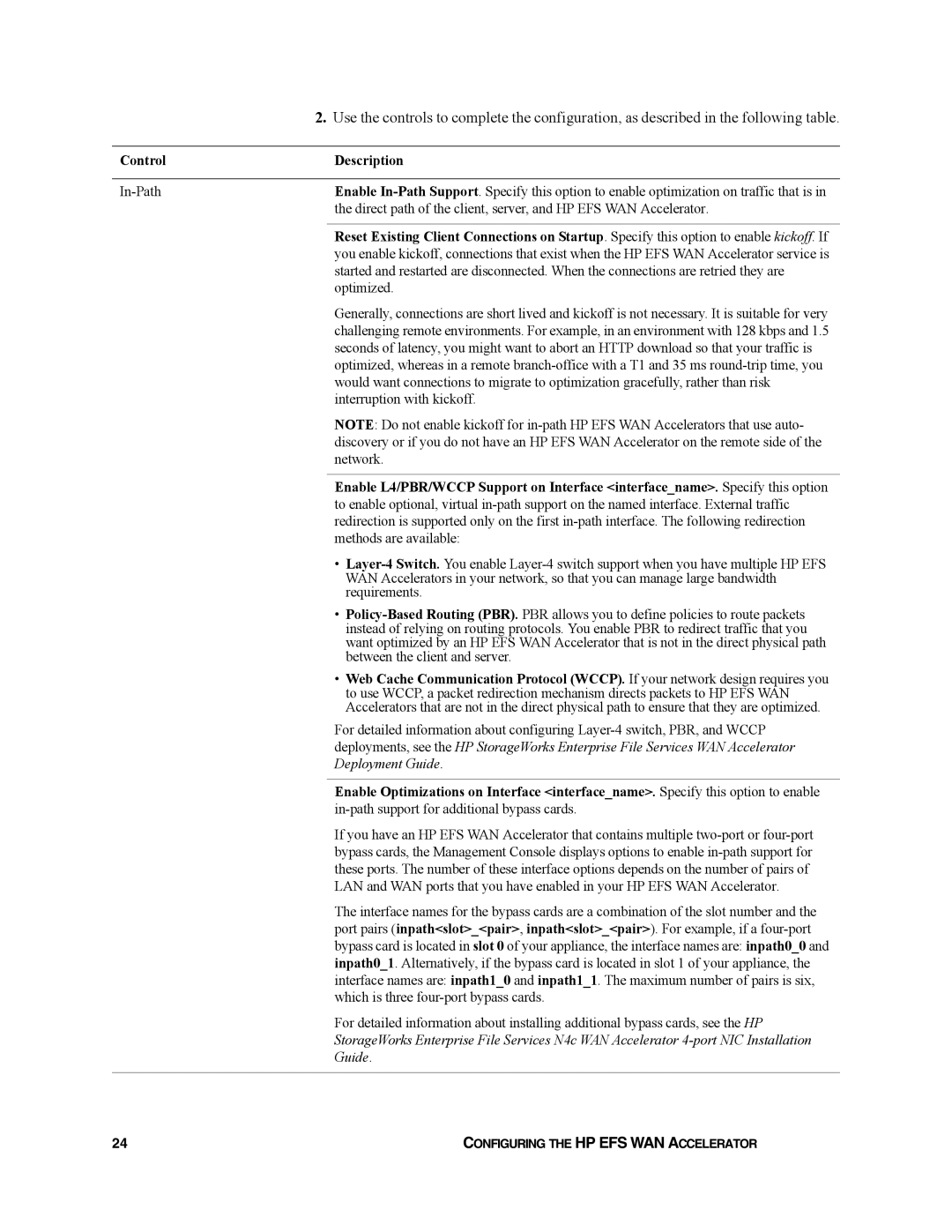
| 2. Use the controls to complete the configuration, as described in the following table. | |
|
|
|
Control |
| Description |
|
|
|
| Enable | |
|
| the direct path of the client, server, and HP EFS WAN Accelerator. |
|
|
|
|
| Reset Existing Client Connections on Startup. Specify this option to enable kickoff. If |
|
| you enable kickoff, connections that exist when the HP EFS WAN Accelerator service is |
|
| started and restarted are disconnected. When the connections are retried they are |
|
| optimized. |
|
| Generally, connections are short lived and kickoff is not necessary. It is suitable for very |
|
| challenging remote environments. For example, in an environment with 128 kbps and 1.5 |
|
| seconds of latency, you might want to abort an HTTP download so that your traffic is |
|
| optimized, whereas in a remote |
|
| would want connections to migrate to optimization gracefully, rather than risk |
|
| interruption with kickoff. |
|
| NOTE: Do not enable kickoff for |
|
| discovery or if you do not have an HP EFS WAN Accelerator on the remote side of the |
|
| network. |
|
|
|
|
| Enable L4/PBR/WCCP Support on Interface <interface_name>. Specify this option |
|
| to enable optional, virtual |
|
| redirection is supported only on the first |
|
| methods are available: |
|
| • |
|
| WAN Accelerators in your network, so that you can manage large bandwidth |
|
| requirements. |
|
| • |
|
| instead of relying on routing protocols. You enable PBR to redirect traffic that you |
|
| want optimized by an HP EFS WAN Accelerator that is not in the direct physical path |
|
| between the client and server. |
|
| • Web Cache Communication Protocol (WCCP). If your network design requires you |
|
| to use WCCP, a packet redirection mechanism directs packets to HP EFS WAN |
|
| Accelerators that are not in the direct physical path to ensure that they are optimized. |
|
| For detailed information about configuring |
|
| deployments, see the HP StorageWorks Enterprise File Services WAN Accelerator |
|
| Deployment Guide. |
|
|
|
|
| Enable Optimizations on Interface <interface_name>. Specify this option to enable |
|
| |
|
| If you have an HP EFS WAN Accelerator that contains multiple |
|
| bypass cards, the Management Console displays options to enable |
|
| these ports. The number of these interface options depends on the number of pairs of |
|
| LAN and WAN ports that you have enabled in your HP EFS WAN Accelerator. |
|
| The interface names for the bypass cards are a combination of the slot number and the |
|
| port pairs (inpath<slot>_<pair>, inpath<slot>_<pair>). For example, if a |
|
| bypass card is located in slot 0 of your appliance, the interface names are: inpath0_0 and |
|
| inpath0_1. Alternatively, if the bypass card is located in slot 1 of your appliance, the |
|
| interface names are: inpath1_0 and inpath1_1. The maximum number of pairs is six, |
|
| which is three |
|
| For detailed information about installing additional bypass cards, see the HP |
|
| StorageWorks Enterprise File Services N4c WAN Accelerator |
|
| Guide. |
|
|
|
24 | CONFIGURING THE HP EFS WAN ACCELERATOR |