MP Configuration Table
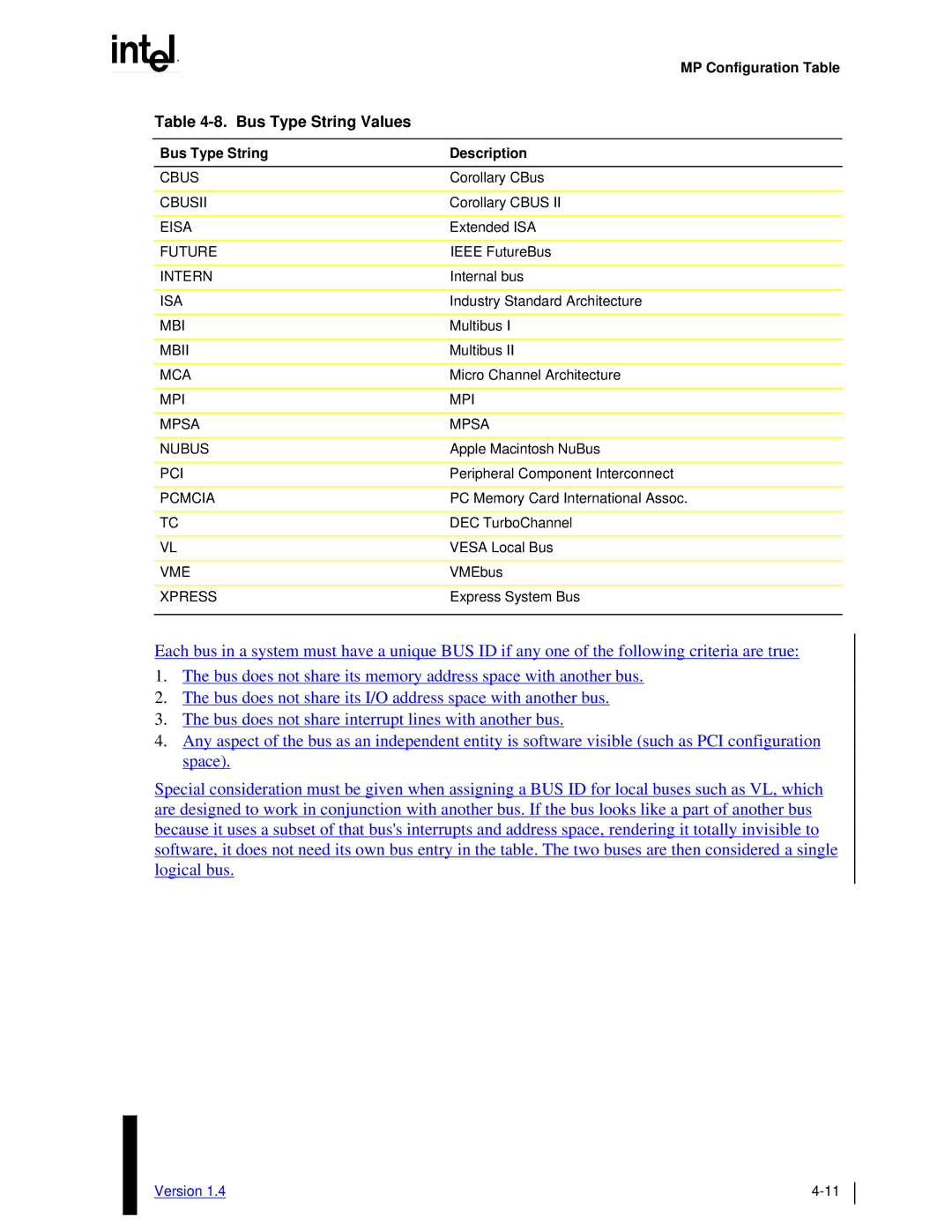
Table 4-8. Bus Type String Values
Bus Type String | Description |
CBUS | Corollary CBus |
|
|
CBUSII | Corollary CBUS II |
|
|
EISA | Extended ISA |
|
|
FUTURE | IEEE FutureBus |
|
|
INTERN | Internal bus |
|
|
ISA | Industry Standard Architecture |
|
|
MBI | Multibus I |
|
|
MBII | Multibus II |
|
|
MCA | Micro Channel Architecture |
|
|
MPI | MPI |
|
|
MPSA | MPSA |
|
|
NUBUS | Apple Macintosh NuBus |
|
|
PCI | Peripheral Component Interconnect |
|
|
PCMCIA | PC Memory Card International Assoc. |
|
|
TC | DEC TurboChannel |
|
|
VL | VESA Local Bus |
|
|
VME | VMEbus |
|
|
XPRESS | Express System Bus |
|
|
Each bus in a system must have a unique BUS ID if any one of the following criteria are true:
1.The bus does not share its memory address space with another bus.
2.The bus does not share its I/O address space with another bus.
3.The bus does not share interrupt lines with another bus.
4.Any aspect of the bus as an independent entity is software visible (such as PCI configuration space).
Special consideration must be given when assigning a BUS ID for local buses such as VL, which are designed to work in conjunction with another bus. If the bus looks like a part of another bus because it uses a subset of that bus's interrupts and address space, rendering it totally invisible to software, it does not need its own bus entry in the table. The two buses are then considered a single logical bus.
Version 1.4 |