24CHAPTER 2: DUAL 56K LAN MODEM FUNCTIONALITY DESCRIPTION
When the LAN Modem receives a packet requesting WAN access, it looks first to see whether the Network ID of the packet matches the Network ID of a configured Private Network. If the Network ID of the packet matches the Network ID of the Private Network, then the call is placed to the Private Network; if it does not match the Network ID of the Private Network, then the call is routed to the first configured ISP connection.
IP Address Translation When the Dual 56K LAN Modem is configured for any type of
is used to enable IP address sharing among the attached workstations.
NAT works by taking the local, private (i.e., not
By translating the local IP addresses of each workstation in this way, the LAN Modem can send out all packets destined for the same remote location over an
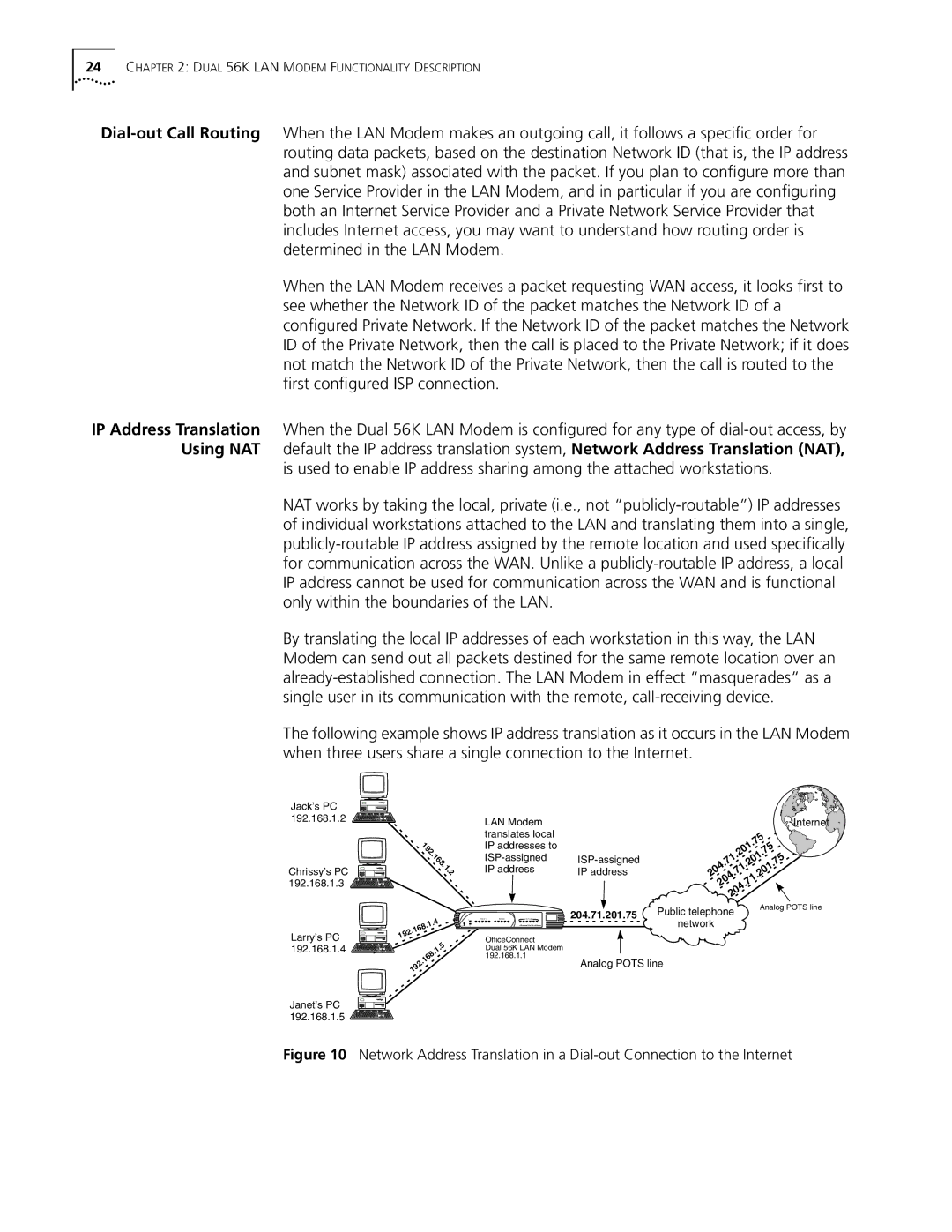
The following example shows IP address translation as it occurs in the LAN Modem when three users share a single connection to the Internet.
Jack’s PC 192.168.1.2
| 192 |
| . |
| 168 |
| . |
Chrissy’s PC | 1 |
. | |
| 2 |
192.168.1.3 |
|
| .4 |
| .1 |
| .168 |
Larry’s PC | 2 |
19 | |
| |
192.168.1.4 | .5 |
.1 | |
| .168 |
| 192 |
Janet’s PC ![]() 192.168.1.5
192.168.1.5 ![]()
LAN Modem |
|
|
|
|
| Internet |
translates local |
|
| .75 |
|
| |
IP addresses to |
|
| 5 |
| ||
| .201 |
|
| |||
.7 | 5 | |||||
.71 | .201 . | |||||
IP address | 204 .71 |
| 7 | |||
IP address | .201 |
| ||||
|
| 204 | .71 |
|
| |
|
|
| 4 |
|
|
|
|
| 20 |
|
|
| |
| 204.71.201.75 | Public telephone |
| Analog POTS line | ||
MODEM 1MODEM 2LAN Status |
|
|
|
| ||
|
| network |
|
|
|
|
OfficeConnect |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dual 56K LAN Modem |
|
|
|
|
|
|
192.168.1.1 | Analog POTS line |
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| ||