Am186äER and Am188äER Microcontrollers User’s Manual
Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. All rights reserved
If YOU have QUESTIONS, WE’RE Here to Help YOU
Customer Service
Hotline and World Wide Web Support
Documentation and Literature
Page
Table of Contents
Chip Select Unit
Timer Control Unit
Chapter DMA Controller
Viii Table of Contents
PCS MCS
List of Figures
Figure A-1
Processor Release Level PRL Register High-Order Byte Values
List of Tables
Xii Table of Contents
Design Philosophy
Introduction and Overview
Purpose of this Manual
Intended Audience
E86 Microcontroller Family
AMD Documentation
Features and Performance
KEY Features and Benefits
Features and Performance
Distinctive Characteristics
Features and Performance
Am186ER Microcontroller Block Diagram
Am188ER Microcontroller Block Diagram
Clock Generation
Application Considerations
Serial Communications Port
Memory Interface
THIRD-PARTY Development Support Products
Programming
Register SET
Programming
Bits 15-12 -Reserved
Processor Status Flags Register
Bit 5 Reserved
Memory Organization and Address Generation
Bit 3 Reserved
Bit 1 Reserved
Instruction SET
I/O Space
Mnemonic Instruction Name
Instruction Set
JB/JNAE
OUT
Data Types
Segments
Segment Register Selection Rules
Segment Register Implicit Segment Selection Rule
Supported Data Types
Addressing Modes
Memory Addressing Mode Examples
Register and Immediate Operands
Memory Operands
PIN Descriptions
System Overview
Pin Terminology
A19-A0 Address Bus output, three-state, synchronous
Aden
Address Latch Enable output, synchronous
Address Enable, Am186ER Microcontroller Only
Bus High Enable, Am186ER Microcontroller Only
Asynchronous Ready input, asynchronous, level-sensitive
Three-state, output, synchronous
Clock Output a output, synchronous
Data Enable output, three-state, synchronous
Clock Output B output, synchronous
DMA Requests input, synchronous, level-sensitive
Maskable Interrupt Request 0 input, asynchronous
Bus Hold Request input, synchronous, level-sensitive
Maskable Interrupt Request 1 input, asynchronous
Slave Select input, asynchronous
Interrupt Acknowledge 0 output, synchronous
Maskable Interrupt Request 2 input, asynchronous
Maskable Interrupt Request 3 input, asynchronous
Interrupt Acknowledge 1 output, synchronous
Midrange Memory Chip Select
Once Mode Request 0 input
Output, synchronous, internal pullup
Automatic Refresh output, synchronous
Peripheral Chip Select 5 output, synchronous
Peripheral Chip Selects output, synchronous
Latched Address Bit 1 output, synchronous
Peripheral Chip Select 6 output, synchronous
System Overview
PIO Pin Assignments-Numeric Listing
PIO No Associated Pin Power-On Reset Status
PIO Pin Assignments-Alphabetic Listing
Associated Pin PIO No Power-On Reset Status
Address Enable input, internal pullup
Reset input, asynchronous, level-sensitive
Read Strobe output, synchronous, three-state
Refresh 2 three-state, output, synchronous
Show Read Enable input, internal pullup
Internal Memory Disable input, internal pullup
Bus Cycle Status output, three-state, synchronous
Bus Cycle Status Bit 6 output, synchronous
Timer Input 0 input, synchronous, edge-sensitive
Serial Data Enables output, synchronous
Serial Clock output, synchronous, three-state
Serial Data input/output, synchronous
Timer Output 0 output, synchronous
Timer Input 1 input, synchronous, edge-sensitive
Timer Output 1 output, synchronous
Once Mode Request 1 input, internal pullup
Write High Byte, Am186ER Microcontroller Only
Power Supply input
Output, three-state, synchronous
Write Low Byte, Am186ER Microcontroller Only
Pins That Are Used by Emulators
BUS Operation
Clkouta
A19-A0 Address AD7-AD0
BUS Interface Unit
Byte Write Enables
Nonmultiplexed Address Bus
Pseudo Static RAM Psram Support
System Overview
Phase-Locked Loop PLL
Clock and Power Management Unit
Maximum and Minimum Clock Frequencies Mode X1/X2
Min
External Source Clock
Crystal-Driven Clock Source
System Clocks
Power-Save Operation
System Overview
Peripheral Control Block
Overview
Peripheral Control Block
Peripheral Control Block Register Map
Timer 1 Count Register
Bit 13 Reserved
Bit 15 Reserved
Reset Configuration Register RESCON, offset F6h
Reset Configuration Register RESCON, Offset F6h
Bits 7-0 Reserved -Value is undefined
Processor Release Level Register PRL, Offset F4h
Bits 7-3 Reserved -Read back as
Power-Save Control Register PDCON, Offset F0h
Divider Factor
Initialization and Processor Reset
Registers not listed in this table are undefined at reset
Peripheral Control Block
Chip Select Unit
Chip Select Unit
Chip Select Timing
Ready and WAIT-STATE Programming
Chip Select Overlap
Chip Select Registers
Bit 15 Reserved-Set to
Upper Memory Chip Select Register UMCS, Offset A0h
Umcs Block Size Programming Values
Memory Block Starting
Bits 6 Reserved- Set to Bits 5-3 Reserved- Set to
Bits 11-8 Reserved
Low Memory Chip Select Register LMCS, Offset A2h
Lmcs Block Size Programming Values
Memory Block Ending
Bits 11-8 Reserved- Set to
Midrange Memory Chip Select Register MMCS, offset A6h
Midrange Memory Chip Select Register MMCS, Offset A6h
Bits 8-3 Reserved -Set to
Bit 15 Reserved- Set to
PCS and MCS Auxiliary Register MPCS, Offset A8h
MCS Block Size Programming
Total Block Individual
Bits 5-3 Reserved -Set to
Peripheral Chip Select Register PACS, offset A4h
Peripheral Chip Select Register PACS, Offset A4h
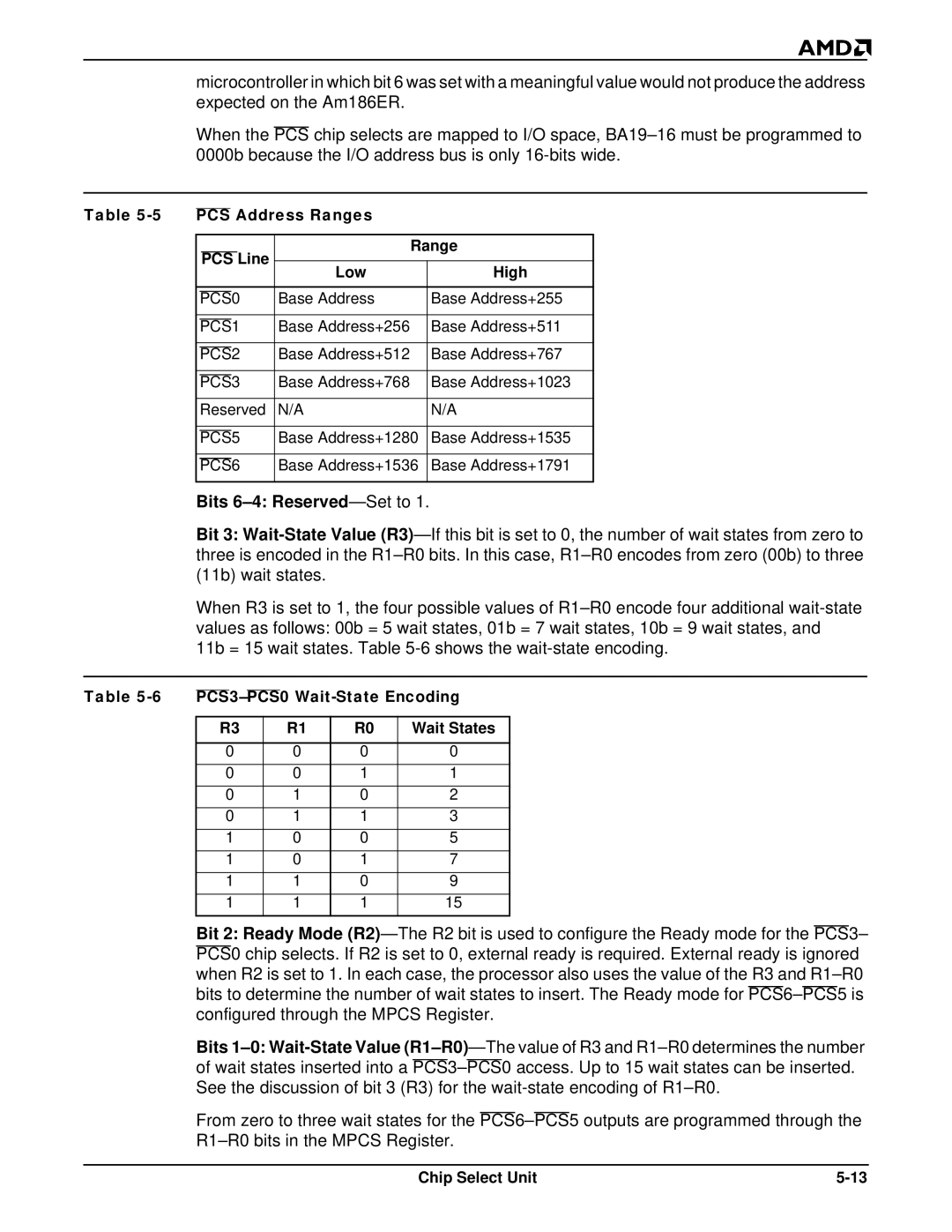
PCS Address Ranges Line
Bits 6-4 Reserved -Set to
Low High
PCS3-PCS0 Wait-State Encoding Wait States
Chip Select Unit
Internal Memory
Interaction with External RAM
Internal Memory
Internal Memory Disable
Show Read Enable
Emulator and Debug Modes
Bits 8-0 Reserved -Set to
Internal Memory Chip Select Register IMCS, Offset ACh
Internal Memory
Memory Partition Register MDRAM, Offset E0h
Refresh Control Unit
Bits 8-0 Reserved -Read back as
Refresh Control Unit
Enable RCU Register EDRAM, Offset E4h
Clock Prescaler Register CDRAM, Offset E2h
Bits 14-9 Reserved -Read back as
Definitions of Interrupt Terms
Interrupt Control Unit
Interrupt Type
Interrupt Vector Table
Maskable and Nonmaskable Interrupts
Interrupt Enable Flag if
Interrupt Mask Bit
Interrupt Priority
Software Exceptions
Am186ER and Am188ER Microcontroller Interrupt Types
Overall
Interrupt Conditions and Sequence
Interrupt Priority
Nonmaskable Interrupts and Software Interrupt Priority
Maskable Hardware Interrupt Priority
Software Exceptions, Traps, and NMI
Divide Error Exception Interrupt Type 00h
Trace Interrupt Interrupt Type 01h
Nonmaskable Interrupt-NMI Interrupt Type 02h
Into Detected Overflow Exception Interrupt Type 04h
Breakpoint Interrupt Interrupt Type 03h
Array Bounds Exception Interrupt Type 05h
Unused Opcode Exception Interrupt Type 06h
External Interrupt Acknowledge Bus Cycles
Interrupt Acknowledge
Interrupt Controller Reset Conditions
Fully Nested Mode
Master Mode Operation
Cascade Mode Interrupt Controller Connections
Cascade Mode
Special Fully Nested Mode
Operation in a Polled Environment
End-of-Interrupt Write to the EOI Register
Master Mode Interrupt Controller Registers
Value of I0CON and I1CON at reset is 000Fh
Priority Level
Bits 15-5 Reserved -Set to
INT4 Control Register I4CON, offset 40h
3 INT4 Control Register I4CON, Offset 40h Master Mode
Bits 15-4 Reserved -Set to
Value of Wdcon at reset is 000Fh
Serial Port Interrupt Control Register SPICON, offset 44h
Bits 15-5 Reserved -Set to Bit 4 Reserved-Set to
10 Interrupt Status Register INTSTS, offset 30h
Interrupt Status Register INTSTS, Offset 30h Master Mode
Bits 15-11 Reserved
Interrupt Request Register REQST, Offset 2Eh Master Mode
12 In-Service Register INSERV, offset 2Ch
In-Service Register INSERV, Offset 2Ch Master Mode
Priority Field Mask Master Mode PR2-PR0
Priority Mask Register PRIMSK, Offset 2Ah Master Mode
14 Interrupt Mask Register IMASK, offset 28h
Interrupt Mask Register IMASK, Offset 28h Master Mode
Bits 14-5 Reserved -Set to
Poll Status Register POLLST, Offset 26h Master Mode
16 Poll Register POLL, offset 24h
Poll Register POLL, Offset 24h Master Mode
Bits 14-5 Reserved
End-of-Interrupt Register EOI, Offset 22h Master Mode
Slave Mode Operation
Slave Mode Interrupt Nesting
Slave Mode Interrupt Controller Registers
These registers are set to 000Fh on reset
20 Interrupt Status Register INTSTS, offset 30h
Interrupt Status Register INTSTS, Offset 30h Slave Mode
21 Interrupt Request Register REQST, offset 2Eh
Interrupt Request Register REQST, Offset 2Eh Slave Mode
22 In-Service Register INSERV, offset 2Ch
In-Service Register INSERV, Offset 2Ch Slave Mode
Priority Field Mask Slave Mode PR2-PR0
Priority Mask Register PRIMSK, Offset 2Ah Slave Mode
24 Interrupt Mask Register IMASK, offset 28h
Interrupt Mask Register IMASK, Offset 28h Slave Mode
25 Specific End-of-Interrupt Register EOI, offset 22h
Bits 15-3 Reserved -Write as
Interrupt Vector Register INTVEC, Offset 20h Slave Mode
Bits 15-8 Reserved -Read as
Bits 2-0 Reserved -Read as
Interrupt Control Unit
Timer Control Unit Register Summary Offsetfrom
Timer Control Unit
Timer Control Unit
Programmable Registers
Timer Operating Frequency
Bits 11-6 Reserved -Set to
Timer Control Unit
Timer 2 Mode and Control Register T2CON, Offset 66h
Bits 12-6 Reserved -Set to
Bits 4-1 Reserved -Set to
TC15-TC0
Value of these registers at reset is undefined
Timer Control Unit
DMA Operation
DMA Controller
DMA Controller Register Summary Offsetfrom
DMA Controller 10-1
10-2 DMA Controller
Programmable DMA Registers
DMA Controller 10-3
DMA Control Registers D0CON, Offset CAh, D1CON, Offset DAh
Synchronization Type
Sync Type
10-4 DMA Controller
DMA Controller 10-5
DMA Transfer Count Registers D0TC, D1TC, offsets C8h and D8h
10-6 DMA Controller
DMA Controller 10-7
10-8 DMA Controller
DMA Controller 10-9
10-10 DMA Controller
DMA Requests
Source Synchronization Timing
Synchronization Timing
Destination Synchronization Timing
DMA Controller 10-11
DMA Priority
DMA Acknowledge
DMA Programming
10-12 DMA Controller
DMA Controller 10-13
DMA Channels on Reset
10-14 DMA Controller
Asynchronous Serial Port
Asynchronous Serial Port Register Summary Offsetfrom
Asynchronous Serial Port 11-1
11-2 Asynchronous Serial Port
Serial Port Control Register SPCT, Offset 80h
Asynchronous Serial Port 11-3
Parity Mode Bit Settings
Serial Port Status Register SPSTS, Offset 82h
Bits 15-7 Reserved -Set to
11-4 Asynchronous Serial Port
Serial Port Transmit Data Register SPTD, Offset 84h
Bits 15-8 Reserved
Asynchronous Serial Port 11-5
11-6 Asynchronous Serial Port
Serial Port Receive Data Register SPRD, Offset 86h
Asynchronous Serial Port 11-7
Serial Port Baud Rate Divisor Register SPBAUD, Offset 88h
11-8 Asynchronous Serial Port
Synchronous Serial Interface
Synchronous Serial Interface Register Summary Offset from
Synchronous Serial Interface 12-1
12-2 Synchronous Serial Interface
Four-Pin Interface
Synchronous Serial Interface 12-3
Synchronous Serial Status Register SSS, Offset 10h
Synchronous Serial Control Register SSC, Offset 12h
Bits 15-6 Reserved -Set to
Bits 3-2 Reserved -Set to
Synchronous Serial Interface 12-5
Bits 15-8 Reserved -Set to
12-6 Synchronous Serial Interface
Synchronous Serial Receive Register SSR, Offset 18h
Synchronous Serial Interface 12-7
SSI Programming
Synchronous Serial Interface Multiple Read
Synchronous Serial Interface Multiple Write
Programmable I/O Pins 13-1
Programmable I/O Pins
13-2
Registers PIOMODE1, 76h PDIR0, 78h PDATA0, 7Ah
PIO Mode 1 Register PIOMODE1, Offset 76h
PIO Mode Registers
PIO Mode 0 Register PIOMODE0, Offset 70h
PIO Mode and PIO Direction Settings Pin Function
PIO Direction 1 Register PDIR1, Offset 78h
PIO Direction Registers
PIO Direction 0 Register PDIR0, Offset 72h
13-4
PIO Data Registers
Programmable I/O Pins 13-5
PIO Data Register 1 PDATA1, Offset 7Ah
PIO Data Register 0 PDATA0, Offset 74h
13-6
Register Summary
Register Summary
Rescon
T1CMPB
Figure A-1 Internal Register Summary
Memory Partition Register Mdram
DMA 0 Control Register D0CON
Internal Memory Chip Select Register Imcs
Serial Port Baud Rate Divisor Register Spbaud
PMODE15-PMODE0
Timer 2 Maxcount Compare a Register T2CMPA
Timer 0 Maxcount Compare B Register T0CMPB
Sfnm
Interrupt Request Register Reqst Master Mode
Interrupt Request Register Reqst Slave Mode
Interrupt Mask Register Imask
Interrupt Vector Register Intvec Slave Mode
Index
Index
Index
Index
Index
Index
Index
Index
Index
Index
Index