MultiProcessor Specification
4.3.3 I/O APIC Entries
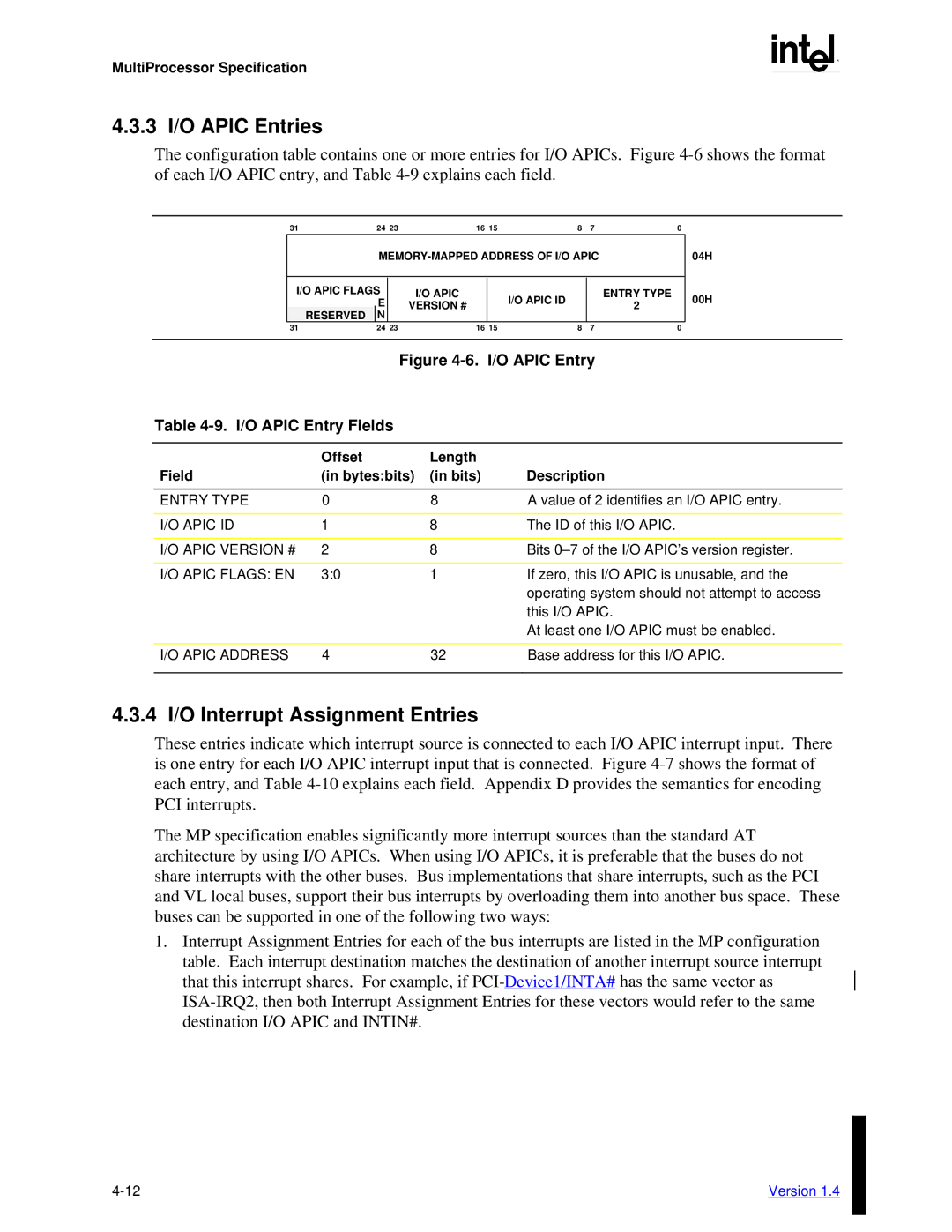
The configuration table contains one or more entries for I/O APICs. Figure
31 | 24 23 | 16 | 15 | 8 | 7 | 0 | |
|
| ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
I/O APIC FLAGS |
| I/O APIC |
| I/O APIC ID |
| ENTRY TYPE | |
| E |
| VERSION # |
|
| 2 | |
RESERVED | N |
|
|
|
|
|
|
31 | 24 23 | 16 | 15 | 8 | 7 | 0 | |
04H
00H
| Figure | I/O APIC Entry | |
Table |
|
| |
|
|
|
|
| Offset | Length |
|
Field | (in bytes:bits) | (in bits) | Description |
|
|
|
|
ENTRY TYPE | 0 | 8 | A value of 2 identifies an I/O APIC entry. |
|
|
|
|
I/O APIC ID | 1 | 8 | The ID of this I/O APIC. |
|
|
|
|
I/O APIC VERSION # | 2 | 8 | Bits |
|
|
|
|
I/O APIC FLAGS: EN | 3:0 | 1 | If zero, this I/O APIC is unusable, and the |
|
|
| operating system should not attempt to access |
|
|
| this I/O APIC. |
|
|
| At least one I/O APIC must be enabled. |
|
|
|
|
I/O APIC ADDRESS | 4 | 32 | Base address for this I/O APIC. |
|
|
|
|
4.3.4 I/O Interrupt Assignment Entries
These entries indicate which interrupt source is connected to each I/O APIC interrupt input. There is one entry for each I/O APIC interrupt input that is connected. Figure
The MP specification enables significantly more interrupt sources than the standard AT architecture by using I/O APICs. When using I/O APICs, it is preferable that the buses do not share interrupts with the other buses. Bus implementations that share interrupts, such as the PCI and VL local buses, support their bus interrupts by overloading them into another bus space. These buses can be supported in one of the following two ways:
1.Interrupt Assignment Entries for each of the bus interrupts are listed in the MP configuration table. Each interrupt destination matches the destination of another interrupt source interrupt that this interrupt shares. For example, if
Version 1.4 |