IXP1200 Network Processor Family ATM
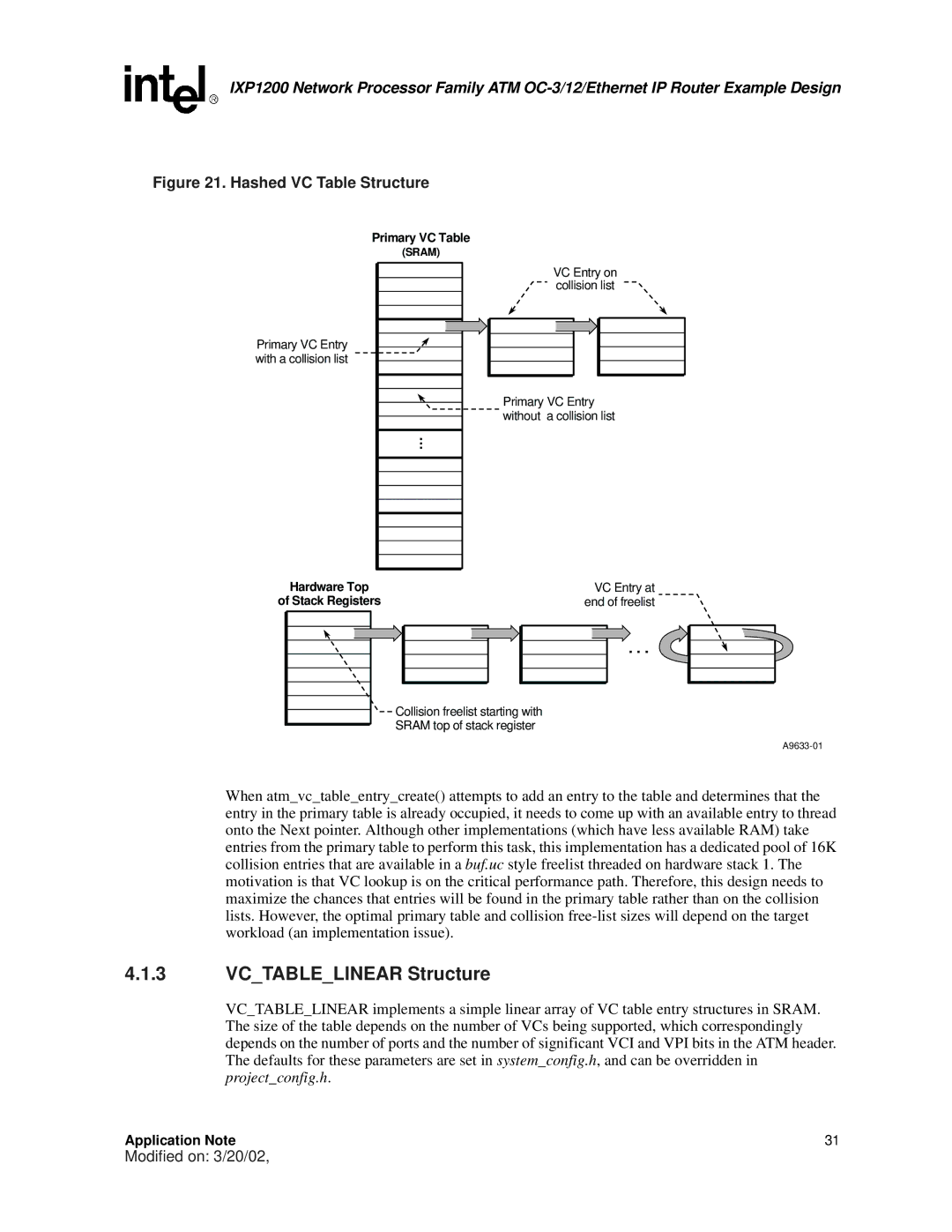
Figure 21. Hashed VC Table Structure
Primary VC Table
Primary VC Entry with a collision list
(SRAM)
…
VC Entry on collision list
Primary VC Entry without a collision list
Hardware Top | VC Entry at |
of Stack Registers | end of freelist |
. . .
Collision freelist starting with
SRAM top of stack register
When atm_vc_table_entry_create() attempts to add an entry to the table and determines that the entry in the primary table is already occupied, it needs to come up with an available entry to thread onto the Next pointer. Although other implementations (which have less available RAM) take entries from the primary table to perform this task, this implementation has a dedicated pool of 16K collision entries that are available in a buf.uc style freelist threaded on hardware stack 1. The motivation is that VC lookup is on the critical performance path. Therefore, this design needs to maximize the chances that entries will be found in the primary table rather than on the collision lists. However, the optimal primary table and collision
4.1.3VC_TABLE_LINEAR Structure
VC_TABLE_LINEAR implements a simple linear array of VC table entry structures in SRAM. The size of the table depends on the number of VCs being supported, which correspondingly depends on the number of ports and the number of significant VCI and VPI bits in the ATM header. The defaults for these parameters are set in system_config.h, and can be overridden in project_config.h.
Application Note | 31 |
Modified on: 3/20/02,