www.ti.com
Peripheral Architecture
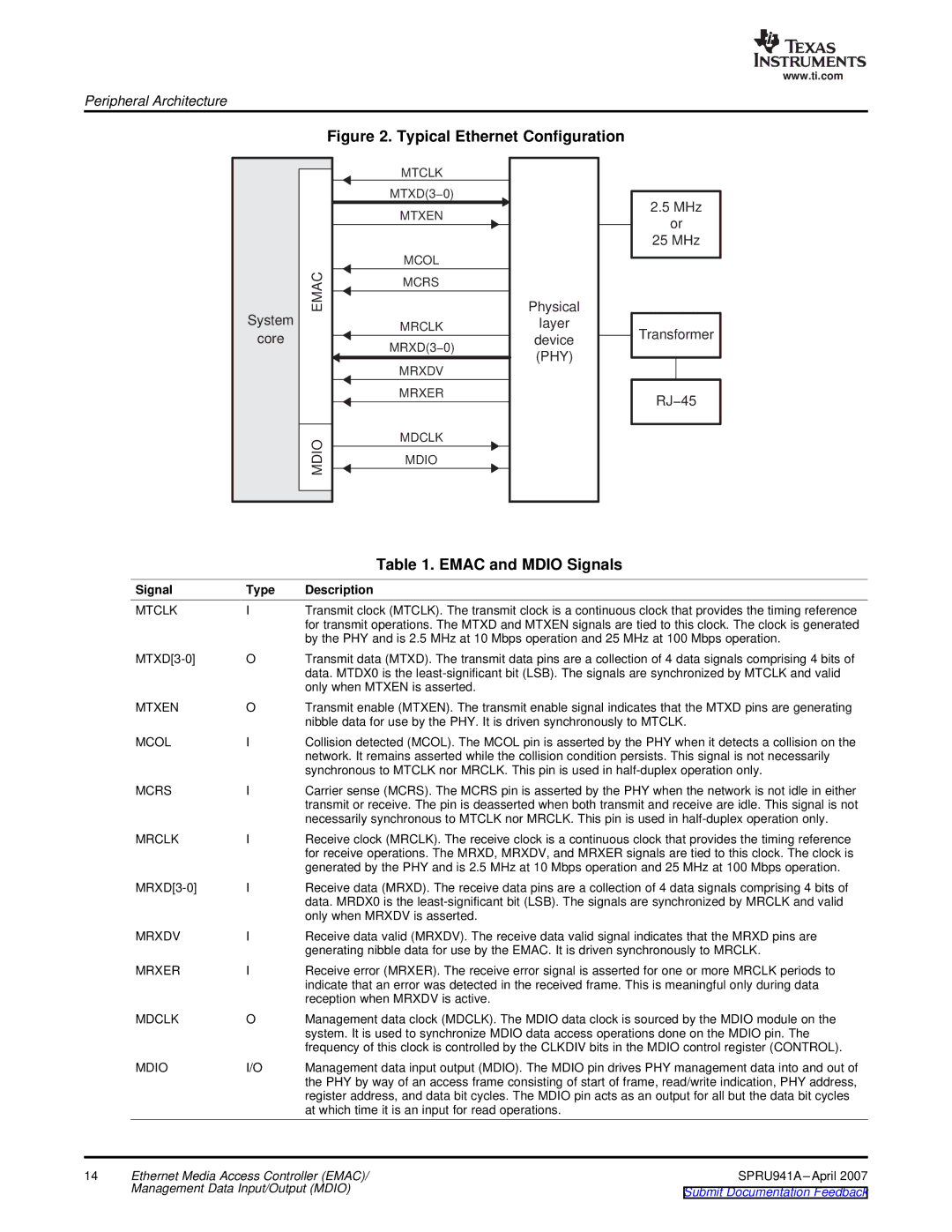
Figure 2. Typical Ethernet Configuration
System
core
EMAC
MDIO
MTCLK
MTXD(3−0)
MTXEN
MCOL
MCRS
MRCLK
MRXD(3−0)
MRXDV
MRXER
MDCLK
MDIO
Physical layer device (PHY)
2.5 MHz
or
25 MHz
Transformer
RJ−45
|
| Table 1. EMAC and MDIO Signals |
Signal | Type | Description |
MTCLK | I | Transmit clock (MTCLK). The transmit clock is a continuous clock that provides the timing reference |
|
| for transmit operations. The MTXD and MTXEN signals are tied to this clock. The clock is generated |
|
| by the PHY and is 2.5 MHz at 10 Mbps operation and 25 MHz at 100 Mbps operation. |
O | Transmit data (MTXD). The transmit data pins are a collection of 4 data signals comprising 4 bits of | |
|
| data. MTDX0 is the |
|
| only when MTXEN is asserted. |
MTXEN | O | Transmit enable (MTXEN). The transmit enable signal indicates that the MTXD pins are generating |
|
| nibble data for use by the PHY. It is driven synchronously to MTCLK. |
MCOL | I | Collision detected (MCOL). The MCOL pin is asserted by the PHY when it detects a collision on the |
|
| network. It remains asserted while the collision condition persists. This signal is not necessarily |
|
| synchronous to MTCLK nor MRCLK. This pin is used in |
MCRS | I | Carrier sense (MCRS). The MCRS pin is asserted by the PHY when the network is not idle in either |
|
| transmit or receive. The pin is deasserted when both transmit and receive are idle. This signal is not |
|
| necessarily synchronous to MTCLK nor MRCLK. This pin is used in |
MRCLK | I | Receive clock (MRCLK). The receive clock is a continuous clock that provides the timing reference |
|
| for receive operations. The MRXD, MRXDV, and MRXER signals are tied to this clock. The clock is |
|
| generated by the PHY and is 2.5 MHz at 10 Mbps operation and 25 MHz at 100 Mbps operation. |
I | Receive data (MRXD). The receive data pins are a collection of 4 data signals comprising 4 bits of | |
|
| data. MRDX0 is the |
|
| only when MRXDV is asserted. |
MRXDV | I | Receive data valid (MRXDV). The receive data valid signal indicates that the MRXD pins are |
|
| generating nibble data for use by the EMAC. It is driven synchronously to MRCLK. |
MRXER | I | Receive error (MRXER). The receive error signal is asserted for one or more MRCLK periods to |
|
| indicate that an error was detected in the received frame. This is meaningful only during data |
|
| reception when MRXDV is active. |
MDCLK | O | Management data clock (MDCLK). The MDIO data clock is sourced by the MDIO module on the |
|
| system. It is used to synchronize MDIO data access operations done on the MDIO pin. The |
|
| frequency of this clock is controlled by the CLKDIV bits in the MDIO control register (CONTROL). |
MDIO | I/O | Management data input output (MDIO). The MDIO pin drives PHY management data into and out of |
|
| the PHY by way of an access frame consisting of start of frame, read/write indication, PHY address, |
|
| register address, and data bit cycles. The MDIO pin acts as an output for all but the data bit cycles |
|
| at which time it is an input for read operations. |
14 Ethernet Media Access Controller (EMAC)/SPRU941A
Management Data Input/Output (MDIO) | Submit Documentation Feedback |
|