Cisco BPX 8600 Series Reference
Release May
Page
Page
Page
About This Manual
Chapter Introduction
BPX Switch Common Core
Chapter General Description
Chapter Service Interface Line Cards
Chapter Network Interface Trunk Cards
Simba
BXM T3/E3, 155,
Chapter ATM Connections
Chapter Tag Switching
Chapter ATM and Frame Relay SVCs SPVCs
Chapter BME Multicasting
Chapter Repair and Replacement 11-1
Chapter Frame Relay to ATM Network Service Interworking 12-1
Chapter Tiered Networks 13-1
Chapter BPX Snmp Agent 14-1
Appendix C BPX Switch Peripherals
Appendix a BPX Node Specifications
Appendix B BPX Switch Cabling Summary
Appendix D AT3-6ME Interface Adapter
Appendix E Glossary Index
F I G U R E S
Xviii Cisco BPX 8600 Series Reference
List of Figures
Dial-Modem Cabling for Auto Answer Dial-In to BPX
T a B L E S
Table A-1
Table B-1
Table B-2
Table B-3
Table C-1
Table C-2
Table C-3
Table C-4
Xxiv Cisco BPX 8600 Series Reference
Cisco WAN Switching Product Name Change
About This Manual
Objectives
Audience
Organization
Chapter Tag Switching
Chapter Repair and Replacement
Chapter Frame Relay to ATM Network and Service Interworking
Appendix a BPX Node Specifications
Related Documentation
Related Documentation
Conventions
Conventions
Xxx Cisco BPX 8600 Series Reference
BPX Capabilities
Introduction
General Description
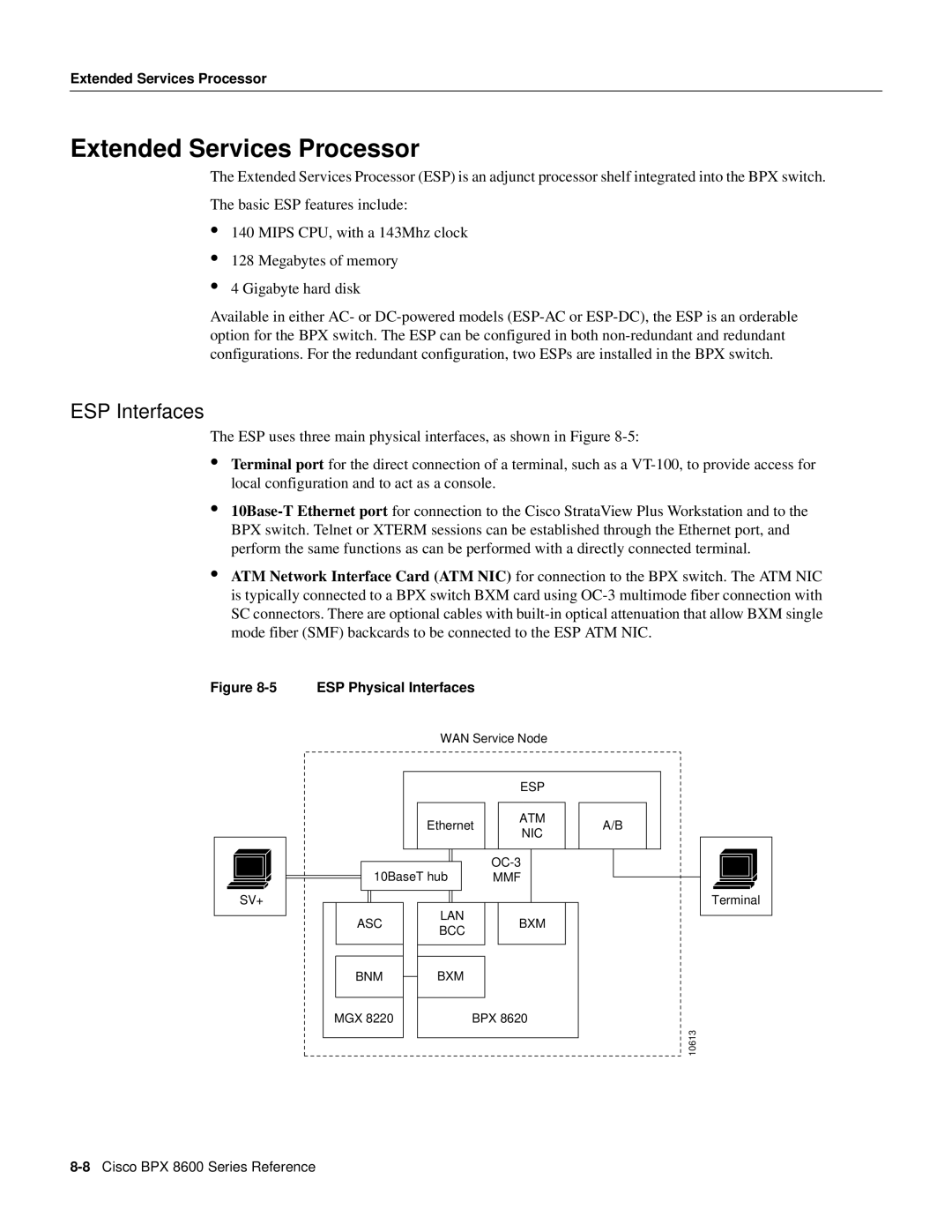
Extended Services Processor
General Description BPX Switch General Configuration Example
Continuing Features with Release
BPX Switch
MGX IGX Switch
New with Release
Continuing Features with Release
Network
IMATM-B
BPX Switch Operation
Access Products
BPX Switch Operation
BPX Switch Operation
BPX Switch with MGX 8220 Shelves
Tag Switching
BPX Switch with Extended Services Processor
Frame Relay to ATM Interworking
Frame Relay to ATM Network Interworking
Additional Information
Service Interworking
Tiered Networks
Routing Hubs and Interface Shelves
BPX Switch Routing Hubs
Tiered Network with BPX Switch and IGX Switch Routing Hubs
Inverse Multiplexing ATM
Virtual Trunking
Virtual Trunking Example
Traffic and Congestion Management
Traffic and Congestion Management
FairShare
Cost-Based AutoRoute
OptiClass
AutoRoute
Congestion Management, VS/VD
Congestion Management, ForeSight
Network Management
Network Management
Network Interfaces
Node Synchronization
Service Interfaces
Statistical Alarms and Network Statistics
Connections and Connection Routing
Switch Software Description
Switch Software Description
Connection Routing Groups
Major Features of Cost-Based AutoRoute
Cost-Based Connection Routing
22Cisco BPX 8600 Series Reference
Network Synchronization
Cost-Based AutoRoute Commands
Network Synchronization
Switch Availability
Node Alarms
Switch Availability
Node Redundancy
Switch Availability
26Cisco BPX 8600 Series Reference
Physical Description
BPX Switch Enclosure
General Description
BPX Switch Exterior Front View
Physical Description
Node DC Powering
Node Cooling
Optional AC Power Supply Assembly
DC Power Entry Module Shown with Conduit Box Removed
Card Shelf Configuration
AC Power Supply Assembly Front View
BPX Switch Card Shelf Front View
Functional Description
Physical Layer
ATM Layer
Functional Description
ATM Cell Headers
ATM Cell Format
Functional Description UNI Header
NNI Header
STI Header
Functional Description STI Header
ATM Cell Addressing
ATM Adaptation Layer
AAL
Smds
IPX and IGX Switch Trunk Interfaces to ATM
11 SAR Adaptation Process
BAM
FastPacket Adaptation to ATM
STI
CAM UNI
SAM UNI
Simple and Complex Gateway Formats
Simple Gateway
Complex Gateway, Frame Relay to ATM Network Interworking
BPX Switch Plug-In Card Summary Card Name Where
BPX Switch Major Groups
BPX Switch Major Groups
BME
Smfxlr
LM-2OC3-SMF
LM-2OC3-SMFLR
Optional Peripherals
Optional Peripherals
BPX Switch Common Core
BPX Switch Common Core Group
Broadband Controller Card BCC-32, BCC-3, BCC-4
Common Core Group Block Diagram
Broadband Controller Card BCC-32, BCC-3, BCC-4
Features
Functional Description
BCC-32 and BCC-3 Block Diagram
BCC Front Panel Indicators
Indicator Function
Front Panel Description
LAN
Card
BCC Front Panel
Gbps Operation with the BCC-4
Back Cards for the BCC-3 and BCC-32
Enter y
Step
Backcard Line Module for BCC-32, Connectors
Connector Function
EXT 1 TMG
EXT 2 TMG
BCC-3-bc or BCC-c Face Plate Connectors
Alarm/Status Monitor Card
Alarm/Status Monitor Card
ASM Front Panel Controls and Indicators
Controls Indicator Function
Status
ACO
Connector Indicator Function
Line Module for the Alarm/Status Monitor Card
LM-ASM Face Plate Connectors
LMI-ASM Face Plate
BPX Switch StrataBus 9.6 and 19.2 Gbps Backplanes
BPX Switch StrataBus 9.6 and 19.2 Gbps Backplanes
18Cisco BPX 8600 Series Reference
Network Interface Trunk Cards
BPX Switch Network Interface Group
BXM Cards, Trunk Mode Summary
Broadband Network Interface Cards BNI-T3 and BNI-E3
Broadband Network Interface Cards BNI-T3 and BNI-E3
Egress
Simplified BNI-T3, BNI-E3 Block Diagram
Ingress
Bandwidth Control
Front Panel Indicators
Loopbacks and Diagnostics
BNI Front Panel Status Indicators
Status LED color Status Description
Status port
LM-3T3 and LM-3E3 Connectors
T3 and E3 Line Modules LM-3T3 and LM-3E3
Port 1 RX TX
Port 2 RX TX
T3 and E3 Line Modules LM-3T3 and LM-3E3
LM-3T3 Face Plate, Typical
LM-3E3 Face Plate, Typica
Broadband Network Interface Cards, BNI-155
Overview
Egress
Ingress
CBR VBR
Simplified BNI-155 Block Diagram
Act Stby Fail Failure Description
7BNI-155 Front Panel
LM-OC3-SMF and LM-OC3-SMFLR Connectors Function
LM-OC3-MMF Connectors Function
OC3, Line Modules SMF, SMFLR, & MMF
OC3, Line Modules SMF, SMFLR, & MMF
LM-2OC3-SMF Face Plate
LM-2OC3-MMF Face Plate
Cabling of BNI Backcard, SMF-2-BC
Cabling of BNI Backcard, SMF-2-BC
20Cisco BPX 8600 Series Reference
BXM Cards, Port UNI Mode Summary
Service Interface Line Cards
BPX Switch Service Interface Group Summary
ASI-1, ATM Service Interface Card
ASI-1, ATM Service Interface Card
Egress
Configuring Connections ATM over ASI Example
Monitoring Statistics
6Cisco BPX 8600 Series Reference
ASI-1 Front Panel
LM-2T3 Module
LM-2T3 Module
Line Module, ASI, 2T3
LM-2E3 Module
LM-2E3 Module
Line Module, ASI, 2E3
ASI-155, ATM Service Interface Card
ASI-155, ATM Service Interface Card
Configuring Connections
ASI-155 Simplified Block Diagram
Service Interface Line Cards
ASI-155 Front Panel
BXM Cards, Access UNI Mode
ASI-155 Line Module, LM-2OC3-SMF
ASI-155 Line Module, LM-2OC3-SMFLR
ASI-155 Line Module, LM-2OC3-MMF
BXM Cards, Access UNI Mode
Tag Switching
BXM T3/E3, 155,
Dynamic Resource Partitioning for SPVCs
Dynamic Resource Partitioning for SPVCs
BXM Cards
BXM Cards
T3/E3 45 Mbps/34Mbps
OC3/STM-1 155.52 Mbps
OC12/STM-4 622.08 Mbps
BPX-T3/E3-BC
Features
BXM Capabilities
T3/E3 45 Mbps/34 Mbps
OC3/STM-1 155.520 Mbps
ATM Layer
BXM Capabilities
Service Types
CBR Service
VBR Service
ABR Service
BXM Front Card Indicators
BXM Front Panel Status Indicators
BXM Front Panel Card Failure indicators
Card Operation
Card
BXM-155 Front Panel, Eight-Port Card Shown
BXM-T3/E3 Front Panel, 12-Port Card Shown
BXM, Backcard Connectors
BXM-622 Backcards
BXM-155 Backcards
BXM-T3/E3 Backcards
SMF-622-2, SMFLR-622-2, and SMFXLR-622-2 Back Card
BXM-155-8 Port Backcard, MMF, SMF, or Smflr
BPX-T3/E3 Back Card, 12-Port Option Shown
Cabling of SMF-622 Series Backcards
Y-Cabling of SMF-622 Series Backcards
BXM Functional Description
Overview, Port UNI Mode
BXM Functional Description
BXM Port Access UNI Ingress Operation
10 BXM Port Access, UNI Egress Operation
Overview, Trunk Mode
BXM Trunk Ingress Operation
BXM Trunk Egress Operation
Detailed Description, Port UNI and Trunk Modes
DeMux/Mux
Ingress and Egress Queue Engines
ACP Subsystem Processor
Fault Management and Statistics
Fault Management and Statistics, Port UNI Mode
Alarms
Performance Monitoring
Fault Management and Statistics, Trunk Mode
Technical Specifications
Technical Specifications
Physical Layer
General Information
General Sonet Notes
General Sonet Notes
Sonet Section, Line, and Path Descriptions
Unit Description
User Commands
Diagnostics
Connection Provisioning
Test
Configuring Connections
Configuration Management
Configuring Connections
Syntax
Configuring Connections Field Value Description
Command Line Interface Examples
Command Line Interface Examples
An example of the addtrk command follows
An example of the cnfln command follows
An example of the cnfportq command follows
An example of the upport command follows
An example of the cnfcls command for class 2 follows
YourID1 BPX Jan 1998 0241 GMT
An example of the cnfabrparm command follows
An example of the dsplns command follows
40Cisco BPX 8600 Series Reference
Resource Partitioning
Dynamic Resource Partitioning for SPVCs
Summary
Resource Partitioning
ASI SVC Resource Partitioning
Shown in the following example Example ASI cnfportq Command
Example BXM cnfport Command
BXM SVC Resource Partitioning
NNI Trunk SVC Resource Partitioning
BNI Trunk SVC Resource Partitioning
TS,NTS,FR,FST,CBR,VBR,ABR
Example BNI cnftrkparm Command
BXM Trunk SVC Resource Partitioning
Example BXM cnftrk Command
ATM Connection Services
ATM Connections
SVCs
SVCs
Traffic Management Overview
Traffic Parameters
QoS Parameters
Other Attributes
BXM Connections
Standard ABR notes
Vsvd Description
ATM Connection Requirements
ATM Connection Requirements
ForeSight Congestion Control
Field Value Description
Addcon Command Syntax
Connection Routing
ATM Connection Configuration
ATM Connection Configuration
CLP0+1
SCR Flow
Default Setting OC12 Range ASI T3/E3 Range ASI-155 Range
BXM T3/E3, OC3
RDF
ICR
RIF
PCR
Cdvt
Vsvd
SCR
IBS
CBR Connections
CBR Policing Definitions ATM Forum TM Spec PCR Flow
VBR and Atfr Connections
VBR Connections
Atfr Connections
Atfr Connection Prompt Sequence
ABR Connections
ABR Notes
ABR and Atfst Connections
ABR Standard Connection Prompt Sequence
Meaning of Vsvd and Flow Control External Segments
Atfst Connections
ABR ForeSight Connection Prompt Sequence
Atfst Connection Prompt Sequence
UBR Connections
UBR Policing Definitions ATM Forum TM Spec PCR Flow
Traffic Policing Examples
Dual-Leaky Bucket An Analogy
CBR Traffic Policing Examples
Traffic Policing Examples
11 CBR Connection, UPC Overview
LP=1
12 CBR.1 Connection with Bucket Compliant
VBR Dual-Leaky Bucket Policing Examples
VBR.1
14 VBR Connection, UPC Overview
Leaky Bucket
Examples
15 VBR Connection, Policing = 4, Leaky Bucket 1 Compliant
CLP=0
VBR.2
LP=0
18 VBR.2 Connection, Leaky Bucket 2 Discarding CLP 0 Cells
VBR.1
VBR.3
ABR Connection Policing
UBR Connection Policing
21 UBR Connection, UPC Overview
Traffic Shaping for CBR, VBR, and UBR
Configuration
Traffic Shaping for CBR, VBR, and UBR
LMI and Ilmi Parameters
Traffic Shaping Rates
ATM and Frame Relay SVCs, and SPVCs
ATM and Frame Relay SVCs and SPVCs
PVCs and SVCs
PVCs
SPVCs
ATM and Frame Relay SVCs and SPVCs
SVCs
BPX Switch and ESP Interfaces
BPX Switch and ESP Interfaces
Interim Inter-switch Protocol Routing
Signaling Plane
Signaling Plane
UNI Signaling Channel
NNI Signaling Channel
UNI Signaling Channels
Network Interworking Between Frame Relay and ATM
Network Interworking Between Frame Relay and ATM
ESP Interfaces
Extended Services Processor
Extended Services Processor
Stand-Alone ESP
Redundant ESPs
Cable Redundancy
ESP Y-Cable Redundancy
Other Redundancy Options
Resource Partitioning
Tag Switching
Introduction
Tag Switching Benefits
Tag Switching Benefits
Tag Switching Overview
Elements in a Tag Switching Network
Tag Switching Operation at Layer
Elements in a Tag Switching Network
Forwarding
Control
Tag Switching in an ATM WAN
Tag Switching in an ATM WAN
Tag Forwarding Information Base Tfib in an ATM Environment
Downstream on Demand Tag Allocation, Conservative Mode Shown
Tag Switching and the BPX
Tag Switching and the BPX
BPX Tag Switching
Virtual Switch Interfaces
BPX Switch VSI Interfaces
Connection Setup, End Points on same VSI Slave
Tag Switching Resource Configuration Parameters
Tag Switching Resource Configuration Parameters
Configuring VSI Lcns
Useful Default Allocations
Details of More Rigorous Allocations
Port VSI Partition LCN Allocation Elements
Requirements
Requirements
List of Terms
Related Documents
Configuration Management
Related Documents
Configuration Criteria
Cnfqbin Command
Cnfrsrc Command
Configuration Criteria
Cnfrsrc Parameter Summary
Example Parameter cnfrsrc Value Description
Configuration Example
Resetcd 4 h
Configuration Example
Dspcds
Status Active Revision CD18
Max PVC bandwidth Partition Enabled e VSI min LCNs
Uptrk 4.1 uptrk 4.2 uptrk
Cnfrsrc
VSI start VPI VSI end VPI VSI min b/w VSI max b/w
22Cisco BPX 8600 Series Reference
Cnfqbin 4.1 10 e 0 65536 95 100
Cnfqbin 4.1 Enable/disable e
Dspqbin 4.1
Addshelf 4.1 vsi 1
Tsc# show controllers VSI descriptor
Checking and Troubleshooting
Checking and Troubleshooting
Dsptrks
Dspnode
Dsprsrc 4.1
Tsc# sho tag tdp disc
Tsc# show tag int
Tsc# reload
Provisioning and Managing Connections
Provisioning and Managing Connections
Statistics
Command Reference
BPX Switch Commands
TSC Commands
Command Reference
Related Commands
Addshelf
Syntax
Attributes
Description for Tag Switching
Example for Tag Switching
Addshelf 11.1 a
Description for Interface Shelves
Example for Interface Shelves
Related Commands dspqbin Parameters-cnfqbin
BPX switch
Cnfqbin
Example
Description
Cnfqbin 4.1 10 e 0 65536 95 100
Parameter cnfrsrc Description
Related Commands Parameters-cnfrsrc
Cnfrsrc
Cnfrsrc Parameter cnfrsrc Description
Here, ax = 256, n1x = 512, and m1x =
10 Port VSI Partition LCN Allocation Elements
Example 1, 8-Port OC3 BXM Configured in Trunk Mode
Cnfrsrc
Port N1x Unallocated Min z1 + n1x, max M1x LCNs
Total Lcns available to
Port VSI Partition =
Example 2, 8-Port OC3 BXM Configured in Port Mode
44Cisco BPX 8600 Series Reference
120 3000 3500 4907 7588 100
IPX switch, IGX switch, BPX switch
Dspcd
Parameters-dspcd
Dspcd
Dspcds
Parameters-dspcds
Syntax dspcds l Example dspcds
Dspcds
KDJ
Dspnode
BPX switch, IGX switch Yes
Dspnode
50Cisco BPX 8600 Series Reference
Related Commands cnfqbin Parameters-dspqbin
Dspqbin
Example dspqbin 4.1
Dspqbin
Example dspqbin 4.1 10 Sample Display
Related Commands cnfrsrc Parameters-dspcds
Dsprsrc
Example dsprsrc 4.1
Dsprsrc
Dsptrks
Dsptrks
Example
Resetcd
Example resetcd 5 H
Yes IPX switch, IGX switch, BPX switch
Resetcd
Yes BPX switch
Upport
Example upport
Upport
System Response
Uptrk
Parameters-uptrk
Optional Parameters-uptrk
Example uptrk
Uptrk
BME Multicasting
BME Features
Standards
Multicasting Benefits
Multicasting Overview
Connection Management Criteria
Connection Management with Cisco StrataView Plus
BME Restrictions
Address Criteria
BME Operation
BME Operation
BME Cell Replication
Group Action Command
Cell Replication Stats
Adding Connections
Group
Multi-Segment Multicast Connections
Multicast Statistics
Alarms
Alarms
Policing
OAM cells
AIS cells
Hot Standby Backup
Hot Standby Backup
Configuration
Configuration
Connection Diagnostics
Configuration Management
Repair and Replacement
Preventive Maintenance
Troubleshooting the BPX Switch
General Troubleshooting Procedures
Troubleshooting the BPX Switch
Troubleshooting the BPX Switch Symptom Probable Cause Remedy
Symptom Probable Cause Remedy
Card Status for the BPX Switch
Displaying the Status of Cards in the Node
Card Type Status Description
BCC
Replacing a Front Card
Replacing Parts
Replacing Parts
Replacing Parts Step
Top of the grille should pop out
Replacing a Line Module
Unlatching the Air Intake Grille
11-8Cisco BPX 8600 Series Reference
Replacing a DC Power Entry Module
Removing a Line Module
DC Power Entry Module with Conduit Box
Replacing an AC Power Supply
AC Power Supply Assembly
Field-Installing a Second AC Power Supply
Removing Blank Filler Panel B side shown
Replacing the Fan Assembly
Replacing the Temperature Sensing Unit
Replacing Card Slot and Fan Fuses on the System Backplane
Card Slot and Fan Fuse Locations on System Backplane
11-16Cisco BPX 8600 Series Reference
Frame Relay to ATM Network and Service Interworking
Frame Relay to ATM Network and Service Interworking
12-2Cisco BPX 8600 Series Reference
Service Interworking
Networking Interworking
Networking Interworking
MUX FRP BUS AIT BNI
ATF Connections, Simplified Example
ATM Layers
ATM Protocol Stack
ATM Protocol Stack
AIT/BTM Interworking and the ATM Protocol Stack
AIT/BTM Interworking and the ATM Protocol Stack
Protocol Stack Operation
AIT/BTM Control Mapping, Frames and Cells
Features
Management, OAM Cells
ATF Summary
Limitations
Some ATF Connection Criteria
Connection Management
Port Management
Addcon Cnfcls Cnfcon Delcon Dspcls Dspcon Dspcons
Channel Statistics
Structure
Cnfport Cnfportq
Clrchstats Cnfchstats Dspchstats Dspchstatcnf Dspchstathist
Dspalms Dspcon Dspport Tstconseg Tstdly
Diagnostics
OAM Cell Support
Virtual Circuit Features
User Commands
Management
AUser Commands
Management
User Interface
Routing
Bandwidth Management
Signaling
Alarms
BPX and IGX Routing Hubs
Tiered Networks
Routing Hubs and Interface Shelves
Routing Hubs and Interface Shelves
Tiered Network with BPX and IGX Routing Hubs
BPX Routing Hubs in a Tiered Network
BPX Routing Hubs in a Tiered Network
Tiered Network Implementation
Definitions
Upgrades
General
Co-locating Routing Hubs and Interface Shelves
Network Management
IPX Interface Shelf Description
ForeSight
Preferred Routing
Local and Remote Loopbacks
Interface Shelf Management
Configuration and Management
Alarm Management of Interface Shelf on the BPX Hub Node
Alarm Management on the IPX Interface Shelf
Port Management
Connection Management
Bandwidth Management
IGX Routing Hubs in a Tiered Network
IGX Routing Hubs in a Tiered Network
IGX Shelves and Routing Hubs, Frame Relay Connections
General
Co-locating Routing Hubs and Shelves
IGX Interface Shelf Description
Shelf Management
User Interface Commands
Alarm Management of Interface Shelf on the IGX Hub Node
Alarm Management on the IGX Interface Shelf
Shelf
Data Connection Commands
Data Channel Commands
Voice Connection Commands
Voice Channel Commands
Cisco StrataView Plus NMS
Cisco StrataView Plus NMS
13-18Cisco BPX 8600 Series Reference
BPX Snmp Agent
Snmp Overview
1shows an Snmp manager and the nodes within a domain
Snmp Overview
Snmp Functions
Snmp Functions
Responses to Get Get-Next Requests
ATM Set Requests
MIB II Support
MIB II Support
Responses to Set Requests
Cisco WAN Switching Proprietary MIB Structure
Switch Service Objects
Switch Connections
Cisco WAN Switching Proprietary MIB Structure
Endpoint Mapping
Bandwidth Class
Endpoint Statistics
14-8Cisco BPX 8600 Series Reference
BPX Node Specifications
General
General
Characteristic T3 DS3
ATM Trunk Interface BXM-T3/E3 Cards
ATM Trunk Interface BXM-155 Cards
ATM Trunk Interface BXM-T3/E3 Cards
SMF LR ~40 KM
ATM Trunk Interface BXM-155 Cards
SMF IR TX SMF IR RX SMF LR TX SMF LR RX
ATM Trunk Interface BXM-622 Cards
ATM Trunk Interface BXM-622 Cards
ATM T3 Trunk Interface BNI-T3, LM-3T3
ATM T3 Trunk Interface BNI-T3, LM-3T3
ATM E3 Trunk Interface BNI-E3, LM-3E3
ATM E3 Trunk Interface BNI-E3, LM-3E3
ATM OC3 Trunk Interface BNI-OC3, LM-OC3
ATM OC3 Trunk Interface BNI-OC3, LM-OC3
ATM Service Interface BXM-T3/E3 Cards
ATM Service Interface BXM-155 Cards
ATM Service Interface BXM-622 Cards
ATM Service Interface BXM-T3/E3 Cards
ATM Service Interface ASI-1, LM-2T3
ATM Service Interface ASI-1, LM-2T3
ATM Service Interface ASI-1, LM-2E3
ATM Service Interface ASI-2, LM-OC3
ATM Service Interface ASI-2, LM-OC3
12Cisco BPX 8600 Series Reference
BPX Switch Cabling Summary
Power Cabling
AC Powered Nodes
Trunk Cabling
DC Powered Nodes
Table B-3 DC Power Wiring Cable Parameter Description
LM-BCC Cabling
Auxiliary and Control Port Cabling
LAN Port Cabling
Modem Cabling
Table B-6 LAN Port Cabling Cable Parameter Description
Table B-7 LAN Port Pin Assignments Pin # Name
LM-BCC Cabling
External Clock Input Cabling
T1 Clock Cabling
E1 Clock Cabling
Table B-12through Table B-15lists E1 clock cabling details
External Alarm Cabling
Standard BPX Switch Cables
External Alarm Cabling
Table B-17 Network Alarm Pin Assignments Description
LM-BCC TBS
Redundancy Y Cable
Table B-19 Redundancy Y-Cables Used On Cisco P/N
Redundancy Y Cable
BPX Switch Peripherals
Cisco StrataView Plus Terminal Control Port, Local Control
Printer
DIP Switch Settings for Okidata
Table C-3 Switch a Settings-Okidata 184 Printer Description
Printer
Table C-4 Switch 1 Settings-Okidata 184 Printer Description
Table C-5 Switch 2 Settings-Okidata 184 Printer Description
Motorola V.34R BPX Switch Dial-In Configuration
BPX Switch Auto-Answer Dial-In to BPX switch
Modems, Dial-In and Dial-Out
Modems, Dial-In and Dial-Out
ATL1
ATSØ=1
AT\N3
AT%C
IPX Auto-Dial to Customer Service
AT\T3
AT\J
AT\Q1
8Cisco BPX 8600 Series Reference
AT3-6ME Interface Adapter
Application
Equipment Description
Interface Connectors
Equipment Description
Table D-1 Rear Panel Connectors Type Description
T3 RX BNC
T3 TX BNC
DB9
FT2
DIP Switches
Table D-2 Front Panel Indicators Color Description
Front and Rear Panel
FT2
Installation
AT3-6ME Configuration
Installation
Table D-3 DIP Switch SW-1 Selection Guide Position Function
Operation
BPX, IGX, or IPX Port Configuration
Power-Up Sequence
Normal Operation
Remote Loop Operation
Terminal Operation
Operation
Table D-7 Command Summary Parameters Meaning
Commands
Table D-6 DIP Switch Settings
Specifications
Specifications Table D-8 Status Display
T3 interface
BPV NNN
Power
Specifications
T2 Interface
Mechanical
12Cisco BPX 8600 Series Reference
Glossary
ARC Alarm Relay Card
ARI Alarm Relay Interface Card
ARM Alarm Relay Module
ASM Alarm/Status Monitor Cards
B8ZS Bipolar with Eight Zero Suppression
Bandwidth reservation
Channel
BC-E1 Backcard E1
BPX Switch
CAS Channel Associated Signalling
Ccdv Compliant Cell Delay Variation
CCS Common Channel Signalling
CGA Carrier Group Alarm
Cell
Cell relay
Circuit line
COS Class of Service
Crosspoint switch
CSU Channel Service Unit
Dacs Digital Access and Control System
DDS Digital Data Service
Dial Access Switching
DS0 Digital Signal
DS1 Digital Signal
DSI Digital Speech Interpolation
DTE Data Terminal Equipment
ECN Explicit Congestion Notification
Fast EIA
Frame Relay Service
Frame forwarding
FPC FastPAD Back Card
Frame relay connection class
IGX Switch
FTC FastPAD Trunk Card
FTM FastPAD Trunk Module
Gateway
IPX Switch
Isdn Integrated Services Digital Network
Junction node
Junction trunk
Local alarm
Major alarm
Minor alarm
Local addressing
Packet switching
NPC Network Processor Card
NPM Network Processor Module
Nrm
Partially-interleaved EIA
PBX private branch exchange
PCM Pulse Code Modulation
PCR Peak Cell Rate
Red alarm
Remote alarm
Robbed bit signaling
921/Q.931
SAR Segmentation and Reassembly
RS-449
SCC System Clock Card
SCM System Clock Module
SVC switched virtual circuit
Speech detection
Split clock
Status Enquiry
Timestamp
Trm
Trunk
Trunk conditioning
Voice Network Switching
VAD Voice Activity Detection
VBR Variable Bit Rate
Virtual circuit
Cable redundancy
Yellow alarm
Cables
ABR STD
Adtf
ASI
ATM
Dlci
ESP
Fbtc
FRF.4 Frtt
Pnni
SAM
Snmp
Spvc
Tftp
TSR
VCI
VPI
Documentation Response Card
Strongly agree Strongly disagree
Business Reply Mail