Thermal/Mechanical Reference Design
The
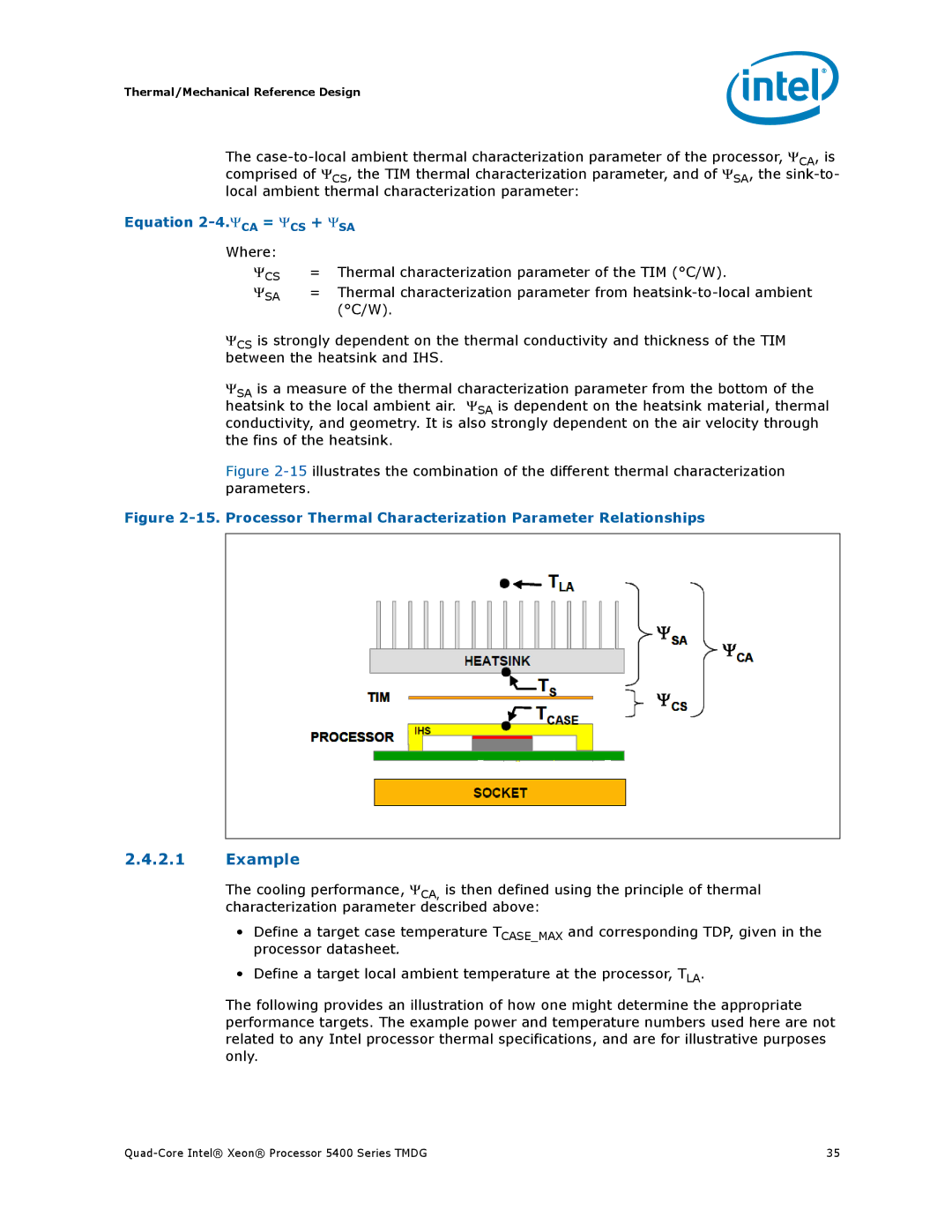
Equation 2-4.ΨCA = ΨCS + ΨSA
Where: |
|
|
ΨCS | = | Thermal characterization parameter of the TIM (°C/W). |
ΨSA | = | Thermal characterization parameter from |
|
| (°C/W). |
ΨCS is strongly dependent on the thermal conductivity and thickness of the TIM between the heatsink and IHS.
ΨSA is a measure of the thermal characterization parameter from the bottom of the heatsink to the local ambient air. ΨSA is dependent on the heatsink material, thermal conductivity, and geometry. It is also strongly dependent on the air velocity through the fins of the heatsink.
Figure 2-15 illustrates the combination of the different thermal characterization parameters.
Figure 2-15. Processor Thermal Characterization Parameter Relationships
2.4.2.1Example
The cooling performance, ΨCA, is then defined using the principle of thermal characterization parameter described above:
•Define a target case temperature TCASE_MAX and corresponding TDP, given in the processor datasheet.
•Define a target local ambient temperature at the processor, TLA.
The following provides an illustration of how one might determine the appropriate performance targets. The example power and temperature numbers used here are not related to any Intel processor thermal specifications, and are for illustrative purposes only.
35 |