Page
Inter
INTEl Corporation
Table of Contents
Page
Introduction
Page
Chapter Part 1 Introduction to Functions of a Computer
Instruction Register and Decoder
Program Counter Jumps, Subroutines and the Stack
Timing
Control Circuitry
Address Registers
Arithmetic/Logic Unit ALU
Wait memory synchronization
Instruction Fetch
Memory Read
Memory Write
Module
Evolution
MCS·SS Microcomputer System
Introduction to MCS-85
Software Compatibility
8155 =CE, 8156 =CE
MCS·S5 Special Peripheral Components
·1. MCS·SS Basic System
MEMil. lOR
Interfacing to MCS·80/8S Programmable Peripheral Components
Programmable Peripherals
Demultiplexing the BUS
Interfacing to Standard Memory
Conclusions THROUGHPUT/COST
Instruction CYCLE/ACCESS Time
System Performance
Distributed Processing
Page
Functional Description
Page
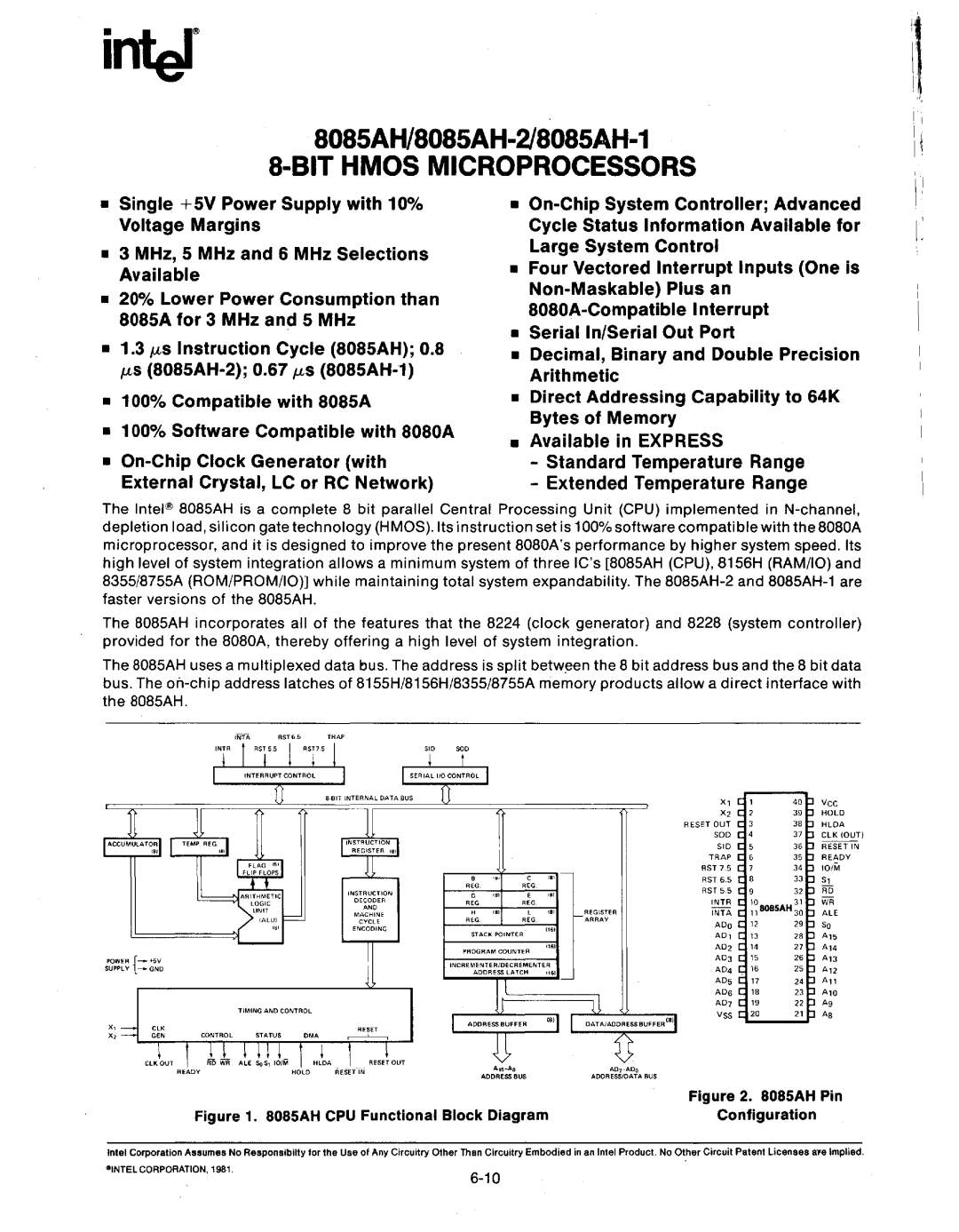
Whatsin the 808SA
·1 808SA CPU Functional Block Diagram
122H
Hexadecimalbinary A7H
Hexidecimal Binary AEH
·28085A Clock Logic
·38085A Hardware and SOFT· Ware RST Branch Locations
·5RIM Read Interrupt Mask
·4INTERRUPT Masks SET Using SIM Instruction
Branched to
When Inter· Rupt occurs
Name Priority
Type
·8BASIC CPU Functions
HOW the MCS·85SYSTEM Works
·9 CPU Timing for Store Accumulator Direct STA Instruction
Functional Description
·12808SA Machine State Chart
·13OPCODE Fetch Machine Cycle of DCX Instruction
Lililili
Memory Write MW
Jl..Jl..Jl..J LIl..Jl..J ~
U- U-U
V V U
Lr \F LrLrU-U-U-U- U
~--r
\J li\ Lr V V- U V u u u U
·21 Hold VS Interrupt NON Halt
RST 7.5 Mask
Resets Sets
RST 5.5 Mask
RST 6~5 Mask
7J==- 10ms.c
= ~
ALE
Signals Function
AS-AI5 101M =x---C
Conclusion
Page
System Operating
Page
Lhld
Mvim
LOA
STA
Address Assignment
System Operation
To , , I X X X
Memory·Mapped
·-·-1
Dynamic RAM Interface
Interfacing to MCS·80 Peripherals
Interfacing to Standard BUS Memories
·3 MCS·80 Peripherals with 110 Mapped
Parts Functions
Minimum MCS-85 System
T1t
Scale =11
System Operation
·8 Expanded System
CPU
System Operation Expanded MCS·85 System
Parts Function
ROM/EPROM
Page
Functional Description
Page
Chapter 8080 Central Processor Unit
Registers
Data Bus Buffer
Arithmetic and Logic Unit ALU
Instruction Register and Control
Machine Cycle Identification
State Transition Sequence
Status Bit Definitions
$ no
Irr\
RL- rL- rL.-h rL-h -h rL-rL- r-L
State Associated Activities
LnLn
IrL
Hold Sequences
~ ~ ~~ w---t. ~~u----t
Wl ~ ~
Page
Page
Page
Page
Condition
Iiii
Instruction Set
Page
011 E 100 H
H,L
H,SP
000 B
\JNN
Label
Instruction and Data Formats
Data Word
Condition Flags
Addressing Modes
Instruction SET Encyclopedia
O o 1 1 o
Instruction SET
P,CY,AC
Xchg
ADD M
R CY
~-1 ~-·
8085, 5
P,AC
«H L
00 0 S S S
DAA
\ r
Address,jng
Cleared
RLC
ORA M
1 1 1 1
CMA
CMC
Condition
«SP
Cycles 2/5 8085,315 States 9/18 8085, 11/17
Pop
Pchl
Flag Word
1 0
16 8085, 18
RIM
NOP
SIM
8085A 8080Al8085A Instruction SET Index
Sossa
808SA
808SA Instruction SET Summary Contd
Device Specifications
Page
Inter
Inter
Absolute Maximum RATINGS·
LC~
Wait
Inter 8080Al8080A·1/8080A·2 Waveforms
Data and Instruction Formats
Instruction Set Summary
Inter8080Al8080A·118080A·2
Inter8080A/8080A·1/8080A·2
8085AH Pin
AH CPU Functional Block Diagram Configuration
8085AH/8085AH-2/8085AH-1
Vee
Pin Description
Interrupt Priority, Restart Address, and Sensitivity
Interrupt and Serial 1/0
Driving the X1 and X2 Inputs
LC Tuned Circuit Clock Driver
Quartz Crystal Clock Driver
MHz Input Frequency External Clock
Driver Circuit
RiD~
001
AH Basic System Timing
AH Machine State Chart
SOS5AH/SOS5AH-2/S0S5AH-1 Absolute Maximum RATINGS·
8085AH/8085AH-2/8085AH-1 Characteristics
8085AH 8085AH-2 8085AH-1
Bus Timing Specification as a Teye Dependent Symbol
TlDW
8085AH/8085AH-2/8085AH-1 Waveforms
IntJ 8085AH/8085AH-2/8085AH-1
I8085AH/8085AH-2/8085AH-1
SA Pin
CPU Functional Block Diagram
= ov ±5%, Vss = OV unless otherwise specified
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Xi Rising to ClK Falling 150
TCYC ClK Cycle Period 320 2000
ClK low Time Standard ClK loading
120 Tnt ClK Rise and Fall Time TXKR Rising to ClK Rising
Address TRD Read or Inta to Valid Data
Symbol Parameter 8085A2 8085A·22 Units Min Max
Ready Setup Time to leading Edge
Trailing Edge of Read to Re·Enabling
Page
Appendix
Page
Appendix AP.PLICATIONS of MCS-85
Baud Rates
MCS-85 Applications
111J
RLm
LlL
R14
PAt8~~P
Additional 808SA Interrupts
As an example letslook at IntelsROM/EPROM family Fig
16K 32K
64K
Memory Addressing
Ihl
YT~~
Static Memories
EJ EJ EJ
Refresh
DMA Direct Memory Access
Data
LXI Sp
During initialization
D5H
A4H
=11
System Timings
OT~
·2Clock Related Timing Vs MHz Considerations
2T-80
Minimum System
Memory Device Compatibility
BOSSA, A-2Memory Compatibility
AddreS? access TAD MEM Chip select access
Address access TAD MEM Chip select access
Output enable TRD MEM
Bus Compatibility Analysis see Figure
Gates Ns ea Flip Flop Return path 2 8216s CAS path from ALE
41 ns
TDHR 160 ns
Bus Compatibility Analysis see Contd
Gates Flip Flops 15 ns 8216s 30 ns Flip flop
200
Schotiky or 1 Htil
Input Current TIL single load 40p,A 6mA Schottky or Htil
10p,A
TIL + 36 MOS
Application Example
333
1 D1
Software
Temperature Sensor Flow Diagram
~.,.-~
Thermistor Resistance Mapping
Clear HL
Has the entire
JNZ search
Return
CRT Interface
RS·232C Interface Schematic
Fi1
Output Routine
HALFPrT
PP-l
POP !?
HO =
+ 6 =
HOi
01H
Bf?E
Cassette Recorder Interface
One Chip Magnetic Tape Interface Schematic
FeNO
But
BLl2
T01 ~1V! A..OCeH
Bf1
JC TIl
Additional Comments
A1·43
Temperature Sensor Code
Temperature Sensor Code Contd
Temperature Sensor Code Contd
Temperature Sensor Code Contd
CRT and Cassette Code
Ep! l
?Ece
E81B
BRm
08,.1
E87B C2760S 104
\/1
ES77 C2760S 102
ES7A Le?
3E01
SEce
06e9
TIl . Repeat Until Full BrTE ASSEt-18LEr
0911 C2OC99 9914 C9
RERn Eight Opta ens
TI2
089E
BlnIN a ,38 Eurcd a
Tu30B
€18F2
RRcr
ErTIN
BITSr
Btl
Page
Workshops
Page
Experience
Intel Workshops
SAN Francisco BAY Area
Boston Area
Chicago Area
Dallas Area
Lab sessions on SDK-8S System Design Kit
Introduction to Microprocessors
MCS-80/85 Microprocessors
Domestic Sales Offices
IntJ
~9Jf69rt,~~9
\.,1
Inter
Service Offices