Installation - 3
In Figure
If because of lead length or other considerations, lead connections cannot be made at the source, a remote distribution terminal may be required. Lead connections can also be
Low Voltage Operation
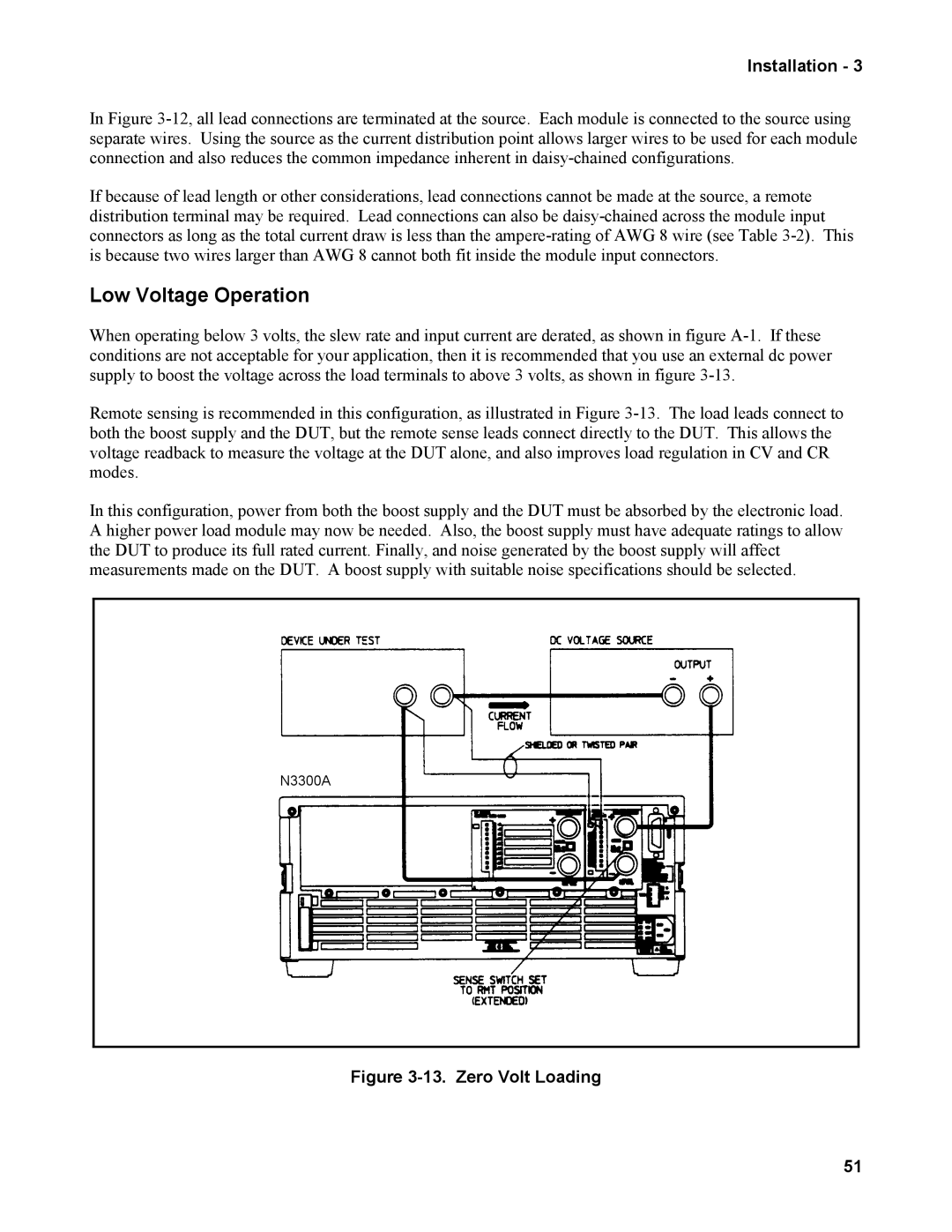
When operating below 3 volts, the slew rate and input current are derated, as shown in figure
Remote sensing is recommended in this configuration, as illustrated in Figure
In this configuration, power from both the boost supply and the DUT must be absorbed by the electronic load. A higher power load module may now be needed. Also, the boost supply must have adequate ratings to allow the DUT to produce its full rated current. Finally, and noise generated by the boost supply will affect measurements made on the DUT. A boost supply with suitable noise specifications should be selected.
N3300A
Figure 3-13. Zero Volt Loading
51