Americas Headquarters
Text Part Number OL-20851-01
Page
N T E N T S
Power Outage
802.1X Authentication and Status
Troubleshooting and Maintenance
Cable Specifications C-2 Network and Access Port Pinouts C-2
Viii
Overview
Audience
Organization
Chapter Description
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Administration
Related Documentation
Cisco Unified IP Phone 8900 Series
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Business Edition
Document Conventions
Cisco Product Security Overview
Convention Description
Boldface font
Important Safety Instructions
An Overview of the Cisco Unified IP Phone
Understanding the Cisco Unified IP Phones 8941
Features on the Cisco Unified IP Phone 8941
What Networking Protocols are Used?
Networking Protocol Purpose Usage Notes
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol chapter
Authentication on Cisco Unified IP Phones section
CDP
Dhcp
See the LLDP-MED and Cisco Discovery Protocol
Nologieswhitepaper0900aecd804cd46d.shtml
SIP
Communications Manager Security Guide
Chapter in the Cisco Unified Communications
Manager System Guide
Related Topics
Feature Overview
Configuring Telephony Features
Related Topic
Understanding Security Features for Cisco Unified IP Phones
Providing Users with Feature Information
Refer to the Troubleshooting Guide for Cisco Unified
Topic Reference
Communications Manager
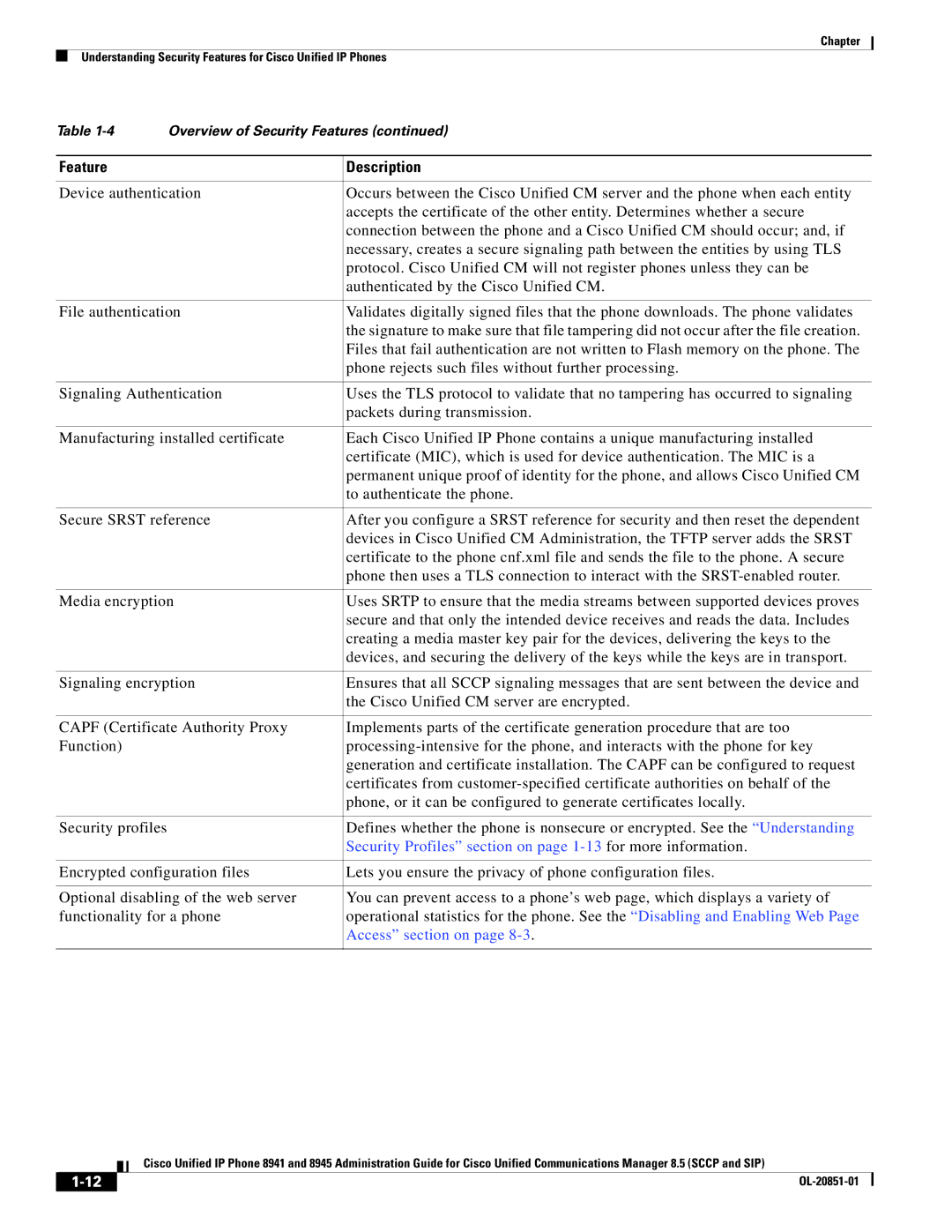
Overview of Supported Security Features
Feature Description
Access section on
Security Profiles section on page 1-13for more information
Configuration Menu section on
Understanding Security Profiles
Identifying Encrypted Phone Calls
Unified IP Phones section on page 1-16for more information
Establishing and Identifying Secure Audio Conference Calls
Feature Used
Initiator’s Phone
Results of Action
Supporting 802.1X Authentication on Cisco Unified IP Phones
Overview
Security Restrictions
Configuring Cisco Unified IP Phones in Cisco Unified CM
Purpose For More Information
Communications Manager Administration Guide
Communications Manager Administration Guide, Cisco
Cisco Communications Manager
Communications Manager Administration Guide, End
Task Purpose For More Information
Unified Communications Manager
Installing Cisco Unified IP Phones
See the Providing Power to the Cisco Unified IP Phone
See the Installing the Cisco Unified IP Phone section
See the Footstand section on
Refer to Cisco Unified IP Phone 8941 and 8945 User
Guide for Cisco Unified Communications Manager
User Guide Administration and System Guides
Terminology Differences
A P T E R
Related Topic
Providing Power to the Cisco Unified IP Phone
Understanding the Phone Startup Process, Network Setup Menu,
Power Guidelines
Power Outage
Power Type Guidelines
Understanding Phone Configuration Files
Obtaining Additional Information about Power
Resolving Startup Problems,
Understanding the Phone Startup Process
Purpose Related Topics
Adding Phones to the Cisco Unified CM Database
Refer to the Cisco Unified Communications Manager
Adding Phones to the Cisco Unified CM Database
Adding Phones with Auto-Registration
Requires MAC Method Address?
Taps
Adding Phones with Auto-Registration and Taps
Adding Phones with Cisco Unified CM Administration
Adding Phones with BAT
Determining the MAC Address for a Cisco Unified IP Phone
OL-20851-01
Before You Begin
Network Requirements
Cisco Unified Communications Manager Configuration
Network and Access Ports
Network and Access Ports, Handset, Speakerphone, Headset,
Handset
Speakerphone
Headset
Audio Quality Subjective to the User
Installing the Cisco Unified IP Phone
See the Network and Access Ports section on
See the Headset section on page 3-3for supported
See the Adding Phones to the Cisco Unified CM
Cisco Unified IP Phone 8941 and 8945 Cable Connections
Reducing Power Consumption on the Phone
Footstand
Chapter Footstand
Higher Viewing Angle
Verifying the Phone Startup Process
Lower Viewing Angle
Hold Mute Speaker
Configuring Startup Network Settings
Configuring Security on the Cisco Unified IP Phone
Before You Begin
Procedure
Configuring Settings on the Cisco Unified IP Phone
Configuration Menus on the Cisco Unified IP Phone
Displaying a Configuration Menu
Select Administrator Settings
Unlocking and Locking Options, Editing Values,
Network Setup Menu, IPv4 Setup Menu Options,
Unlocking and Locking Options
Editing Values
Network Setup Menu
Option Description To Change
Select
Configuration
PC Vlan
Device Phone Phone
IPv4 Setup Menu Options
Related Topics
Security Configuration Menu
802.1X Authentication and Status
Device Phone Phone Configuration
Trust List Menu
Choose Applications Administrator
Settings Security Config
Authentication Device Authentication
Settings Security Setup
OL-20851-01
Configuring Features, Templates, Services, and Users
Feature Description Configuration Reference
Choose System Service Parameter and select
Set Builtin Bridge Enable to On
Configuration System Enterprise Phone
Configuration Device Device Settings
Common Phone Profile
Features and Services Guide, Cisco Call
Features and Services Guide, Call Display
Administration Guide, Directory Number
Forward Maximum Hop Count service parameter
Services Guide, Call Park and Directed Call
Services Guide, Monitoring and Recording
Understanding Directory Numbers
Park
System Guide, Understanding Directory
Numbers
Unified Communications Manager Features
Services Guide
Services Guide, Cisco Web Dialer
CMC
Services Guide, Immediate Divert
Services Guide, Do Not Disturb
Feature, see the Cisco Unified Communications
Manager Features and Services Guide, Hold
Administration Guide, Hunt Group
Communications Manager Feature
Services Guide, Intercom
Refer to Cisco Unified Communications
Manager System Guide, Cisco Unified IP
Features and Services Guide, Malicious
Administration Guide, Message Waiting
Services Guide, Music On Hold
Features and Services Guide Barge
Administration Guide, Phone Button
Features and Services Guide, Quality
Unified IP Phone 8941 and 8945 User Guide
Overview of Supported Security Features
Administration Guide, Conference
Bridge Configuration
Creating Custom Phone Rings section
Services
Administration Guide, Time Period
Bridge Configuration chapter
Administration Guide, Cisco Voice-Mail
Port Configuration
Join and Direct Transfer Policy
Configuring Corporate and Personal Directories
Configuring Corporate Directories
Configuring Personal Directory
Modifying Phone Button Templates
Synchronizer
For PAB, enter the following URL
Configuring Softkey Templates
Supported as a
DND
Setting Up Services
Adding Users to Cisco Unified Communications Manager
Giving Users Access to the User Options Web Pages
Managing the User Options Web Pages
Click Add Selected
Click Device Association
Enter the appropriate search criteria and click Find
Click Save Selected/Changes
Chapter Managing the User Options Web Pages
Chapter Managing the User Options Web Pages
Customizing and Modifying Configuration Files
Customizing the Cisco Unified IP Phone
Creating Custom Phone Rings
DistinctiveRingList File Format Requirements
Configuring a Custom Phone Ring
PCM File Requirements for Custom Ring Types
Configuring the Idle Display
Field Description
OL-20851-01
Model Information Screen
Model Information Screen, Status Menu,
Status Menu
Status Messages Screen
Select Status Messages
Phones with Cisco Unified CM Administration
Network Setup Menu section on page 4-4for
Address. See the Network Setup Menu section
Message Description Possible Explanation and Action
Network Setup Menu section on
Menu section on page 4-4for details
Setup Menu section on page 4-4for details on
Network Statistics Screen
Select Status Network Statistics
Dhcp Disabled
Dhcp Reboot
Dhcp Waiting Coldboot Timeout
SET Dhcp Coldboot
Call Statistics Screen
Select Call Statistics
Voice Quality Metrics
MOS LQK
Security Configuration
Select Administrator Settings Select Security Setup
Monitoring the Cisco Unified IP Phone Remotely
Accessing the Web Page for a Phone
Http//IPaddress
Disabling and Enabling Web Page Access
Device Information
Choose Device Phone
Network Setup
UDI
Description
Description
Network Statistics
Lldp
Device Logs
Streaming Statistics
Stream
Streaming Statistics
Configuring Settings on the Cisco Unified IP Phone chapter
Troubleshooting and Maintenance
Resolving Startup Problems
Chapter Resolving Startup Problems
Identifying Error Messages
Verifying DNS Settings
Choose Tools Control Center Feature Services
Symptom Cisco Unified IP Phone Unable to Obtain IP Address
Cisco Unified IP Phone Resets Unexpectedly
Verifying Dhcp Settings
Verifying the Physical Connection
Identifying Intermittent Network Outages
Checking Static IP Address Settings
Verifying the Voice Vlan Configuration
Verifying that the Phones Have Not Been Intentionally Reset
Eliminating DNS or Other Connectivity Errors
Troubleshooting Cisco Unified IP Phone Security
Checking Power Connection
Problem Possible Cause
General Troubleshooting Tips
Summary Explanation
Locking Options section on page 4-3 for details
Halfduxcollisionexceedthreshold
Resetting or Restoring the Cisco Unified IP Phone
Performing a Basic Reset
Performing a Factory Reset
Operation Performing Explanation
Monitoring the Voice Quality of Calls
Troubleshooting Tips
Metric Change Condition
Where to Go for More Troubleshooting Information
Cleaning the Cisco Unified IP Phone
Chapter Cleaning the Cisco Unified IP Phone
Providing Information to Users Via a Website
How Users Access a Voice Messaging System
How Users Configure Personal Directory Entries
Installing the Synchronizer
Configuring the Synchronizer
Programs Cisco Systems TabSync
Installing the Cisco Unified CM Locale Installer
Support for International Call Logging
OL-20851-01
Physical and Operating Environment Specifications
Specification Value or Range
Cable Specifications
Network and Access Port Pinouts
Network Port Connector
Pin Number Function
Access Port Connector
OL-20851-01
Basic Phone Administration Steps
Example User Information for these Procedures
Adding a User to Cisco Unified CM
Adding a User From an External Ldap Directory
Choose System Ldap Ldap Directory
Click Perform Full Sync Now
Configuring the Phone
Proceed to the section Configuring the Phone, page D-3
Example doe
Appendix Configuring the Phone
Appendix Configuring the Phone
Performing Final End User Configuration Steps
Choose User Management End User
Click Device Associations
Protocol Features
Sccp SIP
Appendix
EFT Draft Cisco Confidential
Tool
Numerics
IN-2
IN-3
IN-4
LLDP-MED
IN-5
MIC
Cast CDP Dhcp Http Rtcp RTP Sccp SIP Srtp TCP Tftp TLS UDP
IN-7
Srst Srtp
IN-8
IN-9
Vlan