Hardware Specification
3.6.2.3Symmetric I/O Mode
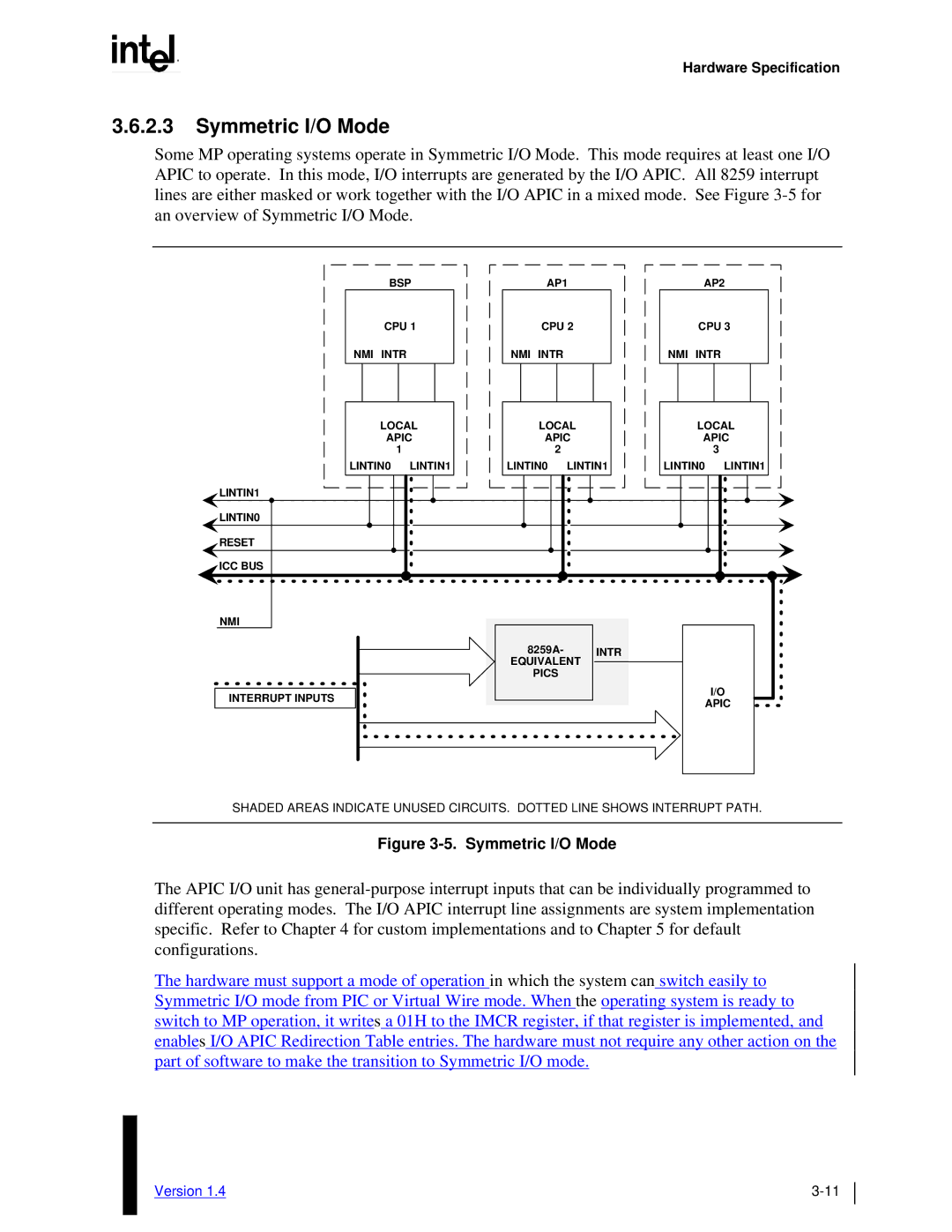
Some MP operating systems operate in Symmetric I/O Mode. This mode requires at least one I/O APIC to operate. In this mode, I/O interrupts are generated by the I/O APIC. All 8259 interrupt lines are either masked or work together with the I/O APIC in a mixed mode. See Figure
BSP |
| AP1 |
| AP2 |
CPU 1 |
| CPU 2 |
| CPU 3 |
| NMI | INTR |
| NMI INTR |
| NMI | INTR | |
|
| LOCAL | LOCAL |
| LOCAL | |||
REG. |
| APIC | APIC |
| APIC | |||
| 1 |
| 2 |
|
|
| 3 | |
MARK | LINTIN0 | LINTIN1 | LINTIN0 | LINTIN1 | LINTIN0 | LINTIN1 | ||
| ||||||||
LINTIN1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
LINTIN0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
RESET |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ICC BUS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NMI |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| 8259A- | INTR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| EQUIVALENT |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
| PICS |
|
|
|
|
INTERRUPT INPUTS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| I/O |
|
|
|
|
|
| APIC | ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
SHADED AREAS INDICATE UNUSED CIRCUITS. DOTTED LINE SHOWS INTERRUPT PATH.
Figure 3-5. Symmetric I/O Mode
The APIC I/O unit has
The hardware must support a mode of operation in which the system can switch easily to Symmetric I/O mode from PIC or Virtual Wire mode. When the operating system is ready to switch to MP operation, it writes a 01H to the IMCR register, if that register is implemented, and enables I/O APIC Redirection Table entries. The hardware must not require any other action on the part of software to make the transition to Symmetric I/O mode.
Version 1.4 |