Thermal/Mechanical Reference Design
CEK, are now commonly using direct chassis attach (DCA) as the mechanical retention design. The mass of the new thermal solutions is large enough to require consideration for structural support and stiffening on the chassis.
2.5.5Thermal Solution Performance Characteristics
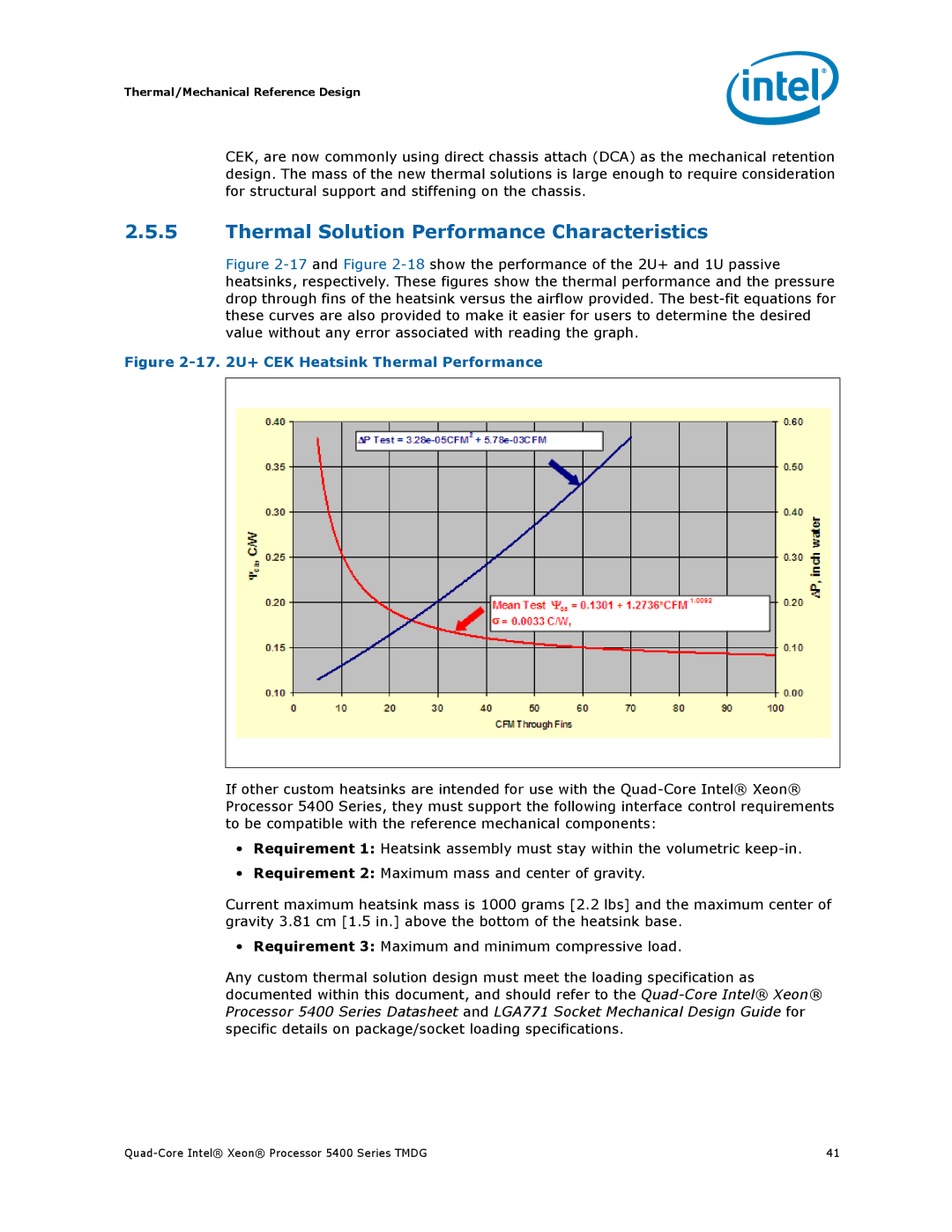
Figure 2-17 and Figure 2-18 show the performance of the 2U+ and 1U passive heatsinks, respectively. These figures show the thermal performance and the pressure drop through fins of the heatsink versus the airflow provided. The best-fit equations for these curves are also provided to make it easier for users to determine the desired value without any error associated with reading the graph.
Figure 2-17. 2U+ CEK Heatsink Thermal Performance
If other custom heatsinks are intended for use with the
•Requirement 1: Heatsink assembly must stay within the volumetric
•Requirement 2: Maximum mass and center of gravity.
Current maximum heatsink mass is 1000 grams [2.2 lbs] and the maximum center of gravity 3.81 cm [1.5 in.] above the bottom of the heatsink base.
• Requirement 3: Maximum and minimum compressive load.
Any custom thermal solution design must meet the loading specification as documented within this document, and should refer to the
41 |