Writing Stateful Rules
Stateful matching improves the accuracy of detection because it adds ordering when specifying behaviors across multiple matching events. State transitions in the
As new states are produced, they are bitwise
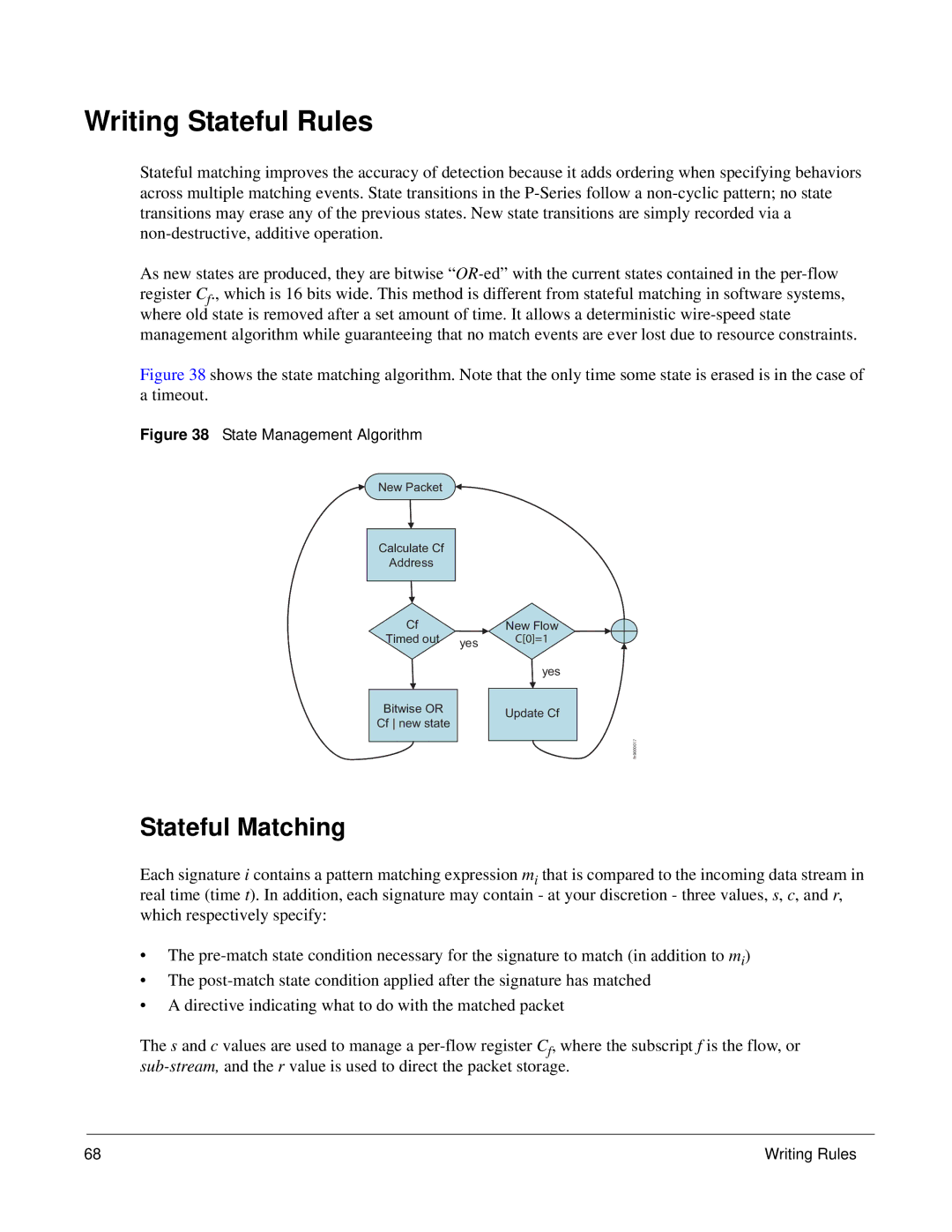
Figure 38 shows the state matching algorithm. Note that the only time some state is erased is in the case of a timeout.
Figure 38 State Management Algorithm
New Packet
Calculate Cf
Address
Cf |
|
Timed out | yes |
|
Bitwise OR
Cf new state
New Flow
C[0]=1
yes
Update Cf
fn9000017
Stateful Matching
Each signature i contains a pattern matching expression mi that is compared to the incoming data stream in real time (time t). In addition, each signature may contain - at your discretion - three values, s, c, and r, which respectively specify:
•The
•The
•A directive indicating what to do with the matched packet
The s and c values are used to manage a
68 | Writing Rules |