Dual 56K LAN Modem
Bayfront Plaza
3Com Corporation
Santa Clara, California
95052-8145
Important Safety Information
Important Safety Information
Wichtige Sicherheits-Informatio nen
Medidas de Seguridad Importantes
Important Notice de Securite
Informazioni Importanti per la Sicurezza
Additional Safety Information
If the unit shows signs of a distinct change in performance
Table of Contents
Installing the Dual 56K LAN Modem
Networking Primer
Page
About this Guide
Shows you where to find specific information in this guide
List conventions that are used throughout this guide
Conventions
Icon Alerts you to
Convention Description
Introduction
Introduction
Local Networking with
Applications
Internet and a Private Network
Local Networking and Dial-out Access with Dial-in Support
Color Description
Description
Front Panel LED Indicator Definitions
Features
Bandwidth Management
Error Control and Data Compression
Remote Management
Protocols
Diagnostics
Upgradeability
Warranty
Modulation Schemes
UAL 56K LAN M Odem
Wan Side The Two
Using the Modem
56K Modems
Channels
Using the Modem Channels
192
Simultaneous Dial-in and Dial-out Connections
Possible, as shown in Figure
Locations two different locations, as shown in Figure
Multilink PPP
Understanding
Other Line Usage
Options
56K LAN Modem’s Manual Call Control
Through an RS-232 serial COM port
Private Networks
Support for Virtual
VPNs
Dual 56K LAN Modem Functionality Description
Before YOU Begin
Package Contents
Before You Begin
Before YOU Begin
TCP/IP Dialog Box for Macintosh Computers
Select Protocol and then click Add
Click Add Select Network Component Type dialog box appears
Select Network Protocol dialog box appears
You may need your Windows NT 4.0 installation CD-ROM
Select TCP/IP Protocol, and then click OK
Select the Protocols tab, as shown in Figure
Dhcp Message Box
Following message appears
Double click Local Area Connection
Click Install
Click Properties
Select Internet Protocol TCP/IP and then click Add
Computer If You Have
Setting Up Your
Static IP Address
For Windows 95 and 98 Users
Set Up Steps for Statically Configured Workstation
Click OK
From the Start menu, select Settings and then Control Panel
For Windows 2000 Users
For Macintosh Users
For Windows NT 4.0 Users
From the Apple menu, select Control Panels, and then TCP/IP
Installation
Installing the Dual 56K LAN Modem
Pass-through Phone ports
You may need to use a country-specific phone adapter optional
Power Cable Connection
Installing the Dual 56K LAN Modem
Main Steps for Typical Configuration
Configuring the Dual 56K LAN Modem for Internet Access
Initial Configuration Welcome Window
Welcome message appears, as shown in Figure
Set Password Window
ISP Wizard appears
Click Continue
Click Continue
LAN Modem Support Web Site
Changing the LAN Modem IP Address for Static IP Users
LAN Modem Main Configuration
Links From the Illustration
Providers
You may wish to bookmark this page for easy future access
10-User Shared WAN Connection Using an 8-Port Ethernet Hub
Connecting an External Hub to the Dual 56K LAN Modem
10BASE-T Hub-to-LAN Modem Connection
Configuring the Dual 56K LAN Modem for Internet Access
Configuration
Before You Start
Displayed on your computer
Click Continue
If do not wish to enter a Password, leave the fields empty
Page
Service Provider Selection Window
Private Network Parameters Window
Under Miscellaneous, make the following selections
IP Address and Subnet mask fields are mandatory
Page
Setting Up Additional Service Provider Profiles
Dual 56K LAN Modem Main Configuration
Providers
LAN Modem
Connecting an External Hub to the Dual 56K LAN Modem
Support Web Site
Modem as they become available
Additional Service
Advanced Configuration
Advanced Configuration
Configuring
Advanced Configuration
Internet Service Provider Parameters window appears
Advanced Configuration
Click Submit
Associating Service
Editing Service
Provider Profiles
Providers with
Using a Connection Script
Connection Script Command Syntax
Click Set Port
Buttons
Click Transmit
Connection Script Example
Additional Configuration Buttons
Parameters
Configuring LAN
Ethernet Parameters window is shown in Figure
Parameters Name
NetBIOS Filtering
Enable Dhcp Server
Local Domain Name
Parameters
Modem Control Parameter Description
Modem Control
Controls
Data Call Parameters Window
Bandwidth on Demand Parameters
Timeout Values
Call Parameters
Outgoing Call Control
Advanced Configuration
Reserving Dhcp
Password
Addresses
Changing Your
Advanced Configuration
Password Protection
Using Selective
Configuring the LAN Modem from a Remote Location
Configuring the LAN Modem Remotely via Another LAN Modem
Administration Password
Analog Modem
Click TCP/IP Settings
Double-clickMake New Connection
Click Check for Upgrades
Basics
Configuring the Dual 56K LAN Modem for DIAL-IN Support
Server-side LAN Modem and a client-side device
Adapter or an Isdn LAN Modem
Configuring the Dual 56K LAN Modem for DIAL-IN Support
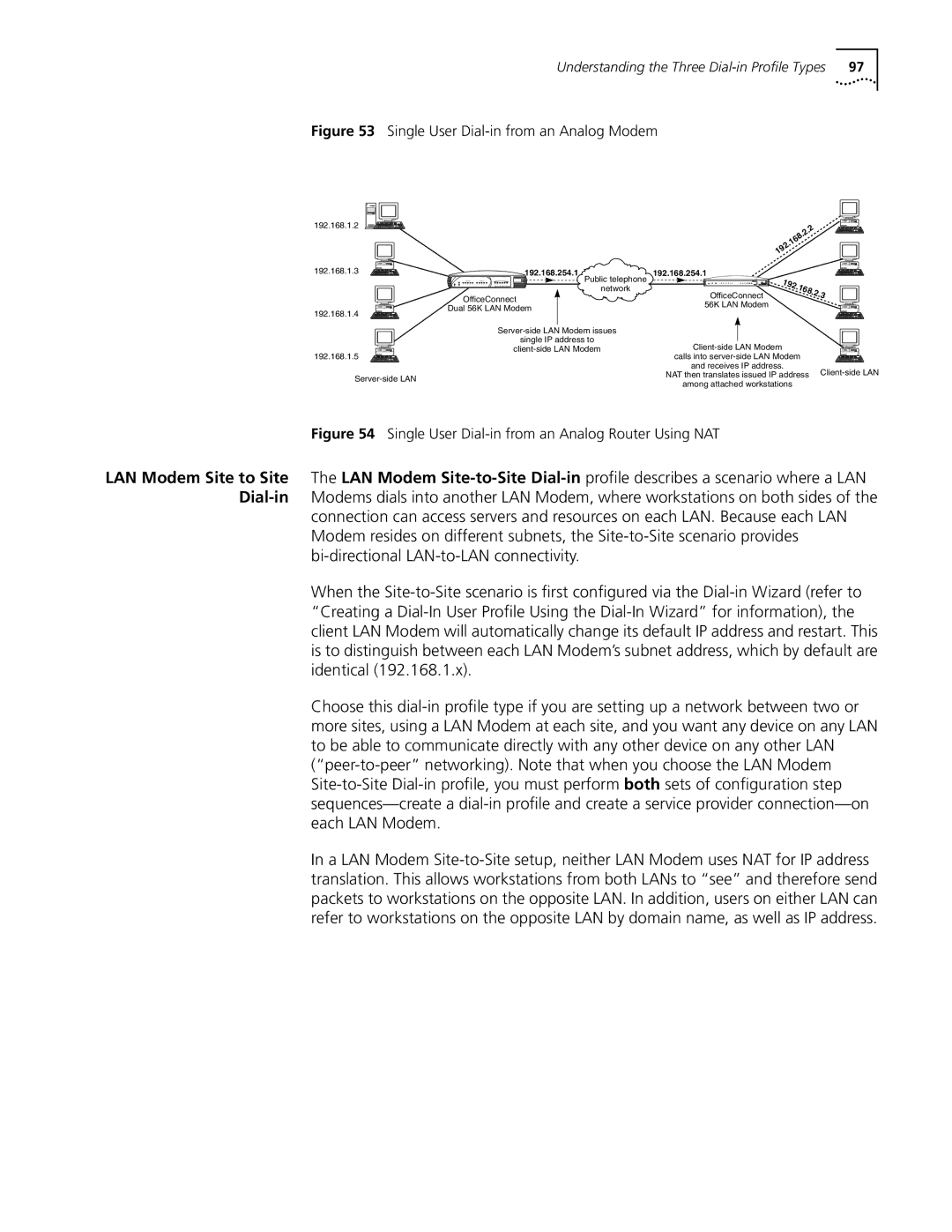
Single User Dial-in from an Analog Modem
LAN Modem Site-to-Site Dial-in Profile Type
Before You Start the Configuration
Click Dial-in User
Dial-In Global Parameters window opens, as shown in Figure
Click Dial-in Global
Page
Dial-in Wizard for Single User Dial-in
Dial-In Wizard Profile Type Selection Window
Dial-In Wizard Password Window
Dial-In Wizard Password window appears, as shown in Figure
Modem Site-to-Site Dial-in
Dial-In Wizard Internet Service Provider Window
Dial-In Wizard Password Window
Dial-In Wizard Site Assignment Window
Dial-in
Configuring an Analog Modem for Dial-out Calling
Part II. Configuring a Client Device for Dial-out Access
Configuring a LAN
Modem Using
Modem LAN
Creating a Private Network Service Provider Profile
Private Network Parameters Window
Under DNS Addresses, leave these values blank
Configuring the Dual 56K LAN Modem for DIAL-IN Support
Dial-in User Selection Screen
Dial-in Users Parameters Screen
WAN Parameters
Callback Parameters
Placing a Call from a Client-side LAN Modem
Using the LAN Modem
Disconnecting Calls
Desktop Manager
Windows only
Click Submit to save your changes
Call Routing Among Service Providers
Click Place Call
Click Make Call
Receiving Calls
Click Hangup Call
Manually
Idle Timeout
Timers Minimum Call Duration
PLACING, Receiving and Disconnecting Calls
Unauthorized opening of the unit will void the warranty
Troubleshooting Maintenance
LAN Status LEDs to isolate problems
Monitoring LEDs
Solutions
Evaluating Symptoms
Solutions
Symptom Possible Cause Solution
Windows 2000 and NT
Windows 95
Macintosh
Internet Explorer
Click Workstations Click the Workstation Configuration tab
Documentation/interop.html
Web browser may be caching older pages
Finding More
Resetting the Dual 56K LAN Modem
Information
Contacting Technical
System Statistics
Description of System Statistics
Current Call Information Description
Call Information
Last Call Information
LAN Modem Clock
Synchronizing
Cycled
Synchronizing the LAN Modem Clock
Troubleshooting and Maintenance
Networking Primer
What is a LAN Modem?
What is a WAN?
What is a network?
Is written as
Becomes
Subnet Masking
Appendix a Networking Primer
What is a network?
Appendix a Networking Primer
Possible Limitations
Appendix a Networking Primer
FAX Modem
Installing and Using the Virtual
Modem Application
Modem Properties window opens
Click Install Modems
Click Add to add the new modem
Virtual Fax Modem Parameters page opens, as shown in Figure
Click the Virtual Fax Modem button
Usage
Creating a Virtual
Creating a Virtual Private Network VPN Tunnel
Private Network VPN
Tunnel
Run Dial-Up Networking Click the Make a New Connection icon
Factory Defaults
Factory Defaults
Appendix D Factory Defaults
Specifications
Specifications
Year 2000 Compliance
Refer to for the Dual 56K LAN Modem specifications
Appendix E Specifications
Glossary
LZS
Glossary
Glossary
OfficeConnect Dual 56K LAN Modem
3Com Corporation Limited Lifetime Warranty
Warranties Exclusive
Regulatory and Aproval Information
FCC Declaration
FCC Part 68 Compliance
Page
TCP/IP
167
168