Instruction Manual
Hazardous Area Oxymitter 4000
There are a few fault conditions where no alarm indication is present and the probe passes cali- bration, but the O2 reading may still be incorrect:
a.Probe passes calibration, but still ap- pears to read high.
1.There may be a leak that is permitting ambient air to mix with the process gases. Since many combustion proc- esses are slightly negative in pressure, ambient air can be sucked into the cell area, biasing the O2 reading upward.
(a)Make sure that the calibration gas line is capped tightly between cali- brations. If autocal is used, make sure the check valve is seating properly.
(b)If an abrasive shield is installed to protect the entire probe from particulate erosion, a leak in the probe flange gasket can allow ambient air to migrate down the annular space between the probe and shield, and then into the cell. Always install a new probe flange gasket when
2.There may be a leak inside the probe itself, permitting the reference air (20.95% O2) to mix with the process gases at the cell. To confirm this leak condition, instrument air will need to be connected for reference. Pressurize the inside (reference side) of the probe by plugging the reference air exhaust port with your finger for 1 minute. The O2 reading should decrease slightly. If the O2 reading increases during this test, there is a leak inside the probe.
(a)Acid condensation inside the probe can degrade the red silicon tube (item 38, Figure
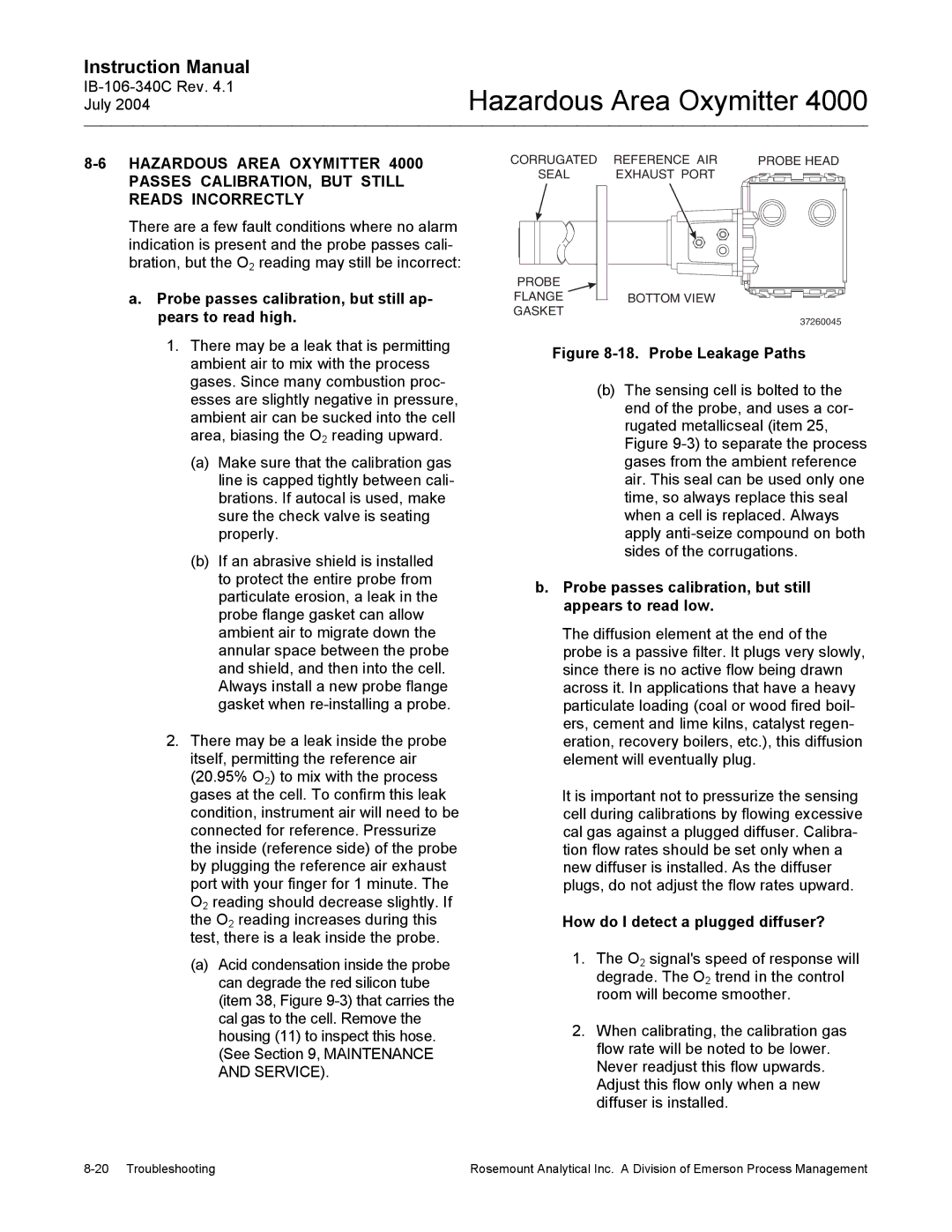
CORRUGATED | REFERENCE AIR | PROBE HEAD |
SEAL | EXHAUST PORT |
|
PROBE |
|
FLANGE | BOTTOM VIEW |
GASKET |
|
37260045
Figure 8-18. Probe Leakage Paths
(b)The sensing cell is bolted to the end of the probe, and uses a cor- rugated metallicseal (item 25, Figure
b.Probe passes calibration, but still appears to read low.
The diffusion element at the end of the probe is a passive filter. It plugs very slowly, since there is no active flow being drawn across it. In applications that have a heavy particulate loading (coal or wood fired boil- ers, cement and lime kilns, catalyst regen- eration, recovery boilers, etc.), this diffusion element will eventually plug.
It is important not to pressurize the sensing cell during calibrations by flowing excessive cal gas against a plugged diffuser. Calibra- tion flow rates should be set only when a new diffuser is installed. As the diffuser plugs, do not adjust the flow rates upward.
How do I detect a plugged diffuser?
1.The O2 signal's speed of response will degrade. The O2 trend in the control room will become smoother.
2.When calibrating, the calibration gas flow rate will be noted to be lower. Never readjust this flow upwards. Adjust this flow only when a new diffuser is installed.
Rosemount Analytical Inc. A Division of Emerson Process Management |