I
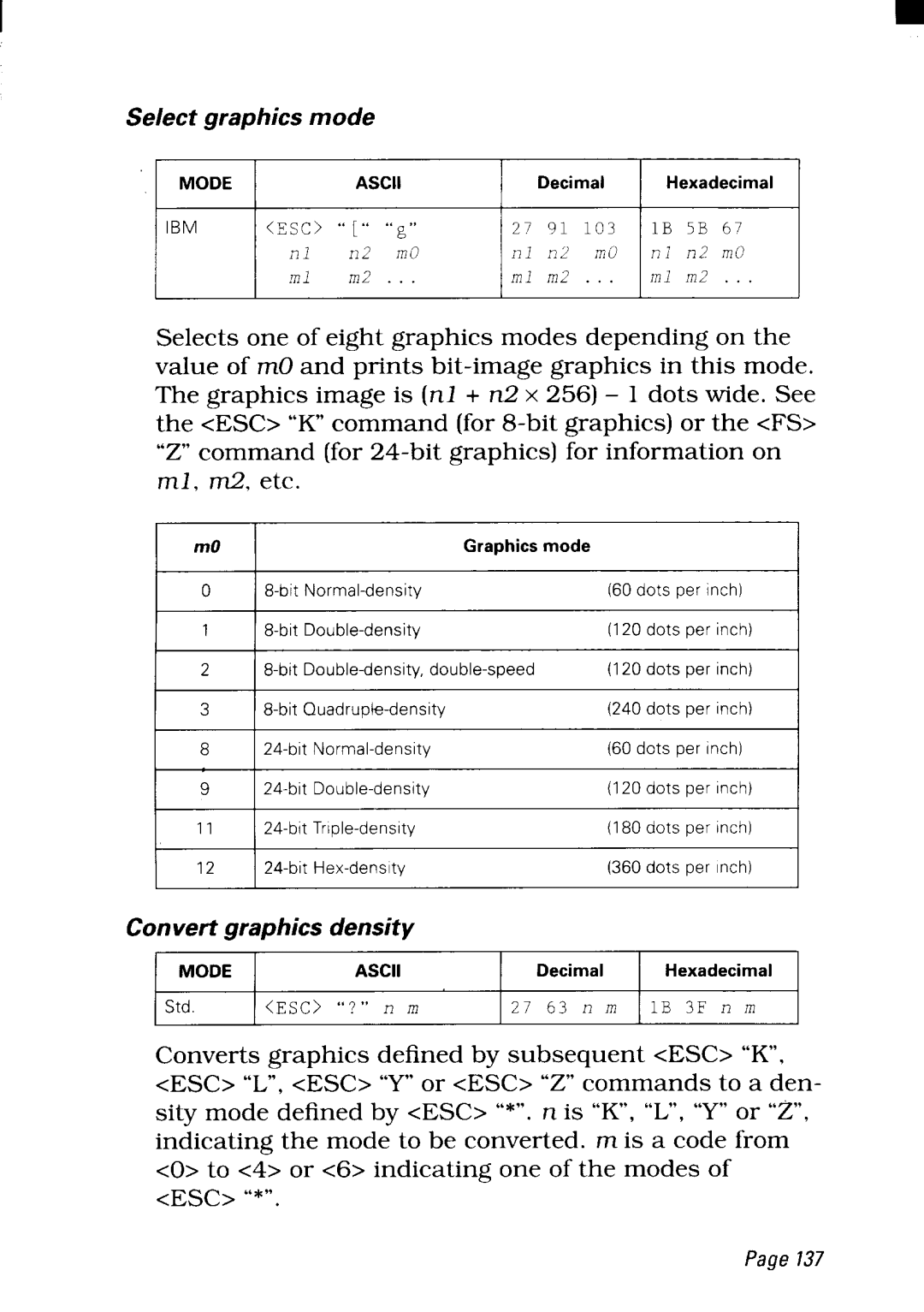
Selectgraphics mode
MODE |
| ASCII |
| Decimal | Hexadecimal | ||
IBM | <~sc> | “[“ “~,, | 27 | 91 | 103 | IB | 5B 67 |
| ,71 | II 2 mO | 111 | ~1~ | /m0 | ?71 | n2 m(? |
| ml | m2 . | ml m2 . | ml m2 | |||
Selects one of eight graphics modes depending on the value of mO and prints
mO |
| Graphicsmode |
|
| |
o |
| (60 dots per inch) |
| ||
11 |
| (120 dots per inch) | I | ||
2 | (120 dots per inch) |
| |||
3 |
| (240 dots per inch) |
| ||
18 | I |
| (6Odots per inch) | I | |
9 |
| (120 dots per inch) |
| ||
11 |
| (180 dots per inch) |
| ||
12 |
| (360 dots per inch) |
| ||
Convert graphics density |
|
|
|
| |
MODE | ASCII |
| Decimal | Hexadecimal |
|
Std. | <ESC> “? “ n m | 27 | 63 n m | IB 3F n m |
|
Converts graphics defined by subsequent <ESC> “K”, <ESC> “L”, <ESC> “Y” or <ESC> “Z” commands to a den- sity mode defined by <ESC> “*”. n is “K”, “L”, “Y” or “2”, indicating the mode to be converted. m is a code from <O>to <4> or <6> indicating one of the modes of <ESC> “*”.
Page137