Virtual routers are disabled by default.
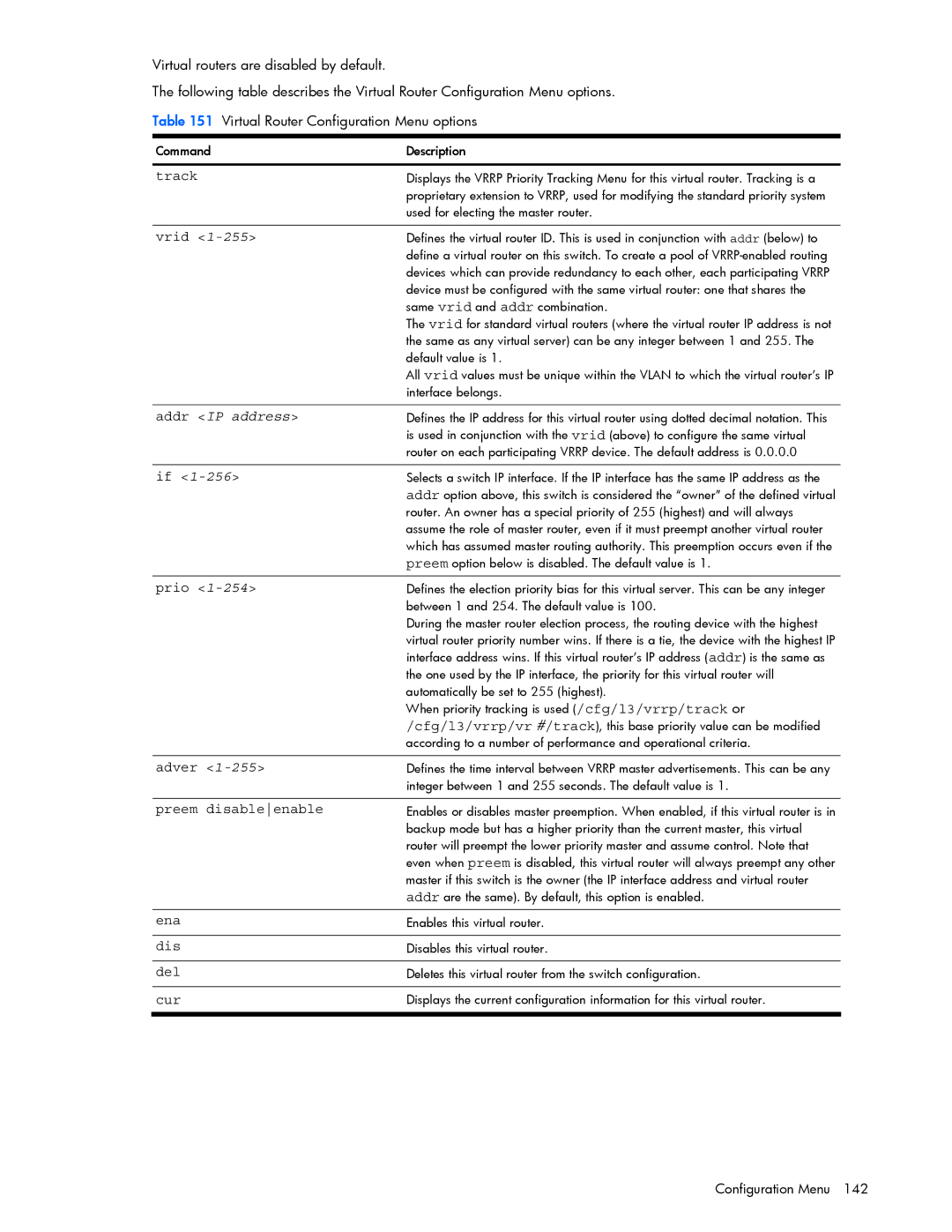
The following table describes the Virtual Router Configuration Menu options.
Table 151 Virtual Router Configuration Menu options
Command | Description |
|
|
track | Displays the VRRP Priority Tracking Menu for this virtual router. Tracking is a |
| proprietary extension to VRRP, used for modifying the standard priority system |
| used for electing the master router. |
|
|
vrid | Defines the virtual router ID. This is used in conjunction with addr (below) to |
| define a virtual router on this switch. To create a pool of |
| devices which can provide redundancy to each other, each participating VRRP |
| device must be configured with the same virtual router: one that shares the |
| same vrid and addr combination. |
| The vrid for standard virtual routers (where the virtual router IP address is not |
| the same as any virtual server) can be any integer between 1 and 255. The |
| default value is 1. |
| All vrid values must be unique within the VLAN to which the virtual router’s IP |
| interface belongs. |
|
|
addr <IP address> | Defines the IP address for this virtual router using dotted decimal notation. This |
| is used in conjunction with the vrid (above) to configure the same virtual |
| router on each participating VRRP device. The default address is 0.0.0.0 |
|
|
if | Selects a switch IP interface. If the IP interface has the same IP address as the |
| addr option above, this switch is considered the “owner” of the defined virtual |
| router. An owner has a special priority of 255 (highest) and will always |
| assume the role of master router, even if it must preempt another virtual router |
| which has assumed master routing authority. This preemption occurs even if the |
| preem option below is disabled. The default value is 1. |
|
|
prio | Defines the election priority bias for this virtual server. This can be any integer |
| between 1 and 254. The default value is 100. |
| During the master router election process, the routing device with the highest |
| virtual router priority number wins. If there is a tie, the device with the highest IP |
| interface address wins. If this virtual router’s IP address (addr) is the same as |
| the one used by the IP interface, the priority for this virtual router will |
| automatically be set to 255 (highest). |
| When priority tracking is used (/cfg/l3/vrrp/track or |
| /cfg/l3/vrrp/vr #/track), this base priority value can be modified |
| according to a number of performance and operational criteria. |
|
|
adver | Defines the time interval between VRRP master advertisements. This can be any |
| integer between 1 and 255 seconds. The default value is 1. |
|
|
preem disableenable | Enables or disables master preemption. When enabled, if this virtual router is in |
| backup mode but has a higher priority than the current master, this virtual |
| router will preempt the lower priority master and assume control. Note that |
| even when preem is disabled, this virtual router will always preempt any other |
| master if this switch is the owner (the IP interface address and virtual router |
| addr are the same). By default, this option is enabled. |
|
|
ena | Enables this virtual router. |
|
|
dis | Disables this virtual router. |
|
|
del | Deletes this virtual router from the switch configuration. |
|
|
cur | Displays the current configuration information for this virtual router. |
|
|
Configuration Menu 142