GNS 530A
Page
Revision Date of Revision Description
Updated per Main SW
Record of Revisions
Initial Release
Copyright
Table of Contents
MESSAGES, ABBREVIATIONS,
GNS 530A Pilot’s Guide and Reference
GNS 530A Pilot’s Guide and Reference
Warranty
Limited Warranty
Blank
Standard Package
Section Introduction
KEY and Knob Functions
Left-hand Keys and Knobs
Right-hand Keys and Knobs
Bottom Row Keys
Blank Direct-to
Takeoff Tour
Powering up the GNS
Flight plan features Section IFR procedures Section
Overview
Acknowledging the database information
Instrument Panel Self-test
Press the ENT Key
Viewing the Checklists
Setting fuel on board to full if not provided by sensor
Returning to the previous page after viewing a message
Satellite Status
Viewing a system message
Press the MSG Key again
Changing the standby Vloc frequency
Selecting COM and Vloc Frequencies
Changing the standby communication frequency
Placing the standby frequency in the active field
Groups
Groups
NAV Pages
Selecting the desired NAV
Direct-to Navigation
Map
Selecting a direct-to destination
Selecting the Default NAV
Default NAV
Press and hold the CLR Key Figure
NAV/COM
Changing the data fields
Selecting a communication or navigation frequency
22 Airport Window
To display the Procedures Page -23, press the Proc Key
IFR Procedures
Selecting an approach, departure, or arrival
Turn the small right knob to select the desired Nrst
Nearest Nrst Pages
Displaying the Nrst pages
Displaying a list of nearby airports
Viewing additional information for a nearby airport
Press the Direct-toKey Press the ENT Key Figure
Press the MSG Key again to return to the previous display
Nearest Nrst Airspace
Viewing an airspace alert message
Viewing additional airspace information
Flight Plans FPL
Creating a new flight plan
Activating the new flight plan
35 Flight Plan Catalog Page Menu
Squelch
Volume
COM Window and Tuning
Section COM
Selecting a COM frequency
Standby Frequency
Auto-Tuning
Selecting a COM frequency for a nearby airport
Selecting a COM frequency for any airport in the flight plan
Nearest Artcc
Stuck Microphone
Quickly tuning and activating
Emergency Channel
Selecting a COM frequency for any airport in the database
Blank
Selecting the desired page group from any
Main page Groups
Section NAV Pages
Selecting the desired page within the group
Default NAV
NAV page Group
Quickly selecting the Default NAV Page from any
Adjusting the Map scale
Selecting Desired On-Screen Data
Selecting a different data item for any data field
Enabling or disabling the auto zoom feature
Restoring Factory Settings
Restoring all six data fields to factory default settings
Dual Unit Considerations
MAP
Selecting a map range
Quickly decluttering the Map Display
Map Detail Level
Selecting the panning function and panning the Map Display
Map Panning
Press the CLR Key to exit the information pages
Airspace Information on the Map
Map Direct-to
Press the ENT Key to display an options menu Figure
Displaying the Map Page Menu
Map Setup
Map
Changing the map orientation
To enable/disable automatic zoom
Press the ENT Key to accept the selected option Figure
Section NAV Pages
Measuring bearing and distance between two points
Distance Measurements
Adding Data Fields to the Map
To turn the data fields off/on
Changing a data field
Restoring the factory default settings
Clearing On-Screen Weather Data
Press the small right knob to remove the cursor
Terrain
Selectable Display Settings
Terrain
Showing or hiding aviation data
Displaying a 120˚ view
Changing the display range
Select the Terrain Page and press the Menu Key
Inhibiting Terrain
Inhibit Mode
Terrain Symbols
Enabling Terrain
Taws
Taws
Enabling Taws
Inhibiting Taws
Press the ENT Key. The Taws system is functional again
Manually testing the Taws system
Taws Symbols
Taws Manual Test
NAV/COM
Press the small right knob to activate the cursor
Viewing usage restrictions for a frequency
Scrolling through the list of frequencies
To return to the NAV/COM Page, press the ENT Key
Satellite Status
Sky View GPS Receiver Status
Should be in view
Using satellite data
GPS Receiver Status Messages
By an altitude serializer
Section DIRECT-TO Navigation
Overview
Press the Direct-toKey, followed by the ENT Key twice
Selecting a Destination by Facility Name or City
Selecting a direct-to destination by facility name or city
Selecting a Destination from the Active Flight Plan
Selecting a direct-to destination from the active flight plan
Selecting a nearby airport as a direct-to destination
Selecting the Nearest Airport as a Direct-to Destination
Shortcuts
Selecting an on-screen waypoint as a direct-to destination
Press the Direct-to Key followed by the ENT Key twice
Selecting a Direct-to destination from the Map
Selecting a direct-to destination from the Map
Specifying a Course to a Waypoint
Cancelling Direct-to Navigation
Cancelling a direct-to
Manually defining the direct-to course
Flight Plan Catalog
Section Flight Plans
Flight Plan Editing
Adding a waypoint to an existing flight plan
Deleting a waypoint from an existing flight plan
Changing the comment line for an existing flight plan
Activating an existing flight plan
Activating Flight Plans
Inverting Flight Plans
Activating an existing flight plan in reverse order
Copying a flight plan to another flight plan catalog location
Copying Flight Plans
Deleting Flight Plans
Deleting a flight plan
Flight Plan Catalog Options
14 Crossfill GNS 530A Pilot’s Guide and Reference
Deleting all flight plans
Sorting the catalog listing by number or comment
Active Flight Plan Options
Accessing the Active Flight Plan Menu
Active Flight Plan
Options shown in -1 are available for Active Flight Plan
Active Flight Plan Page Menu Options
Changing a data field on the Active Flight Plan
Activating a flight plan along a specific leg
23 Active Flight Plan Page Menu
With ‘Load?’ highlighted, press the ENT Key
Selecting a departure for the departure airport
29 Active Flight Plan Page Menu
Removing a waypoint using the CLR Key
Press the CLR Key to display a confirmation window Figure
With ‘Activate?’ highlighted, press the ENT Key
Reviewing a procedure while viewing a flight plan
Activating a specific leg of the active flight plan
Press the ENT Key to select the WPT Page Group
Blank
Section Procedures
Press the Proc Key to display the Procedures
Activating an approach
‘GPS’ Designations
Activating the approach, with vectors to final
NON-PRECISION Approach Operations
Approaches with Procedure Turns
NAV/COM
Flying the Procedure Turn
Refer to -12 for the following steps
Refer to -17 for the following steps
Fly the outbound course
Turn to the final approach course
Flying the Missed Approach
23 ‘Hold Teardrop’ Annunciation
Flying an Approach with a Hold
Refer to -27 for the following steps
29 Approach Mode
Refer to -29 for the following steps
Flying a DME Arc Approach
31 Final Approach
36 Procedures
Refer to -35 for the following steps
38 Approach Mode
Refer to -38 for the following steps
Vectors to Final
Activating vectors-to-final from the Procedures
Selecting ‘VECTORS’ from the Transitions Window
42 Procedures
Flying the Vectors Approach
ATC instructs the pilot to turn right to a heading
When approaching the FAF, a waypoint alert
Refer to -46 for the following steps
Course From Fix Flight Plan Legs
50 Waypoint Alert, Default NAV
PMD VOR
55 Waypoint Alert
On selecting departures
Departure runway in this example
ILS Approaches
59 Waypoint Alert
Selecting an ILS Approach
Used for this approach. Press the ENT Key to
As mentioned, the Vloc receiver must be
Acknowledge the message
Flying the ILS Approach
Refer to -68 for the following steps
Turn to track the ILS approach course
70 CDI Scale Transition
72 Waypoint Alert
Points to Remember for ALL Approaches
Points to Remember for Localizer-based Approaches
Localizer frequency must be active to use Vloc guidance
Blank
Section WPT Pages
WPT page Group
Quickly selecting a WPT
Entering a waypoint facility name or city location
Entering a waypoint identifier
Turn the large right knob to select the next character field
Duplicate Waypoints
First Facility for Charlotte
Airport Location
Selecting a waypoint identifier from a list of duplicates
Radar Radar coverage Yes or No
Airport Location Page Options
Elevation In feet or meters
Selecting an Airport Location Page Menu Option
Airport Runway
Displaying information for each additional runway
Airport Runway Page Options
Adjusting the range of the map image
Selecting an Airport Runway Page Menu Option
Airport Frequency
14 111.55 Highlighted
Atis Asos Awos
To return to the Airport Frequency Page, press the ENT Key
Selecting an Airport Frequency Page Menu Option
Airport Approach
Airport Frequency Page Options
Scrolling through the available approaches and transitions
Airport Approach Page Options
20 Approach Window
Loading an approach from the Airport Approach
Airport Arrival
Scrolling through the available arrivals
24 Arrivals Window
Airport Arrival Page Options
Loading an arrival procedure from the Airport Arrival
Airport Departure
Scrolling through the available departures
Airport Departure Page Options
Loading a departure procedure from the Airport Departure
Press the ENT Key. The cursor moves to the runway field
Following descriptions and abbreviations are used
Intersection
NDB
Freq Frequency in kilohertz kHz
VOR
Selecting a VOR frequency from the VOR
User Waypoint
Creating User Waypoints
Press the ENT Key to accept the selected position
Press the small right knob to remove the flashing cursor
Creating User Waypoints from the Map
Capturing and saving the present position as a user waypoint
Modifying User Waypoints
42 Position Field Selected
User Waypoint Page Options
Viewing a list of all user waypoints
Deleting a user waypoint
User Waypoint List
Press the small right knob to return to the User Waypoint
Select the User Waypoint List, as described in this section
Renaming a user waypoint from the User Waypoint List
Deleting a user waypoint from the User Waypoint List
Deleting all user waypoints from memory
50 User Waypoint List Page Menu
Blank
Section Nrst Pages
Nrst page Group
Quickly selecting a Nrst
Nearest FSS
Nearest Airport
Navigating to a Nearby Waypoint
Frequency Moved to Active Field
Nearest Intersection
Desired Airport Highlighted
Nearest NDB
Nearest VOR
Quickly tuning a VOR’s frequency from the nearest VOR
Viewing additional information for a nearby VOR
Nearest Center Artcc
Nearest User Waypoint
Nearest Flight Service Station FSS
20 FSS Field Selected
Shows ‘Inside of airspace’
Nearest Airspace
Press the MSG Key again to return to the previous
Viewing additional details for an airspace
Listed on the Nearest Airspace
Press the COM Flip-flopKey to activate the selected frequency
Training
See Chart Surface
Prohibited Restricted
Unspecified
Section Vloc Receiver
Ident Audio and Volume
Vloc Window and Tuning
To select a VOR/localizer/ILS frequency
Vloc Ident Window
To select a Vloc frequency from the VOR Page or Nearest VOR
Tuning the Vloc when an approach is active
Frequency Highlighted on Nrst VOR
CDI Key
Highlight ‘Load?’
Quickly selecting an AUX
AUX page Group
Section AUX Pages
Turn the small right knob to select the desired AUX
Selecting a menu option from the Flight Planning
Flight Planning
Following menu options are available
10-3
Flight Planning Page Fuel Planning
Performing fuel planning operations
Flight Planning Page Trip Planning
Performing trip planning operations
Flight Planning Page Density Alt/TAS/Winds
Calculating density altitude, true airspeed, and winds aloft
Flight Planning Page Scheduler
Entering a scheduled message
flashing cursor highlights the first message field
Flight Planning Page Crossfill
Editing a scheduled message
Deleting a scheduled message
10-9
Utility
15 Utility
Selecting a menu option from the Utility
16 Trip Statistics
Utility Page Checklists
Creating a checklist
Inserting a checklist step into an existing checklist
Executing a checklist
Editing a checklist
Deleting a checklist or all checklists
Sorting the checklists by name or entry
Utility Page Flight Timers
Copying a checklist
Viewing, using, or resetting the generic timer
Recording or resetting the departure time
Viewing, using, or resetting total trip time
Utility Page Raim Prediction
Resetting trip statistics readouts
Utility Page Trip Statistics
Predicting Raim availability
Utility Page Software Versions
Utility Page Database Versions
Setup
Utility Page Terrain Database Versions
Selecting a menu option from the Setup
29 Units/Position
±0.3 nm or Auto Approach
Raim Protection
Auto oceanic ±5.0 nm or Auto Enroute
For example, if the buffer is set at 500 feet,
Setup Page CDI/Alarms
31 Restricted Alarm Window
Setup Page CDI Scale/Alarms
Changing the maximum CDI scale
Setting the arrival alarm and alarm distance
Changing the ILS CDI scale
Setting the magnetic variation
Setup Page Units/Position
Changing the units of measure
Mgrs Military Grid Reference System
Changing the position format
Displaying the map datum
Press the ENT Key to accept the selected format
Displaying local time or UTC
Setup Page Date/Time
Setting the local time
Press the ENT Key to accept the selected offset
Setting the minimum runway length and runway surface
Setup Page Display Backlight
Setup Page Nearest Airport Criteria
Changing the backlighting intensity
Configuring the Auxiliary Data Field
Setup Page Data Field Configuration
Abbreviation Data Type
Setting the COM channel spacing
Setup Page COM Configuration
With ‘Restore Defaults?’ highlighted, press the ENT Key
10-30
Displaying the Vertical Navigation
Section Vertical Navigation
Press the Vnav key
Creating a vertical navigation profile
Target Altitude Selected
11-3
Restoring the factory default Vnav settings
Disabling/enabling the vertical navigation Vnav messages
Operating Criteria
System must have a valid 3-D GPS position solution
Introduction
Limitations
Terrain Alerting
Using Terrain
Baro-Corrected Altitude
Unlighted Obstacle
Altitude
When an alert is issued, visual annunciations are displayed
Terrain Alerts
Alert Type Annunciation Pop-Up Alert
Terrain Failure None Terrain Inhibited Terrain Not Available
Shows system status annunciations that may also be issued
Alert Type
Premature Descent Alerting
Is displayed in the Terrain annunciator field
Terrain Failure Alert
Terrain not Available Alert
General Database Information
Database Versions
Updating terrain/obstacle databases
Database Updates
Terrain/Obstacle Database Areas of Coverage
Database Coverage Area
Taws Alerting
Section Taws
Using Taws
1000’
AGL
Taws Alerts
Taws Annunciation Field
Indicates the default configuration
RTC Warning
Forward Looking Terrain Avoidance
Phase of Flight
Pop-Up Alert Aural Message
Taws Inhibit
Functional again
Excessive Descent Rate Alert
Negative Climb Rate After Takeoff Alert NCR
Negative Climb Rate NCR Alert Criteria
Taws not Available Alert
‘FIVE-HUNDRED’ Aural Alert
Taws Failure Alert
Database Information for Taws
13-12
Section Additional Features
Traffic Information Service TIS Interface
TIS Operation
TIS Limitations
TIS Operational Procedures
Above the requesting aircraft Figure
14-3
TIS Audio Alerting
TIS Symbology
Traffic Type
Traffic
TIS Traffic data is displayed on the Traffic Page Figure
Traffic Coasting Banner Age Indicator
TIS Traffic Display Status and Pilot Response
Traffic Warning Window
10 ‘Standby’ Message
‘TA’ annunciation
Traffic Page Display Range
Changing the display range on the Traffic
TA only Only traffic advisories are displayed on the Map
Thumbnail Traffic on Map
Configuring TIS traffic on the Map
Displaying Thumbnail Traffic on the Map
Activating the panning feature and panning the map display
Highlighting TIS Traffic Using Map Page Panning
Power-Up Test
GTX 330 has failed
After Landing
Flight Procedures
Manual Override
Press the ENT Key to confirm
Weather Data Link Interface
Introduction
Nexrad Abnormalities
Weather Products
Nexrad Description
Nexrad Limitations
Nexrad Intensity
Display DBZ Rain Snow Source of Nexrad Echo
Requesting Nexrad Data
Requesting Nexrad data from the Data Link
Requesting Nexrad data from the Map
Data Received Message GDL 49 Only
Follow the preceding steps 4
Press the small right knob
Customizing Nexrad Data on the Weather
To display Nexrad Data on the Weather
Customizing the Nexrad data on Weather
Customizing the Map
Customizing Nexrad Data on the Map
Pattern
Request Shortcuts
Three methods of selecting the Airport Location
Viewing the Data Link Request Log
Sending Position Reports GDL 49 Only
Data Link Request Log Page GDL 49 Only
Data Link Request Log Page is displayed Figure
Requesting graphical Metars from the Data Link
Requesting Graphical Metars
Select the Data Link Page from the AUX Page Group
Metar Request Page has the following user- selectable fields
Select the Map
Displaying graphical Metars on the NAV Weather
Requesting graphical or textual Metars from the Map
Displaying graphical Metars on the NAV Weather
Displaying Textual Metars
Weather Legend
Displaying the Weather Legend
Displaying Temperature/Dewpoints
Displaying Wind Data
Monitoring the Data Link
Troubleshooting
View the Data Link Status
Has been lost
During power-up
‘ ’
‘Data Link has
View’
Standard Aviation Forecast Abbreviations
‘Satellite
Quality is ‘0’
Graphics
Metar Graphics
METARs
Ceiling and Visibility Flight Rules
Wind Speed
Winds
Blank Unknown
Temperature Dewpoints
Temp Dewpoint Display Ranges
14-32
Fault Detection Exclusion
Fault Detection
Detection and Exclusion
PRE-DEPARTURE Verification of FDE
Terminal and En Route Area Navigation Rnav Operations’
Messages
Messages ABBREVIATIONS, & NAV Terms
COM transmitter power has been reduced
Data transfer cancelled version mismatch
Data transfer cancelled crossfill is busy
FPL is full remove unnecessary waypoints
Nm of an arrival airport, when an approach is loaded
Not receiving input data on 429 Channel
Select appropriate frequency for approach
Unit configuration has changed The GNS
Persists, contact a Garmin dealer for assistance
Abbreviations
Fpm
Glideslope Lrg Large Gallons Liters
Feet
Localizer
Heading Millibars of Pressure Inches of Mercury Med Medium
Total Air Temperature
Procedures
Power
Temperature
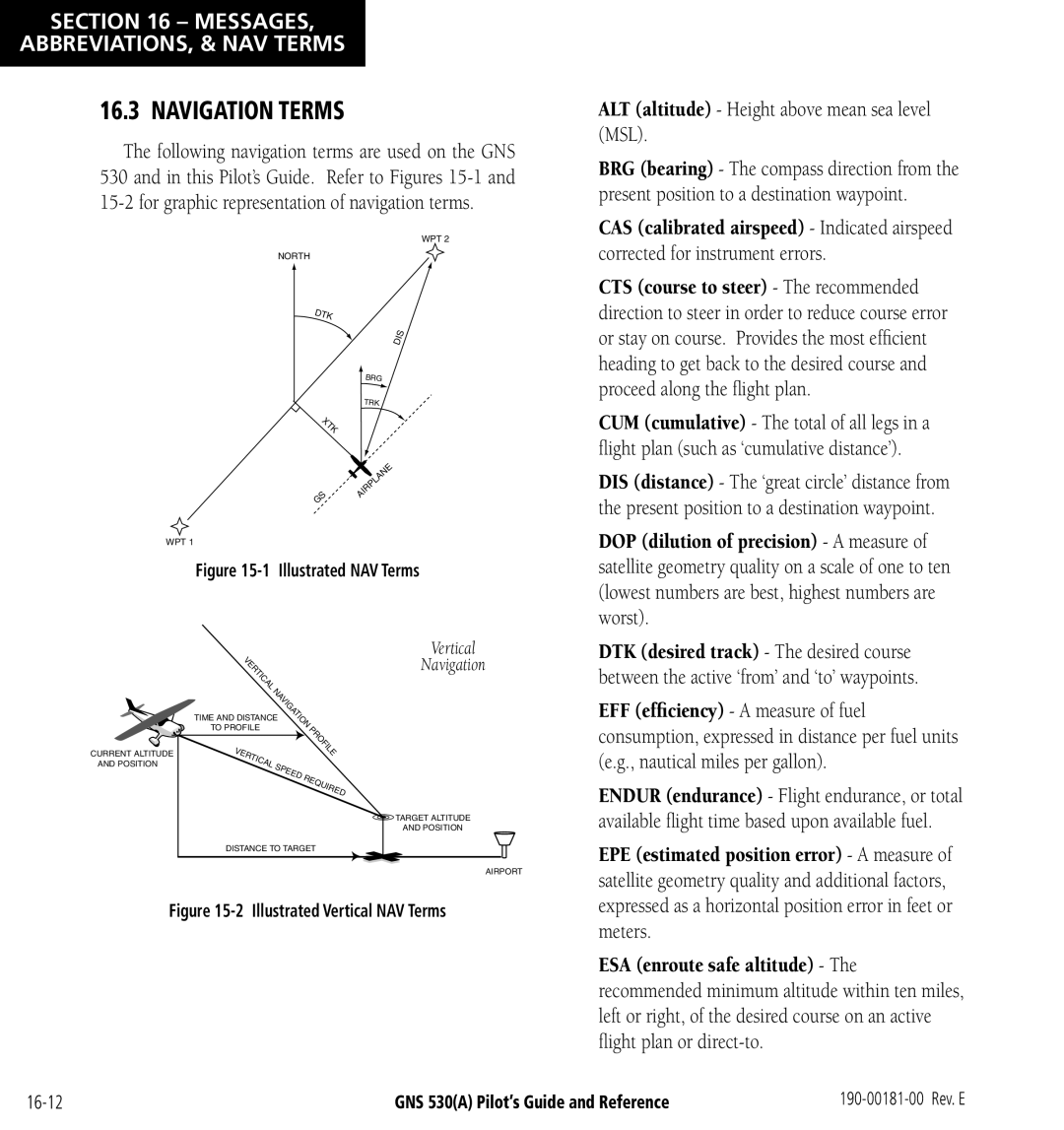
Navigation Terms
Expressed as a horizontal position error in feet or meters
ALT altitude Height above mean sea level MSL
16-13
16-14
Appendix a Data Card USE
To insert the NavData or Terrain Data card Figure A-2
To remove the NavData or Terrain data card Figure A-2
Figure A-3 Swing Arm Handle Operation
Update Rate Once per second, continuous Accuracy
Unit Weight Pounds installed 3.9 kg
Temperature
Unit Size 25’W x 11.00’D x 4.60’H
Appendix B Specifications
What is RAIM, and how does it affect approach operations?
Appendix C MAP Datums
Can I file slant Golf ‘/G’ using my GPS?
What does the OBS key do and when do I use it?
Annunciator
How do I fly the GPS with an autopilot and DG heading bug?
Figure C-4 ‘SUSP’ Annunciation
flashing turn advisory ‘TURN to ###’
When does the CDI scale change, and what does it change to?
Enroute/Oceanic
CDI Comparison GPS vs. VOR
Index
GPS
Map orientation 3-10
Index
Index
Blank
Page
503.391.3411 f