DART 200 CDPD Modem User’s Guide | 5 DART Supported Protocols |
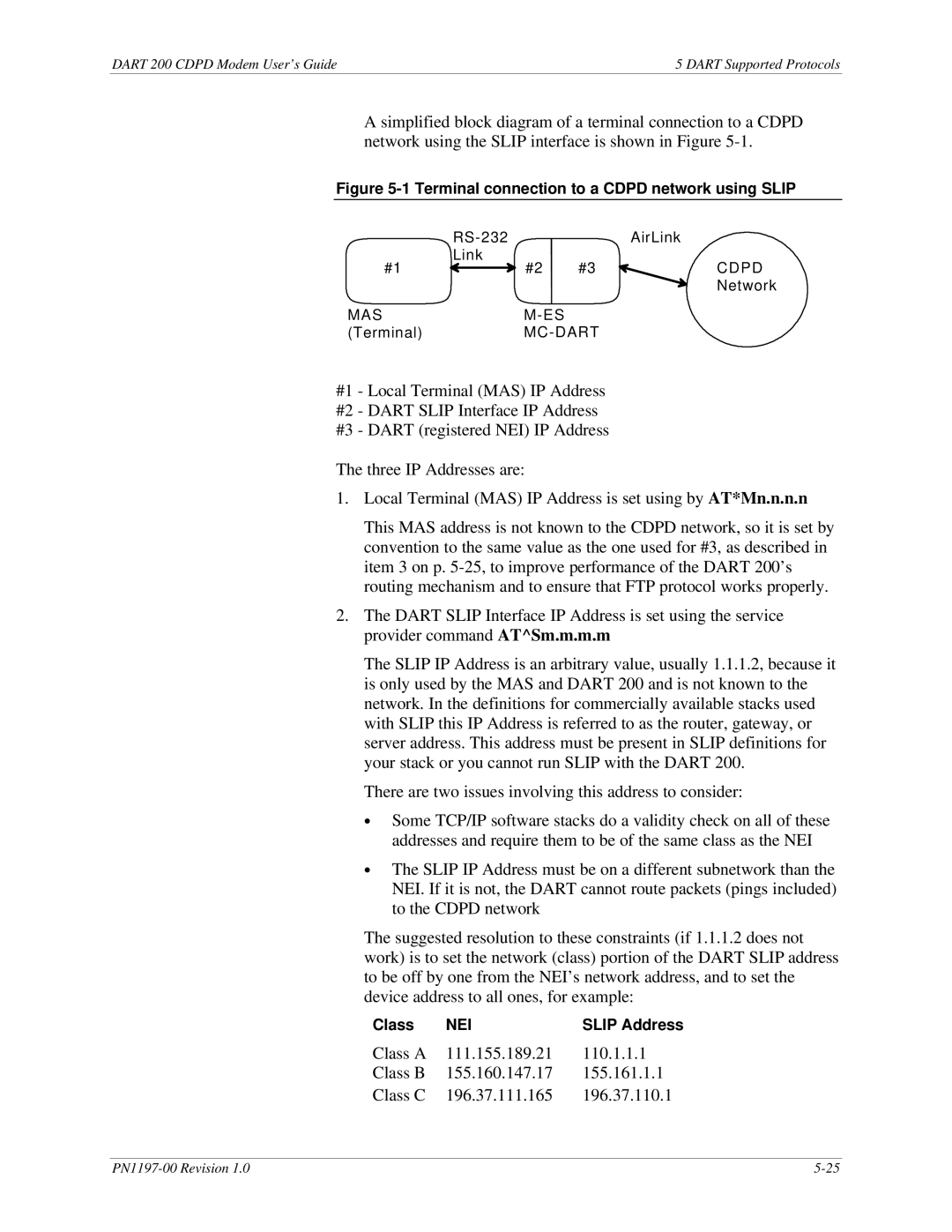
A simplified block diagram of a terminal connection to a CDPD network using the SLIP interface is shown in Figure
Figure 5-1 Terminal connection to a CDPD network using SLIP
|
| AirLink | |
Link | #2 | #3 | CDPD |
#1 | |||
|
|
| Network |
MAS |
|
| |
(Terminal) |
| ||
#1 - Local Terminal (MAS) IP Address
#2 - DART SLIP Interface IP Address
#3 - DART (registered NEI) IP Address
The three IP Addresses are:
1.Local Terminal (MAS) IP Address is set using by AT*Mn.n.n.n
This MAS address is not known to the CDPD network, so it is set by convention to the same value as the one used for #3, as described in item 3 on p.
2.The DART SLIP Interface IP Address is set using the service provider command AT^Sm.m.m.m
The SLIP IP Address is an arbitrary value, usually 1.1.1.2, because it is only used by the MAS and DART 200 and is not known to the network. In the definitions for commercially available stacks used with SLIP this IP Address is referred to as the router, gateway, or server address. This address must be present in SLIP definitions for your stack or you cannot run SLIP with the DART 200.
There are two issues involving this address to consider:
∙Some TCP/IP software stacks do a validity check on all of these addresses and require them to be of the same class as the NEI
∙The SLIP IP Address must be on a different subnetwork than the NEI. If it is not, the DART cannot route packets (pings included) to the CDPD network
The suggested resolution to these constraints (if 1.1.1.2 does not work) is to set the network (class) portion of the DART SLIP address to be off by one from the NEI’s network address, and to set the device address to all ones, for example:
Class | NEI | SLIP Address |
Class A | 111.155.189.21 | 110.1.1.1 |
Class B | 155.160.147.17 | 155.161.1.1 |
Class C | 196.37.111.165 | 196.37.110.1 |