Page
Unsecure System message is displayed
Security Configurator, Unsecure System Message
Page
Access Control Group Tab on the MSC
Access Control Groups
ACG Icons
Access Control Group Tab on a Non-MSC
Adding a Server to the ACG
Deleting a Server from the ACG
Click Yes. Security is removed from all servers in the ACG
Removing Security from all Servers in the ACG
Generating New Security Keys
Restoring the ACG to Its Last Saved Configuration
Accessing a Switch
ASG Icons
Access Sub-Groups
Creating an ASG
Click New. The New Access Sub-Group dialog box is displayed
ASG Creation Example
Reserved Indices Examples
Deleting an ASG
Adding a Server to an ASG
Restoring an ASG to Its Last Saved Configuration
Editing an ASG
Security Configurator, Edit Access Sub Group Dialog Box
About Offline ASGs
Backup Master Eligible Systems
Backup Masters
Backup Master Tab and Controls
Creating a Backup Master
System16 as Backup Master
Reassigning a Backup Master as the New MSC from the Old MSC
Click the Backup Master tab
Security Configurator, Backup Master Warning Dialog Box
Modes of Operation emlxadm
Interactive Mode emlxadm
Information similar to the following is displayed
CLI Mode emlxadm
# emlxadm SUNW,emlxs@2 getnumdevs
Getnumdevs
Command Descriptions emlxadm
Getdevlist
Getlogiparams wwpn
Returns the FC login parameters of this HBA port Example
Gethostparams
Getsympname
Devlogin wwpn
Setsympname string
Getsymnname
Getstate wwpn
Devlogout wwpn
Devremove wwpn
Linkstatus did
Getfwrev
Downloadfcode filename
Downloadfw filename
Downloads the specified FCode image file to the HBA Example
Downloadboot filename
Getbootrev
Getdumpsize
Forcedump
Resethard
Resetlink wwpn or zero for local link
Forces the HBA to perform a hardware reset Example
Gettopology
Forces the HBA to perform a core firmware reset Example
Resethardcore
Diag test parameters or diag code cmdcode hex
Parmgetnum
Returns the total number of configurable parameters Example
Parmgetlist
Returns a list of configurable parameters Example
Page
Parmset label value
Parmget label
Example This example attempts to set a static parameter
Gethostattrs
Msgbuf all or number -i interval
Displays all of the current host HBA API attributes Example
= Seagate ST39103FC
Getportattrs index, wwn or all
Getpath index
Displays a help menu of utility commands Example
Bootcode enable or disable
Getvpd
Exits the utility program Example
Hba
Repeats the last command Example
Modes of Operation emlxdrv
Interactive Mode emlxdrv
Emlxdrv utility program can be run in two modes Interactive
CLI Mode emlxdrv
Setemlxs alias
Command Descriptions emlxdrv
Setemlxssun
Setemlxsall
Setlpfcnonsun
Setlpfc alias
Cleardev alias
Clearemlxs
Clearlpfc
Clearnonsun
Clearsun
Clearall
General Situations
General Situations
SAN Management Workstation Does Not
Access Control Groups Situations
Security Configurator Situations Access Control Groups ACG
HBAnyware Security Configurator Access Sub-Groups Situations
Security Configuration Situations Access Sub-Groups ASG
HBAnyware Security Configurator Backup Masters Situations
HBAnyware Security Configurator Situations Backup Masters
Cannot modify the Security Configurator
Error Message Situations
Error Message Situations
Following error message is displayed when
Master Security Client Situations
Master Security Client Situations
Master Security Client Situations
Log Message Types
Introduction
Message Log Example
Severity Levels
Severity Levels
Following is an example of a message on the system console
Miscellaneous Events
Msgid 0004 Error
Msgid 0001 Debug
Msgid 0002 Notice
Driver Events
HBA Initialization Events
Msgid 0240 Error Adapter Reset Failed
Msgid 0201 Error Adapter Initialization Failed
Msgid 0202 Debug Adapter Initialization
Msgid 0210 Debug Adapter Transition
Memory Management Events
Service Level Interface SLI Events
Msgid 0450 Error Iocb Invalid
Msgid 0432 Debug Ring Reset
Msgid 0452 Debug Iocb Error
Msgid 0440 Debug Adapter Msg
Node Events
Mailbox Events
Msgid 0602 Notice Node Create Failed
Msgid 0603 Debug Node Updated
Msgid 0610 Debug Node Destroy
Msgid 0611 Debug Node Closed
Link Events
ELS Events
General I/O Packet Events
Msgid 0931 Error Packet Transport Error
Msgid 0922 Notice Packet Flush Timeout
Msgid 0911 Debug TXQ Watchdog
Msgid 0920 Debug Packet Flush
IP Traffic Events
FCP Traffic Events
Solaris SFS Events
Msgid 1311 Debug Echo Diagnostic Completed
Msgid 1310 Warning Diagnostic Error
Msgid 1312 Warning Echo Diagnostic Failed
Msgid 1313 Debug BIU Diagnostic Completed
Ioctl Events
Firmware Download Events
Common Transport Events
Msgid 1621 Debug Unsolicited CT dropped
Msgid 1630 Error Invalid CT command found
Msgid 1622 Debug CT reply
Different use cases will drive different migration scenarios
Use Cases
Sample Script File Details
Operational Differences Between lpfc and SFS
Startemlxsmigration.sh
Finishemlxsmigration.sh
Migrating Automatically
Migrating a Configuration without FC Boot
Things to Know Before You Migrate
Limitations
Migrating Manually
Migrating Non-emlxs HBAs to emlxs HBAs
Migrating a Configuration with FC Boot
Shut down the server and get to the ok prompt
For an Emulex boot HBA