IXP1200 Network Processor Family ATM
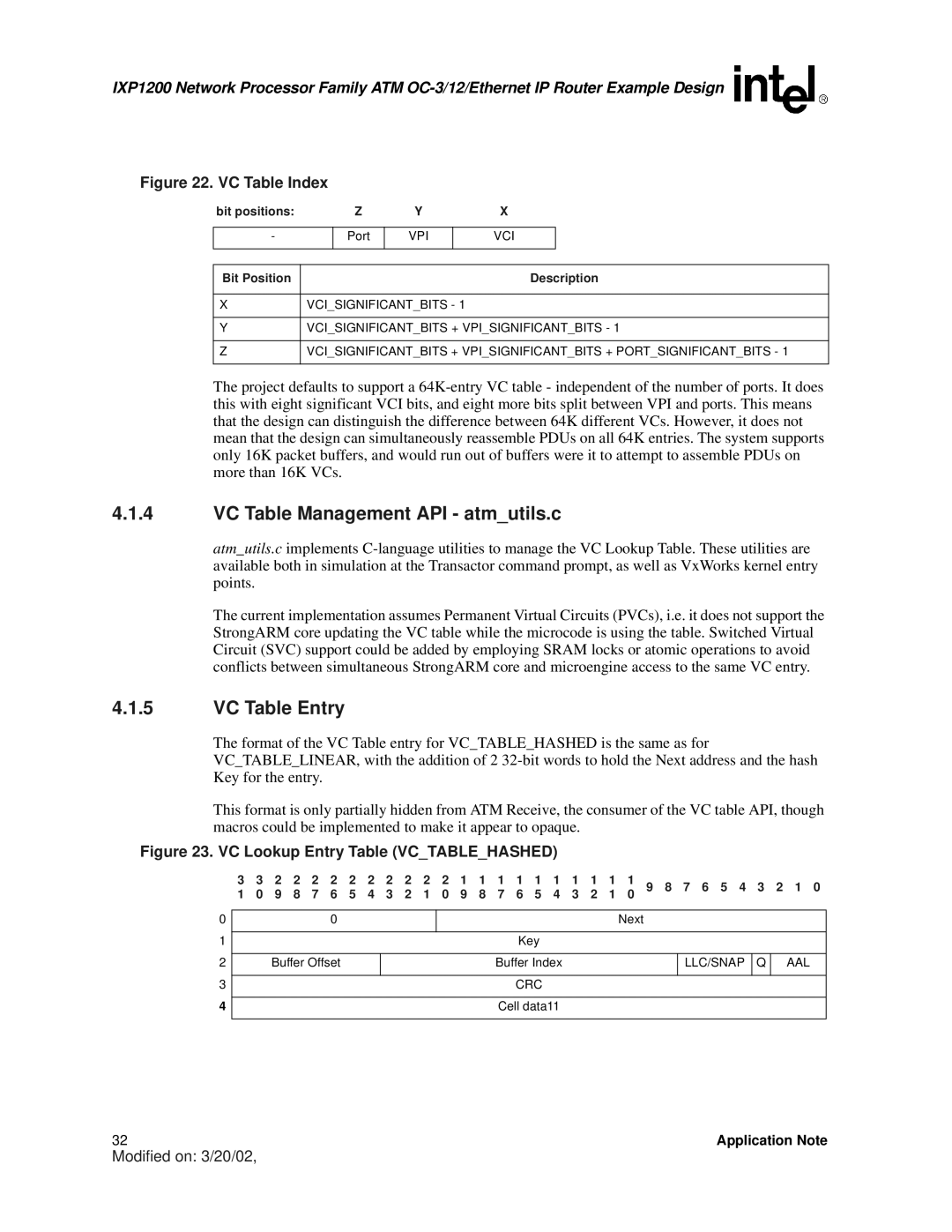
Figure 22. VC Table Index
bit positions: | Z | Y | X |
-
Port
VPI
VCI
Bit Position | Description |
XVCI_SIGNIFICANT_BITS - 1
YVCI_SIGNIFICANT_BITS + VPI_SIGNIFICANT_BITS - 1
ZVCI_SIGNIFICANT_BITS + VPI_SIGNIFICANT_BITS + PORT_SIGNIFICANT_BITS - 1
The project defaults to support a
4.1.4VC Table Management API - atm_utils.c
atm_utils.c implements
The current implementation assumes Permanent Virtual Circuits (PVCs), i.e. it does not support the StrongARM core updating the VC table while the microcode is using the table. Switched Virtual Circuit (SVC) support could be added by employing SRAM locks or atomic operations to avoid conflicts between simultaneous StrongARM core and microengine access to the same VC entry.
4.1.5VC Table Entry
The format of the VC Table entry for VC_TABLE_HASHED is the same as for
VC_TABLE_LINEAR, with the addition of 2
This format is only partially hidden from ATM Receive, the consumer of the VC table API, though macros could be implemented to make it appear to opaque.
Figure 23. VC Lookup Entry Table (VC_TABLE_HASHED)
3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | ||
1 | 0 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
0 |
|
|
|
|
| 0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Next |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Key |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||||||||
2 |
|
| Buffer Offset |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Buffer Index |
|
|
|
|
|
| LLC/SNAP | Q |
| AAL |
| ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| CRC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Cell data11 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
32 | Application Note |
Modified on: 3/20/02,