CommanderTM
Safety
California Proposition 65 Warnings
Electric Shock can kill
Welding Sparks can cause fire or explosion
Iii
Précautions DE Sûreté
Sûreté Pour Soudage a L’Arc
Master Table of Contents for ALL Sections
Table of Contents Installation Section
Installation
Technical Specifications Commander 500 K1639-1
Safety Precautions
Location / Ventilation
Storing
Stacking
High Temperature Operation
Lifting
Towing
High Altitude Operation
PRE-OPERATION Engine Service
Muffler Outlet Pipe
Spark Arrester
Auxiliary Power Receptacles
Standby Power Connections
Welding Output Cables
Machine Grounding
Company
Table of Contents Operation Section
Safety Instructions
Operation
Operating Instructions
General Description
Design Features and Advantages
Recommended Applications
Controls and Settings
K1639-1 Commander 500 Standard Model
Welding Capability
RUN/STOP Switch
Idler Switch
Start Pushbutton
Fuel Level Gauge and Light
Weld Mode Output Control
Welding Terminals Switch
Table B.1 Weld Mode and Output Control Functions
Hour Meter
Auxiliary Power Controls
Engine Operation
Starting the Engine
BREAK-IN Period
Typical Fuel Consumption
Welder Operation
Stick Welding
Constant Current CC Welding
TIG Welding
Commander 500 Settings When Using the K799 HI-FREQ Unit
Commander 500 Settings When Using the K930-1 TIG Module
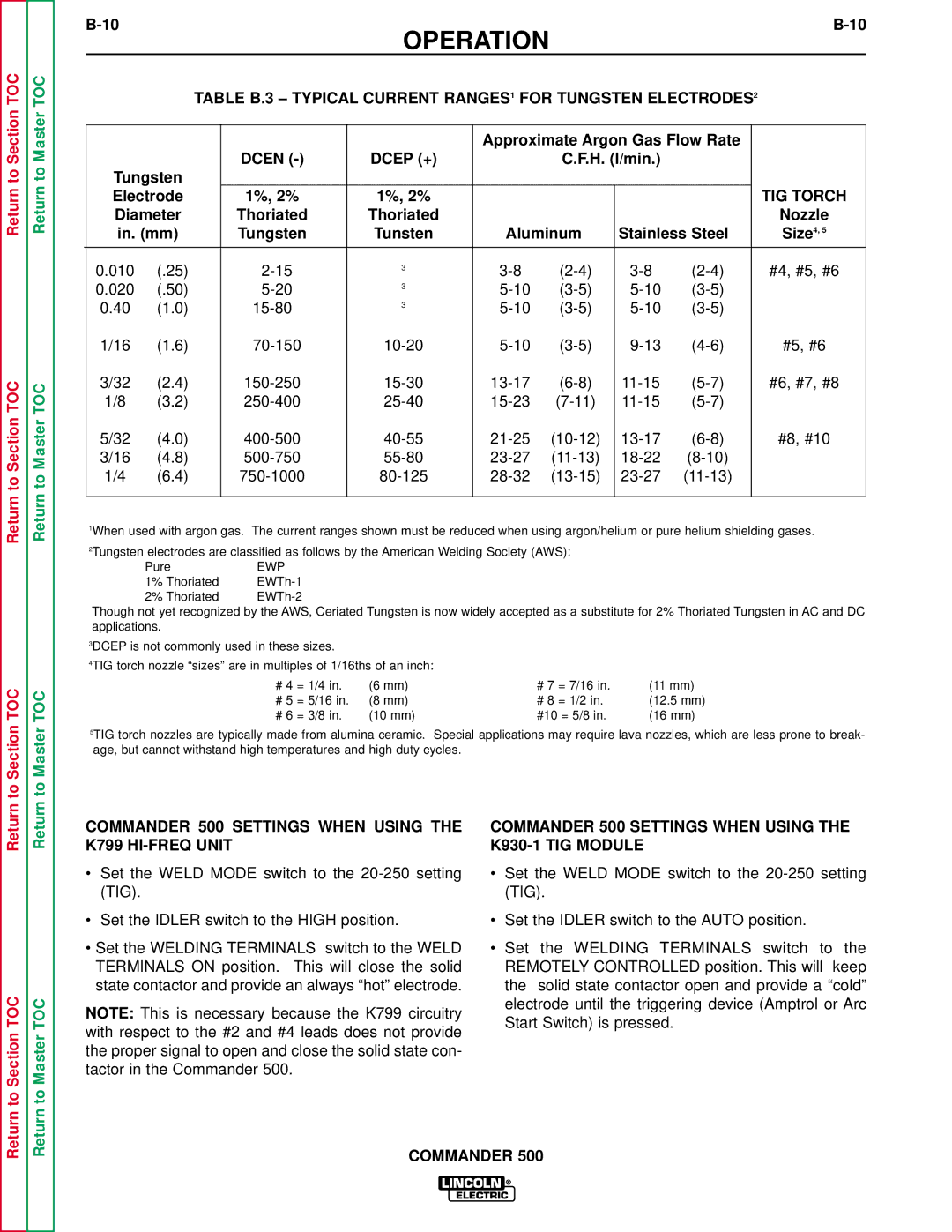
Table B.3 Typical Current RANGES1 for Tungsten ELECTRODES2
TIG Torch
Auxiliary Power Operation
Wire Feed Constant Voltage Welding
Simultaneous Welding and Auxiliary Power Loads
ARC Gouging
Extension Cord Recommendations
Permissible Permissible Auxiliary
Table of Contents Accessories Section
Accessories
OPTIONS/ACCESSORIES
Field Installed Options
Stick Welding Accessories
Semiautomatic Welding Accessories
Connection of Lincoln Electric Wire Feeders
Other Wire Feeders for the Commander
High Frequency Generators for TIG Applications
To Work Electrode Cable To Wire Feed Unit
ING CV
ING CV
ING CV
Figure C.5 Commander 500/LN-23P Connection Diagram
ING Terminals Always on
Table of Contents Maintenance Section
Maintenance
Routine and Periodic Maintenance
Engine Maintenance
Daily
Figure D.1 OIL Drain and Refill
Figure D.2 Fuel PRE-FILTER/WATER Separator Assembly
Fuel Filters
Figure D.3 Secondary Fuel Filter
AIR Filter
Maintenance
Frequency Maintenance Required
Table D.2 Engine Maintenance Parts Manufacturer Part Number
Battery Maintenance
Connecting a Battery Charger
WELDER/GENERATOR Maintenance
Figure D.5 Major Component Locations
Commander
Table of Contents Theory of Operation Section
Commander
Theory of Operation
Weld WINDINGS, RECTIFIER, Power Modules and Feedback
Analog Control Power Supply Board and Weld Control Board
Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor Igbt Operation
Pulse Width Modulation
6E-6
Minimum Output
Maximum Output
External DC Solid State Inductor ARC Source Switch Diode
Chopper Technology Fundamentals
70-80VDC
Table of Contents
Troubleshooting & Repair Section
Section F-1
Troubleshooting & Repair
HOW to USE Troubleshooting Guide
PC Board Troubleshooting Procedures
PC Board can be damaged by static electricity
Troubleshooting Guide
Observe Safety Guidelines
Detailed in the beginning of this manual
Perform the Rotor Resistance
Justment Test
Function Problems
Charging Circuit Test
Engine Problems
Shutdown
Perform the Idler Solenoid
Problems Possible Areas
Symptoms Misadjustments Course of Action
Engine Starting Diagnostic Chart
START-UP and OCV Diagnostic Chart
Return
Case Cover Removal and Replacement Procedure
Description
Materials Needed
Case Cover Removal Replacement Procedure
Procedure
Figure F.1
Case Front Knobs Removal and Replacement Procedure
Removal
Power Module Capacitor Discharge Procedure
Procedure
Idler Solenoid Test
Test Description
Test Procedure
Figure F.5 Idler Solenoid Leads
Shutdown Solenoid Test
Figure F.6 Shutdown Solenoid Lead Terminals
Engine Throttle Adjustment Test
Figure F.7 Strobe Mark Location Mark Blower Paddle Here
Strobe-tach Method
Locking NUT
28F-28
Frequency Counter Method
Oscilloscope Method
Rotor Resistance Test
Test Procedure
Flashing and Rotor Voltage Test
10 11 12 13 14 15
Lead # 201A
Troubleshooting & Repair
Stator Voltage Test
Figure F.13 Front Control Panel Removal Screws
Troubleshooting & Repair
Auxiliary Power and Weld Windings Test
Auxiliary Leads #5B, #5E, #8, #9, #11, #12
Behind Panel
W6W1
Weld Winding Lead Connections
Analog Power Supply PC Board Voltage Test
Control Circuit Input Power
40F-40
J41
Analog Control Power Supply PC Board Test
Test Points Component Tested Voltage Reading
Output Rectifier Bridge Test
Perform the Power Module Capacitor Discharge Procedure
Troubleshooting & Repair
Figure F.20 Diode Lead Removal
Power Module Test
Temperature Switch
Power Module PC Board Diode Lead D4 Positive + Strap
W10
Check Igbt For Shorts
When all tests are complete
Check Diode Module
Charging Circuit Test
Figure F.24 Engine Alternator Location
#239 #281 #238
Scope Settings
Normal Open Circuit Voltage Waveform 115VAC Supply
High Idle no Load
15.8 ms Volts 50V5ms
Normal Open Circuit Voltage Waveform Stick
MAX TAP MAX Control POT High Idle no Load
Volts 50V5ms
Normal Weld Voltage Waveform Stick CC
Machine Loaded to 500 Amps AT 40 Volts
Volts 20V0.1ms
Normal Weld Voltage Waveform Wire CV
Normal TIG Mode Voltage Waveform
Loaded to 200A 16 Volts
Volts 10V50ms
Normal Open Circuit Voltage Waveform Wire CV TAP
MAX Control POT High Idle no Load
Shutdown Solenoid Removal and Replacement
Figure F Shutdown Solenoid Lead Connections
Reassembly
Figure F Shutdown Solenoid Linkage ARM Assembly
Description
Control Panel Removal Screws Front Green Ground Lead
Figure F Power Module Capacitor Lead Removal
Troubleshooting & Repair
Replacement Procedure
Description
Power Module PC Board Removal
Figure F.30 Power Module PC Board
Power Module PC Board Replacement
Diode Module Replacement
Diode Module Removal
Output Rectifier Bridge Diode Removal and Replacement
Refer to Figure F.32 Turn the engine off
Return Section TOC
Diode Stud Size Foot Pounds Inch Pounds
STATOR/ROTOR Removal and Replacement
Preparation and Lead Removal Procedure
Leads #229 #242D
Plug Fuel Lines Bolts
#200D #5P #201 #201A
Filter Field Diode Capacitor
Figure F.35 Brush Holder and Lead Removal
#232M
Figure F.37 Alternator Shroud Removal Screws Acoustical Foam
Figure F.38 Lift Frame and Associated Component Removal
Stator Removal Procedure
Figure F.39 Stator Removal
Rotor Removal Procedure
Reassembly Notes
Lead Reconnection Checklist
Engine
Output Panel and Control BOX
Welder CV Wire Output
Retest After Repair
Engine RPM
Welder DC Stick Output
Touch Start TIG Mode Output
Auxiliary Power Output
Electrical Diagrams
Table of Contents Electrical Diagrams Section
Electrical Diagrams
Schematic Complete Machine Commander
G3834
Schematic Battery PC Board
PC Board Assembly Battery PC Board
Return to Section
Schematic Chopper PC Board
PWM Input
PC Board Assembly Chopper PC Board
Return to Section Return to Section TOC
Schematic Peripheral PC Board
PC Board Assembly Peripheral PC Board
Return to Section
Schematic Power Supply Analog PC Board
PC Board Assembly Power Supply Analog PC Board
PC Board Reference QTY Designators Description
Schematic PULL-COIL PC Board
PC Board Assembly PULL-COIL PC Board
MOSFET/HEATSINK ASBLY,T12704-82&S1810
Schematic Weld Control PC Board Sheet
Electrical Diagrams
Electrical Diagrams
Electrical Diagrams
Electrical Diagrams
PC Board Assembly Weld Control PC Board
RESISTOR,SMD,METAL FILM,1/10W,150OHMS
SVM Error Reporting Form