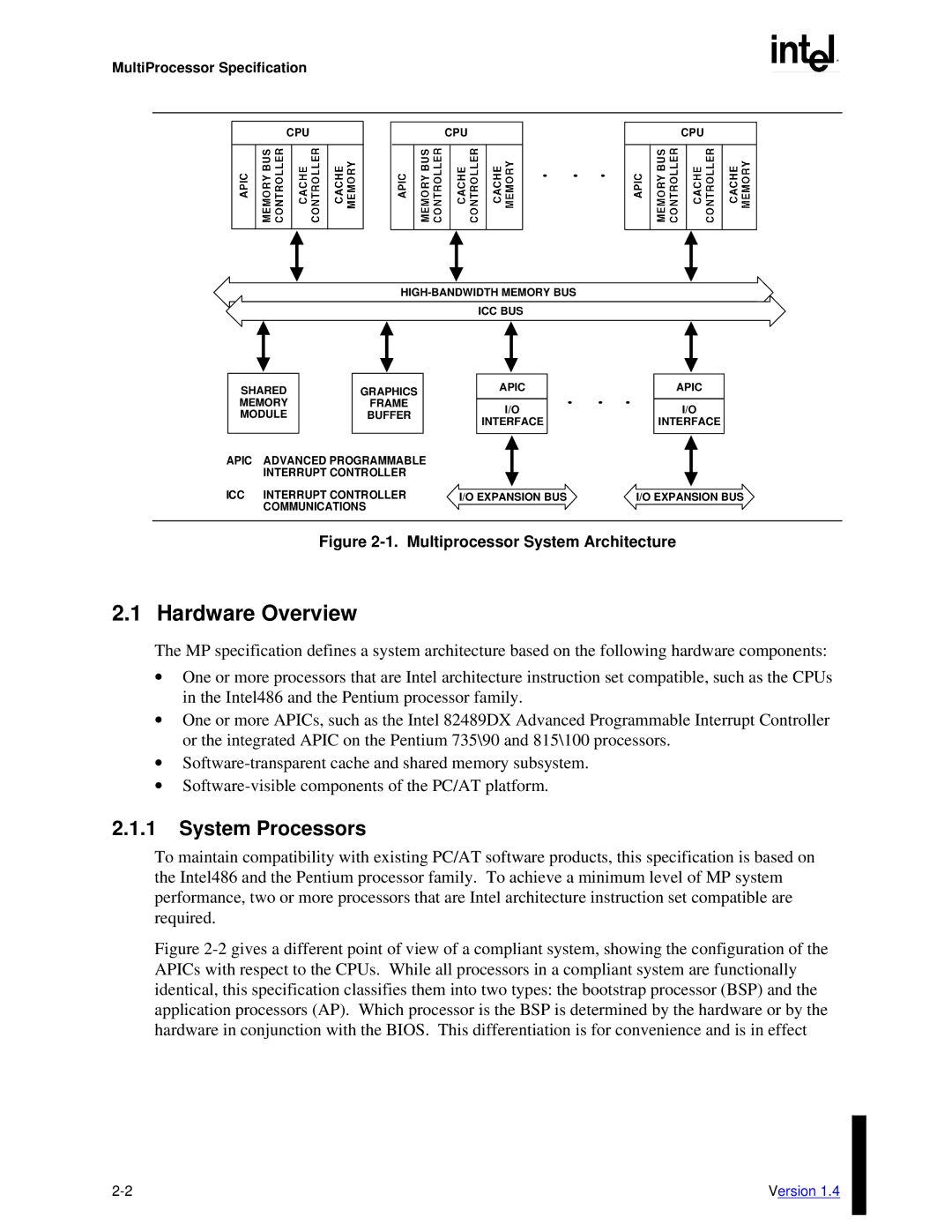
MultiProcessor Specification
CPU
CPU
CPU
ICC BUS
SHARED |
| GRAPHICS |
MEMORY |
| FRAME |
MODULE |
| BUFFER |
|
|
|
APIC ADVANCED PROGRAMMABLE INTERRUPT CONTROLLER
APIC
I/O
INTERFACE
APIC
I/O
INTERFACE
ICC INTERRUPT CONTROLLER | I/O EXPANSION BUS | I/O EXPANSION BUS |
COMMUNICATIONS |
|
|
|
|
|
Figure 2-1. Multiprocessor System Architecture
2.1 Hardware Overview
The MP specification defines a system architecture based on the following hardware components:
∙One or more processors that are Intel architecture instruction set compatible, such as the CPUs in the Intel486 and the Pentium processor family.
∙One or more APICs, such as the Intel 82489DX Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller or the integrated APIC on the Pentium 735\90 and 815\100 processors.
∙
∙
2.1.1System Processors
To maintain compatibility with existing PC/AT software products, this specification is based on the Intel486 and the Pentium processor family. To achieve a minimum level of MP system performance, two or more processors that are Intel architecture instruction set compatible are required.
Figure 2-2 gives a different point of view of a compliant system, showing the configuration of the APICs with respect to the CPUs. While all processors in a compliant system are functionally identical, this specification classifies them into two types: the bootstrap processor (BSP) and the application processors (AP). Which processor is the BSP is determined by the hardware or by the hardware in conjunction with the BIOS. This differentiation is for convenience and is in effect
Version 1.4 |