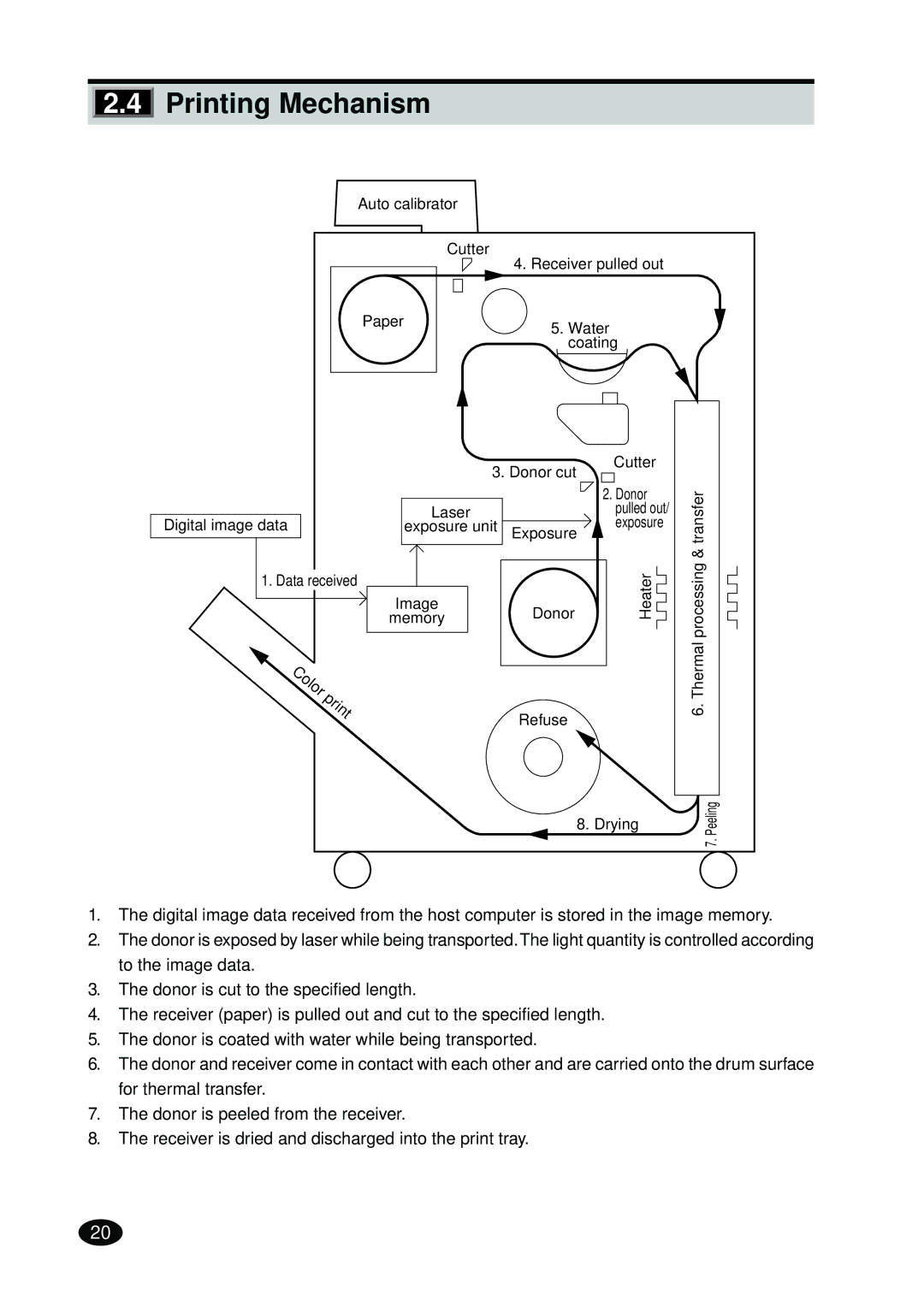
2.4Printing Mechanism
Auto calibrator |
|
Cutter | 4. Receiver pulled out |
| |
Paper | 5. Water |
| |
| coating |
|
|
|
| 3. Donor cut |
| Cutter | |
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
| 2. Donor | |
|
|
|
| Laser |
|
| pulled out/ |
Digital image data |
|
|
| exposure unit | Exposure |
| exposure |
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
| Heater | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| memory | Donor |
| |
1. Data | re | ceived |
| ||||
|
|
|
| ||||
|
|
|
| Image |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Refuse
8. Drying
6. Thermal processing & transfer
7. Peeling
1.The digital image data received from the host computer is stored in the image memory.
2.The donor is exposed by laser while being transported.The light quantity is controlled according to the image data.
3.The donor is cut to the specified length.
4.The receiver (paper) is pulled out and cut to the specified length.
5.The donor is coated with water while being transported.
6.The donor and receiver come in contact with each other and are carried onto the drum surface for thermal transfer.
7.The donor is peeled from the receiver.
8.The receiver is dried and discharged into the print tray.
20