www.ti.com
Peripheral Architecture
2.5.5.21No Match (NOMATCH) Flag
This flag is set by the EMAC in the SOP buffer descriptor, if the received packet did not pass any of the EMAC’s address match criteria and was not discarded because the RXCAFEN bit was set in the RXMBPENABLE. Although the packet is a valid Ethernet data packet, it was only received because the EMAC is in promiscuous mode.
2.6EMAC Control Module
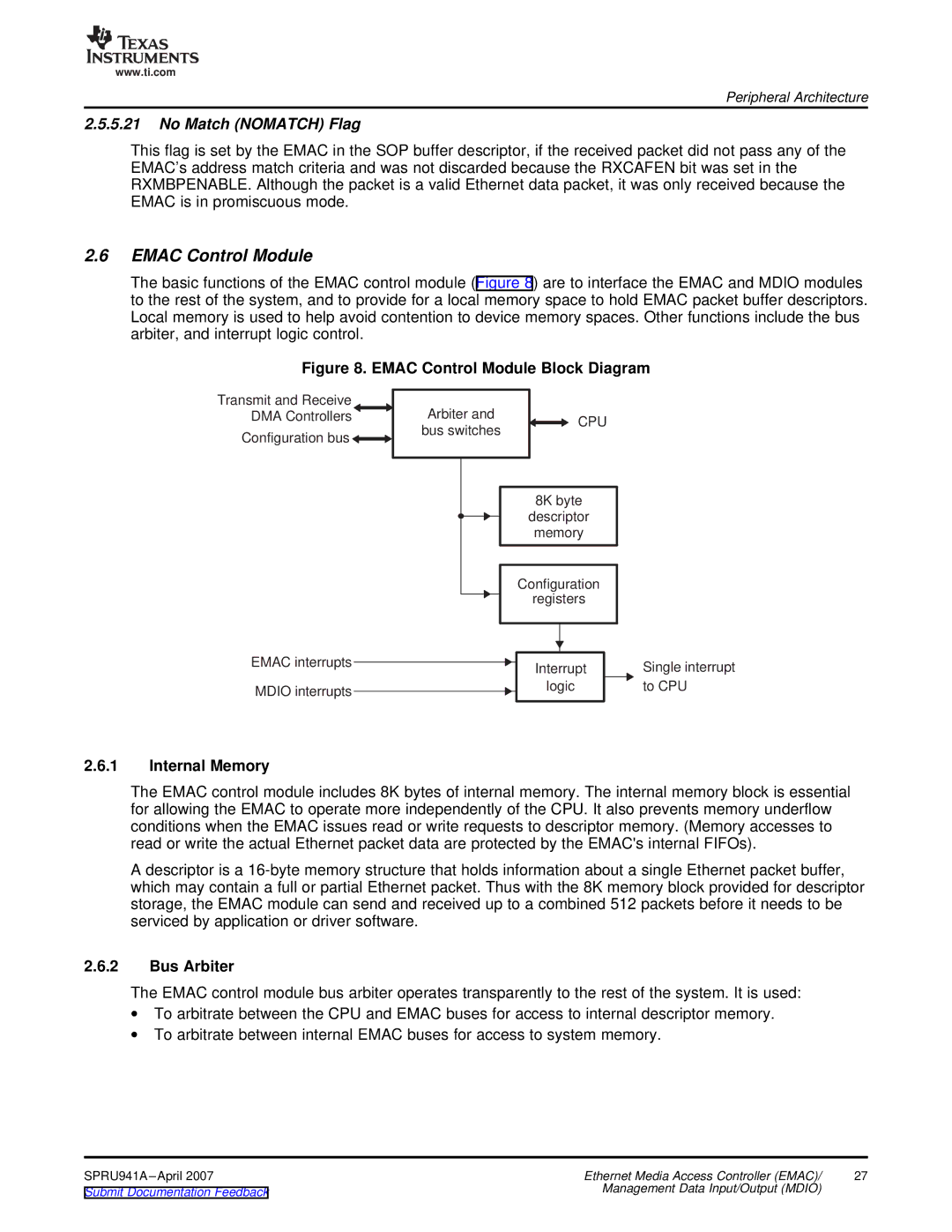
The basic functions of the EMAC control module (Figure 8) are to interface the EMAC and MDIO modules to the rest of the system, and to provide for a local memory space to hold EMAC packet buffer descriptors. Local memory is used to help avoid contention to device memory spaces. Other functions include the bus arbiter, and interrupt logic control.
Figure 8. EMAC Control Module Block Diagram
Transmit and Receive DMA Controllers
Configuration bus ![]()
![]()
EMAC interrupts
MDIO interrupts
Arbiter and |
|
| CPU |
bus switches |
|
| |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
8K byte
descriptor memory
Configuration
registers
|
|
|
|
| Single interrupt |
| Interrupt |
|
| ||
| logic |
|
| to CPU | |
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.6.1Internal Memory
The EMAC control module includes 8K bytes of internal memory. The internal memory block is essential for allowing the EMAC to operate more independently of the CPU. It also prevents memory underflow conditions when the EMAC issues read or write requests to descriptor memory. (Memory accesses to read or write the actual Ethernet packet data are protected by the EMAC'sinternal FIFOs).
A descriptor is a
2.6.2Bus Arbiter
The EMAC control module bus arbiter operates transparently to the rest of the system. It is used:
∙To arbitrate between the CPU and EMAC buses for access to internal descriptor memory.
∙To arbitrate between internal EMAC buses for access to system memory.
SPRU941A
Submit Documentation Feedback | Management Data Input/Output (MDIO) |
|