Hardware Guide
M160 Internet Router Hardware Guide
Iii
USA
Table of Contents
Chapter Junos Internet Software Overview
Part Initial Installation
Chapter Unpacking the Router
Procedures
Connecting the Router and Performing Initial Configuration
Part
Table of Contents
Appendixes
Appendix C
Part Index
M160 Internet Router Hardware Guide Xii Table of Contents
Xiii
List of Figures
Reinstalling a Routing Engine
Installing a Power Supply
M160 Internet Router Hardware Guide Xvi List of Figures
List of Tables
Xviii
Documentation Conventions
About This Guide
Objectives
Audience
Convention Description Examples
Icon Meaning Description
Community-ids
List of Technical Publications
API
Requesting Support
Documentation Feedback
M160 Internet Router Hardware Guide Xxiv Requesting Support
Product Overview
Product Overview
System Description
System Overview
System Redundancy
Field-Replaceable Units FRUs
Safety Requirements, Warnings, and Guidelines
Page
Chassis
Hardware Component Overview
Front of Chassis
Rear of Chassis with Component Cover in Place
Rear of Chassis with Component Cover Removed
Packet Forwarding Engine
Chassis Physical Specifications Description Value
Midplane
Midplane
Physical Interface Cards PICs
Flexible PIC Concentrators FPCs
PIC Components
Front of Chassis with Four-PIC FPC Installed in Slot FPC0
FPC Components
FPC Types
FPC1 and FPC2
Packet Forwarding Engine Clock Generators PCGs
Label Color State Description
Switching and Forwarding Module SFM
PCG Components
States for PCG LEDs
SFM Components
Switching and Forwarding Module
States for SFM LEDs Label Color Description
Host Module
Routing Engine
Routing Engine Components
Routing Engine
Miscellaneous Control Subsystem MCS
MCS Components
States for MCS LEDs Label Color Description
Craft Interface
Craft Interface
Alarm LEDs and Alarm Cutoff/Lamp Test Button
LCD and Navigation Buttons
LCD Idle Mode
LCD in Idle Mode
LCD Alarm Mode
Host Module LEDs
FPC LEDs and Offline Button
States for Host Module LEDs Label Color Description
States for FPC LEDs Label Color Description
Connector Interface Panel CIP
Routing Engine Management Ports
Connector Interface Panel
Bits Input Ports
Alarm Relay Contacts
Alarm Relay Contacts and Bits Input Ports
Power System
Power Supply
State Description
States for Power Supply LEDs Label
Circuit Breaker Box
Electrical Specifications for Power Supply Description
Cooling System
Fuses
Airflow through the Chassis
Cooling System Components
Airflow through the Chassis
Cable Management System
M160 Internet Router Hardware Guide Cable Management System
Routing Engine Software Components
Junos Internet Software Overview
IPv4 Routing Protocols
Routing Protocol Process
Junos Internet Software Overview
IPv6 Routing Protocols
Routing Policy
Routing and Forwarding Tables
VPNs
Management Process
Interface Process
Chassis Process
Snmp and MIB II Processes
Tools for Accessing and Configuring the Software
Software Upgrades
Tools for Monitoring the Software
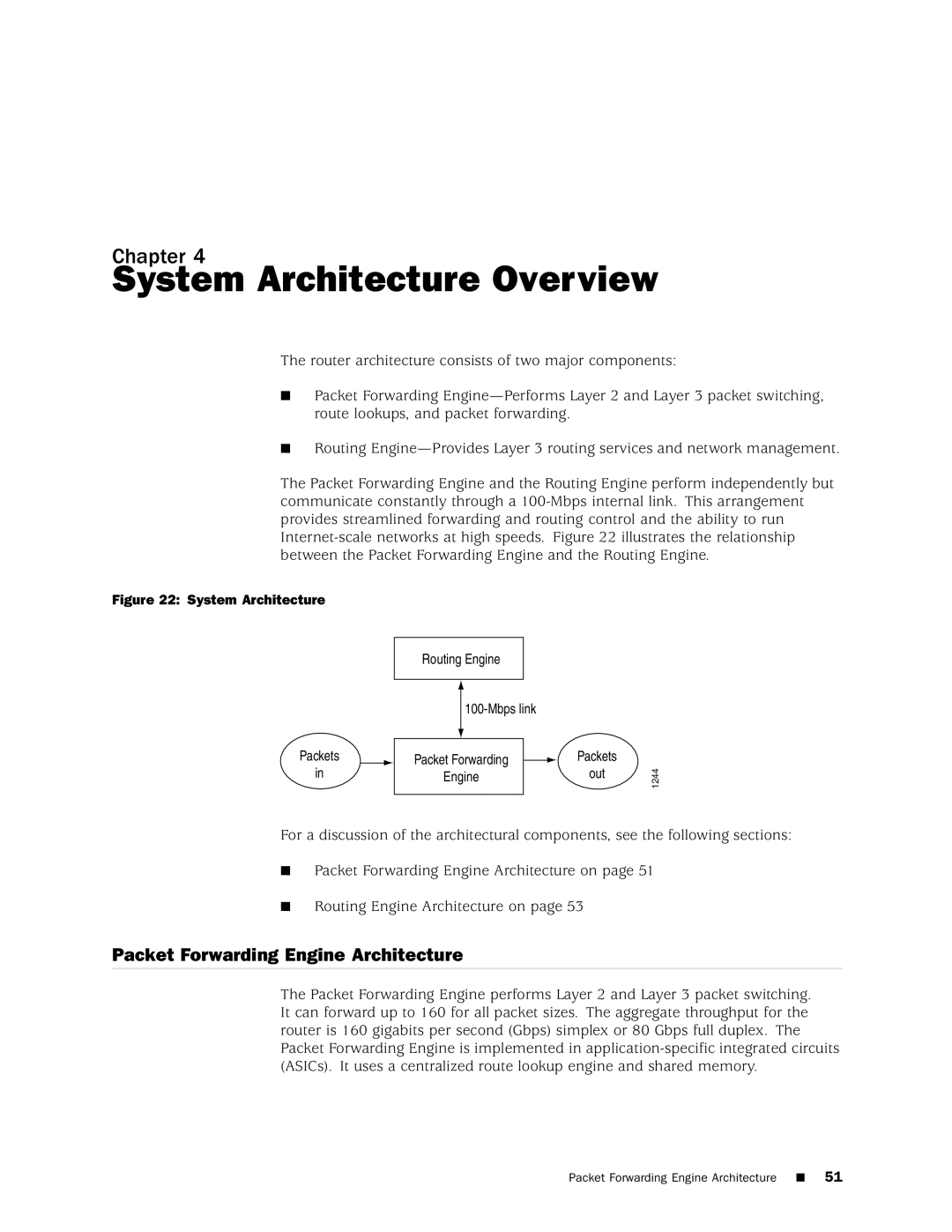
Packet Forwarding Engine Architecture
System Architecture Overview
Data Flow through the Packet Forwarding Engine
Packet Forwarding Engine Components and Data Flow
Routing Engine Architecture
Routing Engine Architecture
Routing Engine Functions
Packets Out
Page
Initial Installation
Initial Installation
Rack Requirements
Preparing for Router Installation
Rack Size and Strength
Typical Center-Mount Rack
Spacing of Mounting Holes
Clearance Requirements for Airflow and Hardware Maintenance
Routing Node Environmental Specifications
Connection to Building Structure
Fire Safety Requirements
Routing Node Environmental Specifications Description Value
Fire Suppression
Fire Suppression Equipment
Power Guidelines, Requirements, and Specifications
Radio Frequency Interference
Site Electrical Wiring Guidelines
Distance Limitations for Signaling
Router Power Requirements
Component Power Requirements Power Requirement Amps
Power consumption for maximum configuration
Chassis Grounding
Power, Connection, and Cable Specifications
Shows a typical source cabling arrangement
Preparing for Router Installation
Power and Grounding Cable Connections
Network Cable Specifications and Guidelines
Fiber Optic and Network Cable Specifications
Signal Loss in Multimode and Single-Mode Fiber-Optic Cable
Attenuation and Dispersion in Fiber-Optic Cable
Calculating Power Budget for Fiber-Optic Cable
Calculating Power Margin for Fiber-Optic Cable
Attenuating to Prevent Saturation at SONET/SDH PICs
Routing Engine Interface Cable and Wire Specifications
Site Preparation Checklist
Site Preparation Checklist Item or Task
Date
Item or Task Performed By Date
Unpacking the Router
Tools and Parts Required
Unpacking the Router
M160 Internet Router Hardware Guide
Component Quantity
Generic Inventory of Router Components Installed in Chassis
M160 Internet Router Hardware Guide Unpacking the Router
Installing the Chassis Using a Mechanical Lift
Installing the Router Using a Mechanical Lift
M160 Internet Router Hardware Guide
Router Component Weights Approximate Weight lb Weight kg
Installing the Router without a Mechanical Lift
Removing Components from the Chassis
Installing the Router without a Mechanical Lift
Removing the Rear Component Cover
Removing the Power Supplies
Removing the SFMs
Removing an SFM
Removing the MCSs
Removing an MCS
Removing the PCGs
Removing a PCG
Removing the Routing Engines
Removing a Routing Engine
Removing the Rear Upper Impeller Assembly
Removing the Rear Upper Impeller Assembly
Removing the Rear Lower Impeller Assembly
Removing the Fan Tray
Removing the Rear Lower Impeller Assembly
Removing the FPCs
FPC Removal Checklist Slot Media Types Date Removed
Installing the Router without a Mechanical Lift
Removing an FPC
Removing the Front Impeller Assembly
Removing the Front Impeller Assembly
Installing the Chassis into the Rack
Attaching the Lifting Handle
Installing the Chassis in a Rack
Reinstalling Components into the Chassis
Reinstalling the Front Impeller Assembly
Reinstalling the Front Impeller Assembly
Reinstalling the FPCs
Reinstalling an FPC
Reinstalling the Fan Tray
Reinstalling the Fan Tray
Reinstalling the Rear Lower Impeller Assembly
Reinstalling the Rear Lower Impeller Assembly
Reinstalling the Rear Upper Impeller Assembly
Reinstalling the Rear Upper Impeller Assembly
Reinstalling the Routing Engines
Reinstalling a Routing Engine
Reinstalling the PCGs
Reinstalling a PCG
Reinstalling the MCSs
Reinstalling an MCS
Reinstalling the SFMs
Reinstalling the Power Supplies
Reinstalling the Rear Component Cover
Reinstalling a Power Supply
Connecting the Router and Performing Initial Configuration
Connecting the Router to Management and Alarm Devices
113
Connecting to a Management Console or Auxiliary Device
Connecting to a Network for Out-of-Band Management
Connecting PIC Cables
Connecting to an External Alarm-Reporting Device
M160 Internet Router Hardware Guide
Connecting Power to the Router
Providing Power to the Router
M160 Internet Router Hardware Guide
Connecting Power and Grounding Cables
Powering On the Router
M160 Internet Router Hardware Guide
Configuring the Junos Internet Software
Configure the router’s domain name
Commit the configuration to activate it on the router
Page
125
Page
Routine Maintenance Procedures
Maintaining Hardware Components
Maintaining Cooling System Components
Removing the Air Filter
Maintaining the Air Filter
Installing the Air Filter
Cleaning the Air Filter
Maintaining the Fan Tray and Impellers
Installing the Air Filter
User@host show chassis routing-engine
Maintaining Host Module Components
User@host show chassis environment mcs
Maintaining Packet Forwarding Engine Components
User@host show chassis fpc
Maintaining FPCs
Show chassis Fpc pic-status
Maintaining PICs and PIC Cables
135
Maintaining the PCGs
User@host show chassis sfm detail
Maintaining SFMs
User@host show chassis environment pem
Maintaining Power Supplies
User@host show chassis alarms
139
Replacing Hardware Components
Tools and Parts Required Tool or part Components
Replacing the CIP and Routing Engine Interface Port Cables
Removing the CIP
Tool or part Components
Service, and System Basics Command Reference
Removing the CIP
Installing the CIP
Installing the CIP
Replacing Connections to Routing Engine Interface Ports
Routing Engine Interface Ports and Alarm Relay Contacts
Replacing the Console or Auxiliary Cable
Replacing the Management Ethernet Cable
Serial Port Connector
Replace Alarm Relay Wires
Replacing Cooling System Components
Replacing the Fan Tray
Removing the Fan Tray
Installing the Fan Tray
Installing the Fan Tray
Replacing the Front Impeller Assembly
Removing the Front Impeller Assembly
Removing the Front Impeller Assembly
153
Replacing the Rear Lower Impeller Assembly
Installing the Front Impeller Assembly
Installing the Rear Lower Impeller Assembly
Removing the Rear Lower Impeller Assembly
Installing the Rear Lower Impeller Assembly
Replacing the Rear Upper Impeller Assembly
Removing the Rear Upper Impeller Assembly
Installing the Rear Upper Impeller Assembly
Installing the Rear Upper Impeller Assembly
Replacing Host Module Components
Replacing an MCS
Removing an MCS
User@host request chassis routing-engine master switch
Installing an MCS
Installing an MCS
Removing the PC Card
Removing and Insert the PC Card
Removing the PC Card
Insert the PC Card
Removing a Routing Engine
Replacing a Routing Engine
User@host show chassis routing-engine
167
Installing a Routing Engine
Replacing an FPC
Replacing Packet Forwarding Engine Components
Removing an FPC
171
Installing an FPC
173
User@hostrequest chassis fpc slot slot-numberonline
175
Removing a PCG
Replacing a PCG
177
Installing a PCG
Removing a PIC
Replacing a PIC
Service, and System Basics Command Reference
Removing a PIC
Installing a PIC
M160 Internet Router Hardware Guide
183
Installing a PIC
Removing a PIC Cable
Replace PIC Cables
Installing a PIC Cable
187
Removing an SFM
Replacing an SFM
Installing an SFM
Removing an SFP
Replace an SFP
Installing an SFP
M160 Internet Router Hardware Guide
Replacing Power System Components
Replacing the Circuit Breaker Box
Removing the Circuit Breaker Box
Service, and System Basics Command Reference
Removing the Circuit Breaker Box
Installing the Circuit Breaker Box
M160 Internet Router Hardware Guide
Removing a Power Supply
Replacing a Power Supply
Removing a Power Supply
Rear of Power Supply Showing Midplane Connectors
Installing a Power Supply
Disconnecting Power from the Router
Disconnecting and Connecting Power
201
Disconnecting Power Cables
Connecting Power to the Router
203
Replacing a Fuse
Connecting Power and Grounding Cables
205
Color Component Fuse Rating Quantity Locations
Fuse Specifications
Troubleshooting Hardware Components
Overview of Troubleshooting Resources
Command-Line Interface
LEDs on the Craft Interface
LEDs
Chassis and Interface Alarm Messages
Chassis Alarm Messages Component LCD Message CLI Message
LEDs on Hardware Components
Component LCD Message CLI Message
SONET/SDH Interface Alarm Messages
Blown Fuse Indicators
Juniper Networks Technical Assistance Center
Troubleshooting the Cooling System
Troubleshooting Packet Forwarding Engine Components
Troubleshooting FPCs
Troubleshooting PICs
Troubleshooting the Power System
All LEDs on Both Supplies Are Off
All LEDs on One Supply Are Off or LED States Are not Correct
217
Page
Appendixes
Appendixes
Definition of Safety Warning Levels
Safety and Regulatory Compliance Information
Safety Guidelines and Warnings
223
General Safety Guidelines and Warnings
Qualified Personnel Warning
Restricted Access Area Warning
Preventing Electrostatic Discharge Damage
Placing a Component into an Electrostatic Bag
Electrical Safety Guidelines and Warnings
M160 Internet Router Hardware Guide
DC Power Electrical Safety Guidelines
General Electrical Safety Guidelines
Copper Conductors Warning
DC Power Disconnection Warning
DC Power Grounding Requirements and Warning
DC Power Wiring Sequence Warning
DC Power Wiring Terminations Warning
Grounded Equipment Warning
Case of Electrical Accident
Power Disconnection Warning
TN Power Warning
Installation Safety Guidelines and Warnings
Installation Instructions Warning
Chassis Lifting Guidelines
Rack-Mounting Requirements and Warnings
241
M160 Internet Router Hardware Guide
243
Ramp Warning
Laser and LED Safety Guidelines and Warnings
Class 1 Laser Product Warning Class 1 LED Product Warning
General Laser Safety Guidelines
Laser Beam Warning
Radiation From Open Port Apertures Warning
Maintenance and Operational Safety Guidelines and Warnings
Battery Handling Warning
Jewelry Removal Warning
Lightning Activity Warning
Operating Temperature Warning
Product Disposal Warning
EMC
Agency Approvals
Japan
Compliance Statements for EMC Requirements
Canada
European Community
Locating Component Serial Numbers
Contacting Customer Support and Returning Hardware
Attached to the component body
Craft Interface Serial Number ID Label
CIP Serial Number ID Label
Craft Interface Serial Number ID Label
DC Power Supply Serial Number ID Label
MCS Serial Number ID Label
FPC Serial Number ID Label
PIC Serial Number ID Label
PCG Serial Number ID Label
PIC Serial Number ID Label
Routing Engine Serial Number ID Label
Contacting Customer Support
SFM Serial Number ID Label
Information You Might Need to Supply to Jtac
Return Procedure
Tools and Parts Required
Packing the Routing Node for Shipment
M160 Internet Router Hardware Guide
Packing Components for Shipment
Page
RJ-45 Connector Pinout Signal
Cable Connector Pinouts
DB-9 Connector Pinout Signal Direction Description
Data numbering Form Signal
RJ-48 Cable Pinouts for E1 and T1 PICs
Data numbering
Form Signal
RX/Ring/- --RX/Ring
RJ-48 Pin on T1/E1 DB-15 Pin
V.35 Cable Pinouts for EIA-530 PIC
Fast Ethernet 48-port Cable Pinouts
DB-25 Pin Signal 35 Pin Description
RJ-21 Pin Assignments Ethernet Port Numbers
Fast Ethernet 48-port PIC
18, 30 19, 31 20, 32 21, 33 10, 22, 34 11, 23, 35
Index
Index
Airflow
Symbols
PIC
EMC EMI
MCS
PCG
SONET/SDH
Rear lower impeller assembly installation instructions
Power supply
SFP
Wiring, electrical See electricity Cable pinouts