Standalone (SA) Mode |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| www.ti.com | |
|
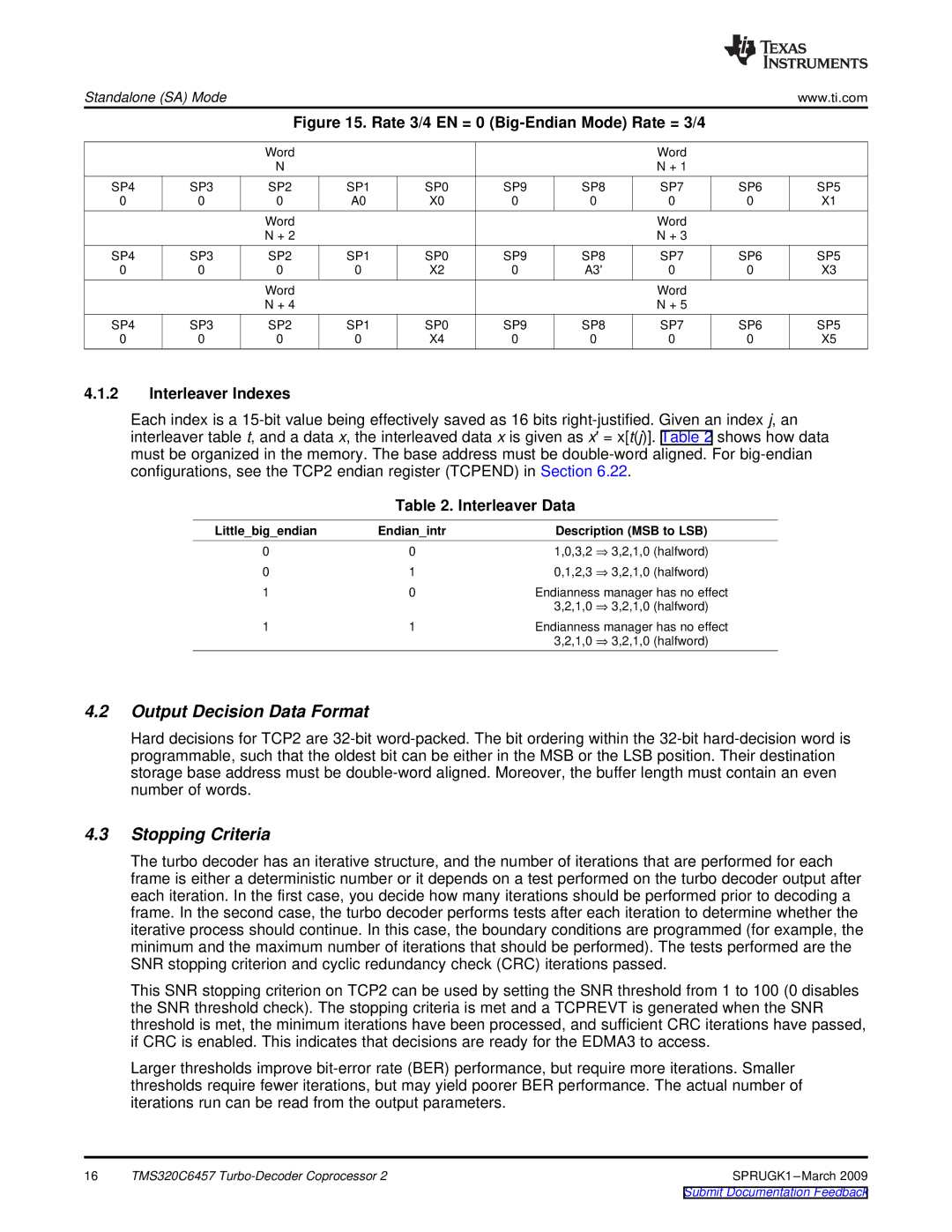
| Figure 15. Rate 3/4 EN = 0 |
|
| |||||
|
| Word |
|
|
|
| Word |
|
|
|
| N |
|
|
|
| N + 1 |
|
|
SP4 | SP3 | SP2 | SP1 | SP0 | SP9 | SP8 | SP7 | SP6 | SP5 |
0 | 0 | 0 | A0 | X0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | X1 |
|
| Word |
|
|
|
| Word |
|
|
|
| N + 2 |
|
|
|
| N + 3 |
|
|
SP4 | SP3 | SP2 | SP1 | SP0 | SP9 | SP8 | SP7 | SP6 | SP5 |
0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | X2 | 0 | A3' | 0 | 0 | X3 |
|
| Word |
|
|
|
| Word |
|
|
|
| N + 4 |
|
|
|
| N + 5 |
|
|
SP4 | SP3 | SP2 | SP1 | SP0 | SP9 | SP8 | SP7 | SP6 | SP5 |
0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | X4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | X5 |
4.1.2Interleaver Indexes
Each index is a
Table 2. Interleaver Data
Little_big_endian | Endian_intr | Description (MSB to LSB) |
0 | 0 | 1,0,3,2 ⇒ 3,2,1,0 (halfword) |
0 | 1 | 0,1,2,3 ⇒ 3,2,1,0 (halfword) |
1 | 0 | Endianness manager has no effect |
|
| 3,2,1,0 ⇒ 3,2,1,0 (halfword) |
1 | 1 | Endianness manager has no effect |
|
| 3,2,1,0 ⇒ 3,2,1,0 (halfword) |
4.2Output Decision Data Format
Hard decisions for TCP2 are
4.3Stopping Criteria
The turbo decoder has an iterative structure, and the number of iterations that are performed for each frame is either a deterministic number or it depends on a test performed on the turbo decoder output after each iteration. In the first case, you decide how many iterations should be performed prior to decoding a frame. In the second case, the turbo decoder performs tests after each iteration to determine whether the iterative process should continue. In this case, the boundary conditions are programmed (for example, the minimum and the maximum number of iterations that should be performed). The tests performed are the SNR stopping criterion and cyclic redundancy check (CRC) iterations passed.
This SNR stopping criterion on TCP2 can be used by setting the SNR threshold from 1 to 100 (0 disables the SNR threshold check). The stopping criteria is met and a TCPREVT is generated when the SNR threshold is met, the minimum iterations have been processed, and sufficient CRC iterations have passed, if CRC is enabled. This indicates that decisions are ready for the EDMA3 to access.
Larger thresholds improve
16 | TMS320C6457 |