2 - General Information
If the ac line is selected via the GPIB as the trigger source, triggers will be generated once for each cycle of ac input power. An ac line frequency of 60 Hz produces a trigger period of 16.67 ms; 50 Hz line frequency produces a trigger period of 20 ms.
The
The electronic load has a status reporting capability to keep track of trigger operations. Refer to 'Status Reporting' in the Programming Guide.
Slew Rate and Minimum Transition Time
Slew rate is defined as the change in current, resistance, or voltage over time. A programmable slew rate allows a controlled transition from one load setting to another to minimize induced voltage drops on inductive power wiring, or to control induced transients on a test device (such as would occur during power supply transient response testing).
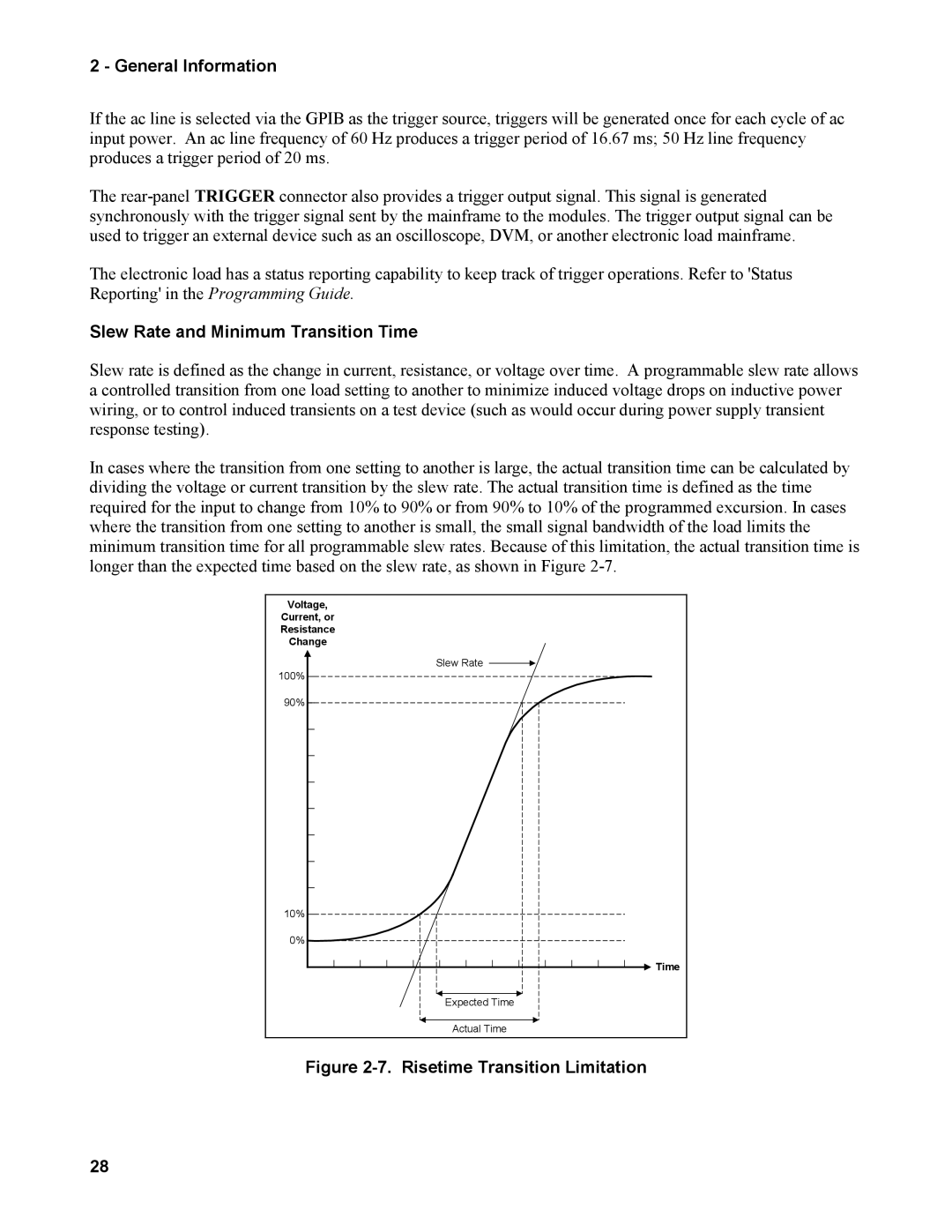
In cases where the transition from one setting to another is large, the actual transition time can be calculated by dividing the voltage or current transition by the slew rate. The actual transition time is defined as the time required for the input to change from 10% to 90% or from 90% to 10% of the programmed excursion. In cases where the transition from one setting to another is small, the small signal bandwidth of the load limits the minimum transition time for all programmable slew rates. Because of this limitation, the actual transition time is longer than the expected time based on the slew rate, as shown in Figure
Voltage, |
Current, or |
Resistance |
Change |
Slew Rate |
100% |
90% |
10% |
0% |
Time |
Expected Time |
Actual Time |
Figure 2-7. Risetime Transition Limitation
28