Advanced Operations
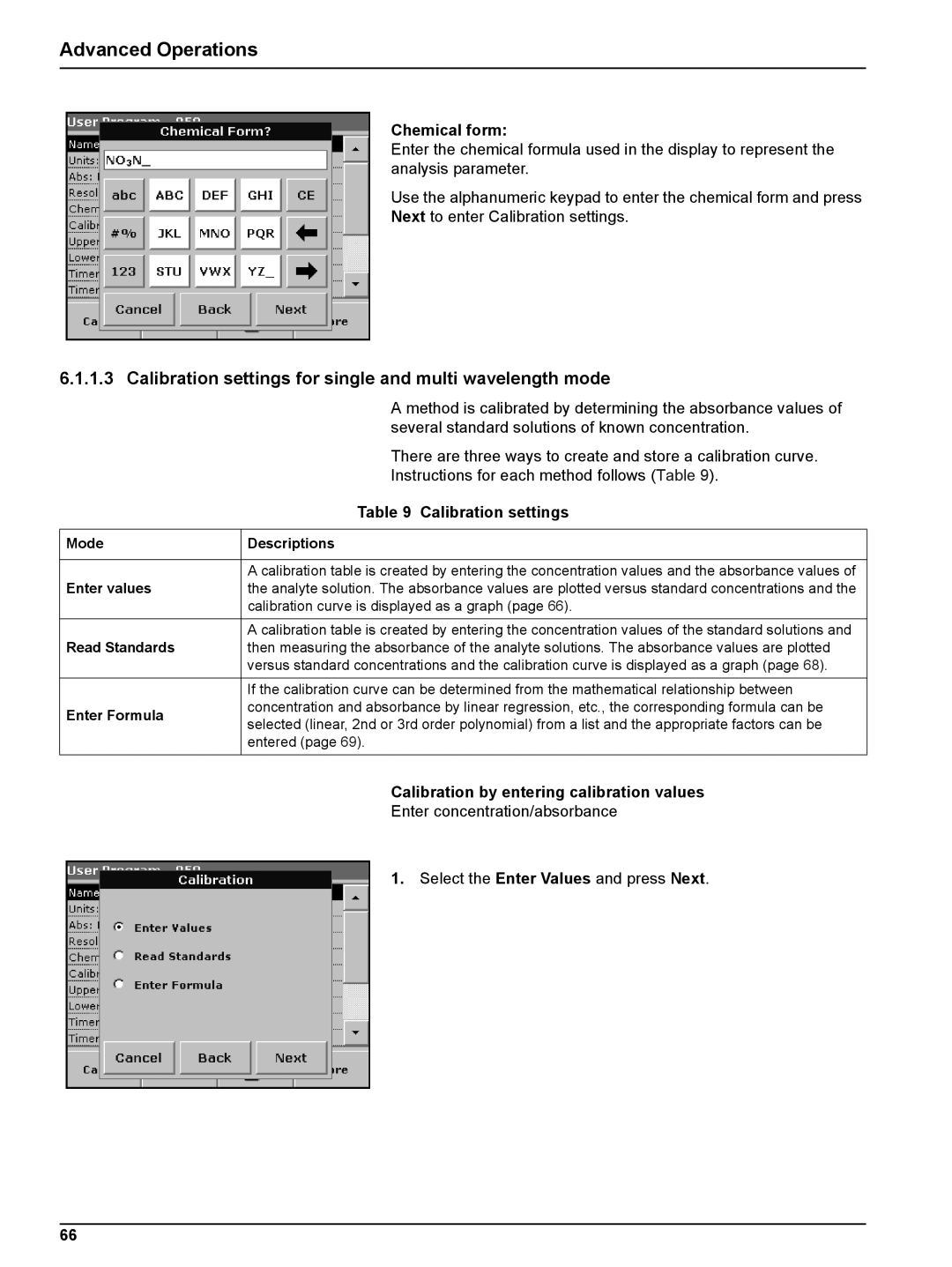
Chemical form:
Enter the chemical formula used in the display to represent the analysis parameter.
Use the alphanumeric keypad to enter the chemical form and press Next to enter Calibration settings.
6.1.1.3 Calibration settings for single and multi wavelength mode
| A method is calibrated by determining the absorbance values of | |
| several standard solutions of known concentration. | |
| There are three ways to create and store a calibration curve. | |
| Instructions for each method follows (Table 9). | |
| Table 9 Calibration settings | |
|
| |
Mode | Descriptions | |
|
| |
| A calibration table is created by entering the concentration values and the absorbance values of | |
Enter values | the analyte solution. The absorbance values are plotted versus standard concentrations and the | |
| calibration curve is displayed as a graph (page 66). | |
| A calibration table is created by entering the concentration values of the standard solutions and | |
Read Standards | then measuring the absorbance of the analyte solutions. The absorbance values are plotted | |
| versus standard concentrations and the calibration curve is displayed as a graph (page 68). | |
|
| |
| If the calibration curve can be determined from the mathematical relationship between | |
Enter Formula | concentration and absorbance by linear regression, etc., the corresponding formula can be | |
selected (linear, 2nd or 3rd order polynomial) from a list and the appropriate factors can be | ||
| ||
| entered (page 69). | |
|
| |
| Calibration by entering calibration values | |
| Enter concentration/absorbance | |
| 1. Select the Enter Values and press Next. |
66