Intel Server Board SE7520JR2
C78844-002
Revision History Intel Server Board SE7520JR2
Revision
Date Revision Modifications Number
Iii
Intel Server Board SE7520JR2 Disclaimers
Table of Contents
Intel Server Board SE7520JR2 Table of Contents
RTC
Table of Contents Intel Server Board SE7520JR2
System Bios
113
Vii
Platform Management
Viii C78844-002
Error Reporting and Handling
149
175
201
216
Design and Environmental Specifications
202
FCC USA
225
Appendix a Integration and Usage Tips 221
222
Xii Revision C78844-002
Intel Server Board SE7520JR2 List of Figures
Xiii
List of Tables Intel Server Board SE7520JR2
Xiv
Intel Server Board SE7520JR2 List of Tables
Xvi
Xvii
This page intentionally left blank
Xviii Revision C78844-002
Chapter Outline
Intel Server Board SE7520JR2 Introduction
Revision C78844-002
Server Board Use Disclaimer
Introduction Intel Server Board SE7520JR2
Server Board SE7520JR2 Feature Set
Server Board SE7520JR2 SKU Availability
Server Board Overview Intel Server Board SE7520JR2
32 33
SE7520JR2 Board Layout Revision C78844-002
Ref # Description
Server Board Dimensions Revision C78844-002
Server Board SE7520JR2 Block Diagram Revision C78844-002
Functional Architecture Intel Server Board SE7520JR2
Processor Voltage Regulators
Reset Configuration Logic
Processor Sub-system
Processor Module Presence Detection
Processor Support Matrix
Common Enabling Kit CEK Design Support
Processor Support
Processor Family FSB Frequency Support
Mixed Processor Steppings
Jumperless Processor Speed Settings
Processor Mis-population Detection
Mixed Processor Models
Multiple Processor Initialization
Processor Thermal Control Sensor
Intel E7520 Chipset
CPU Thermal Sensors
Processor Thermal Trip Shutdown
MCH Memory Sub-System Overview
Memory Controller Hub MCH
Front Side Bus FSB
PCI Express
Full-height Riser Slot
PCI-X Hub PXH
Hub Interface
Low Profile Riser Slot
SMBus Interface
3 I/O Controller Hub ICH5-R
2.3 I/OxAPIC Controller
PCI Interface
Sata Controller
Low Pin Count LPC Interface
Universal Serial Bus USB Controller
Enhanced Power Management
Advanced Programmable Interrupt Controller Apic
3.8 RTC
Memory Sub-System
Memory Sizing
Memory Population
1GB 2GB
1GB 2GB 4GB
Supported DDR-266 Dimm Populations
DDR-266 & DDR-333 Dimm population rules are as follows
DDR2 400 Dimm population rules are as follows
Supported DDR-333 Dimm Populations
ECC Memory Initialization
Memory Test
Memory Feature On-board Professional Advanced
Memory Monitoring
Memory Monitoring Support by Server Management Level
Memory Rasum Features
Dram ECC Intel x4 Single Device Data Correction x4 Sddc
Integrated Memory Scrub Engine
Retry on Uncorrectable Error
Integrated Memory Initialization Engine
Dimm Sparing Function
Four Dimm Memory Mirror Configuration
Memory Mirroring
Dimm
I/O Sub-System
PCI Subsystem
Logging Memory RAS Information to the SEL
1.3 P64-Express Dual x4 PCI Bus Segment
1.1 P32-A 32-bit, 33-MHz PCI Subsystem
1.2 P64-A and P64-B 64-bit, 100MHz PCI Subsystem
PCI Riser Slots
PCI Scan Order
PCI Bus Numbering
Device Number and Idsel Mapping
PCI Device
Bus# / Device# / Function#
PCAD28
Split Option ROM
Interrupt Routing
Apic Interrupt Routing
PCI Interrupt Routing/Sharing
Interrupt
Legacy Interrupt Sources
Serialized IRQ Support
Interrupt Definitions
Interface
IRQ Scan for Pciirq
ICH5-R PXH Ioapic PCI-E Interface
Intr
IRQ
PCI Interrupt Mapping Diagram
4.1.1 53C1030 Summary of Features
Scsi Support
4.1 LSI* 53C1030 Dual Channel Ultra320 Scsi Controller
Revision C78844-002
IDE Support
Zero Channel RAID
Sata Support
Ultra ATA/100
IDE Initialization
Intel RAID Technology Option ROM
Video Support
Sata RAID
Video Modes
Video Memory Interface
Signal Name Type Description
Video Memory Interface
Column Address Select
Enabled
Network Interface Controller NIC
Dual video
Super I/O Chip
NIC Connector and Status LEDs
USB 2.0 Support
GPIOs
GPIOE12/XA9
Zzbiosrolling GPIOE45/LED2
GPIOE11/XA10
XBUSA9 GPIOE13/XA8
Serial Port B
Serial Ports
Serial Port a
Serial Port Multiplexer Logic
Rear RJ45 Serial B Port Configuration
BMC
Floppy Disk Support
Bios Flash
Removable Media Drives
Keyboard and Mouse Support
Configuration and Initialization
Memory Space
1MB
DOS Compatibility Region
DOS Compatibility Region Revision C78844-002
System Bios
Add-in Card Bios and Buffer Area
Extended System Bios
DOS Area
Extended Memory
Extended Memory Map Revision C78844-002
Main Memory
High Bios
1.2.5 I/O Apic Configuration Space
PCI Memory Space
SMM Space Table
System Management Mode Handling
Global Enable High Enable Tseg Enable Compatible High H
Range
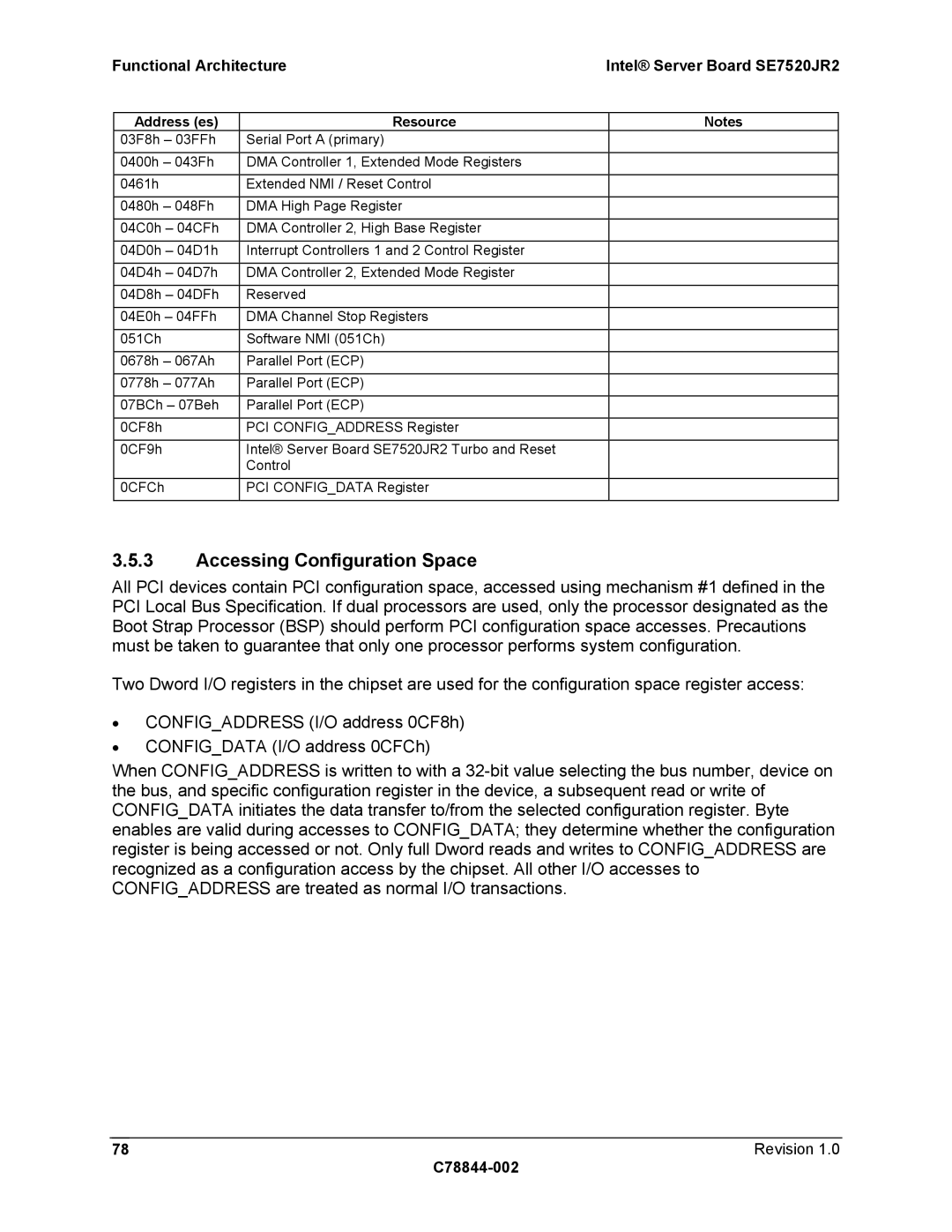
2 I/O Map
O Map
Address es Resource
Revision
Accessing Configuration Space
Configaddress Register
Clock Generation and Distribution
Bios Identification String
System Bios Intel Server Board SE7520JR2
Intel Server Board SE7520JR2 System Bios
Flash Architecture and Flash Update Utility
Bios Power On Self Test Post
User Interface
Splash Screen/Diagnostic Window
System Diagnostic Screen
System Activity Window
Bios Boot Popup Menu
Quiet Boot / OEM Splash Screen
Post Activity Window
Please select boot device
Bios Setup Utility
Bios Setup Keyboard Command Bar Options
Localization
Entering Bios Setup
Bios Setup, Main Menu Options
Main Menu
Bios Setup, Advanced Menu Options
Advanced Menu
English
Disabled
Processor Configuration Sub-menu
Bios Setup, Processor Configuration Sub-menu Options
CPU Cpuid
Both
IDE Configuration Sub-menu
Bios Setup IDE Configuration Menu Options
A1-3rdM/A2-4thM
Mixed P-ATA-S-ATA Configuration with only Primary P-ATA
Host & Device
ATA M-S
SWDMA0-0
Auto
Cdrom Armd
SWDMA0-1
Bios Setup, Floppy Configuration Sub-menu Selections
Floppy Configuration Sub-menu
Super I/O Configuration Sub-menu
Bios Setup, Super I/O Configuration Sub-menu
Bios Setup, USB Configuration Sub-menu Selections
USB Configuration Sub-menu
USB Mass Storage Device Configuration Sub-menu
HiSpeed
PCI Configuration Sub-menu
Bios Setup, PCI Configuration Sub-menu Selections
Memory Configuration Sub-menu
Bios Setup, Memory Configuration Sub-menu Selections
Dimm 3A
Boot Menu
Bios Setup, Boot Menu Selections
Dimm 3B
This is
Boot Settings Configuration Sub-menu Selections
Bios Setup, Boot Settings Configuration Sub-menu Selections
Off
2.3.4 Removable Drive Sub-menu Selections
Boot Device Priority Sub-menu Selections
2.3.3 Hard Disk Drive Sub-menu Selections
2.3.5 Atapi Cdrom drives sub-menu selections
Limited
Bios Setup, Security Menu Options
Security Menu
Minute
Server Menu
Bios Setup, Server Menu Selections
Disable BSP
Stays Off
100 C78844-002
Bios Setup, System Management Sub-menu Selections
System Management Sub-menu Selections
Stay On
Bios Setup, Serial Console Features Sub-menu Selections
Serial Console Features Sub-menu Selections
Event Log Configuration Sub-menu Selections
Bios Setup, Event Log Configuration Sub-menu Selections
Feature Options Help Text
Rolling Bios and On-line Updates
Bios Setup, Exit Menu Selections
Exit Menu
Recovery Mode
Flash Update Utility
Flash Bios
User Binary Area
Configuration Reset
Bios Recovery
104 Revision C78844-002
OEM Binary
Security
Revision 105 C78844-002
Security Features Operating Model
Operating Model
106 Revision C78844-002
Scenario #3
Scenario #1
Scenario #2
107
Extensible Firmware Interface EFI
Operating System Boot, Sleep, and Wake
Password Clear Jumper
EFI Shell
Advanced Configuration and Power Interface Acpi
Sleep and Wake Functionality
Revision 109 C78844-002
On to Off OS present
Power Switch Off to On
On to Off OS absent
On to Sleep Acpi
Sleep to On Acpi
System Sleep States
C78844-002 111
PXE Bios Support
Console Redirection
112 Revision C78844-002
Suppoted Management Features by Tier
Revision 113 C78844-002
Intel Management
Platform Management Intel Server Board SE7520JR2
114 Revision C78844-002
Platform Management Architecture Overview
PC87427
Ipmi Messaging, Commands, and Abstractions
1 5V Standby
116 Revision C78844-002
Ipmi ‘Sensor Model’
Revision 117 C78844-002
Private Management Busses
Management Controllers
118 Revision C78844-002
Revision 119 C78844-002
120 Revision C78844-002
On-Board Platform Management Features and Functionality
Revision 121 C78844-002
External Interface to the mBMC
Power Control Interfaces
Server Management I2C Buses
Server Management I2C Bus ID Assignments
MBMC Hardware Architecture
Revision 123 C78844-002
Power Supply Interface Signals
124 Revision C78844-002
Power Supply Control Signals
Revision 125 C78844-002
Power-down Sequence
Power Control Sources
Power-up Sequence
System Reset Control
Power button assertion
Reset Control Sources
Control Panel System Reset
Reset button assertion
Power LED
Combined power and reset button assertion
Control Panel Indicators
SSI Power LED Operation
Degraded Condition
Fault / Status LED
Non-Critical Condition
Chassis ID LED
Diagnostic Interrupt Button Control Panel NMI
Power Button
Reset Button
Chassis Intrusion
Baseboard Fan Control
Secure Mode Operation
Watchdog Timer
MBMC Peripheral SMBus
Timestamp Clock
Sensor Data Record SDR Repository
SEL Erasure
Initialization Agent
SMI Generation
Field Replaceable Unit FRU Inventory Devices
NMI Generation
Event Message Reception
MBMC Self Test
Messaging Interfaces
Revision 135 C78844-002
LAN Interface
LAN Channel Capacity
LAN Channel Capability Options
Event Filtering and Alerting
Platform Event Filtering PEF
136 Revision C78844-002
Alert over LAN
Action Priority Delayed Type
MBMC Sensor Support
PEF Action Priorities
Platform Sensors for On-Board Platform Instrumentation
138 Revision C78844-002
Event Readable
Sensor Name Reading Event Data Record Type Triggers
Revision 139 C78844-002
Sensor # Event Event Offset Assert Readable
Value/Offsets Action Type
140 Revision C78844-002
Ierr
ID LED
Revision 141 C78844-002
Number Type Triggers Deassert Offsets
IMM BMC Sensor Support
142
Sensor Event Event Offset Assert Readable
Intel Server Board SE7520JR2 Platform Management
143 C78844-002
144
Lvds Scsi
OEM
FRB1, FRB2
FRB3
VRM
Dimm
Wired For Management WFM
System Management Bios Smbios
Vital Product Data VPD
1 FRB1 BSP Self-Test Failures
Fault Resilient Booting FRB
Intel Server Board SE7520JR2 Error Reporting and Handling
2 FRB2 BSP Post Failures
Error Reporting and Handling Intel Server Board SE7520JR2
3 FRB3 BSP Reset Failures
OS Watchdog Timer Operating System Load Failures
150 Revision C78844-002
AP Failures
Treatment of Failed Processors
Revision 151 C78844-002
Memory Error Handling
Memory Error Handling in RAS Mode
152 Revision C78844-002
Memory Error Handling in non-RAS Mode
Memory Error Handling mBMC vs Sahalee
Revision 153 C78844-002
Dimm Enabling
Single-bit ECC Error Throttling Prevention
Memory Error Handling in non-RAS mode
154 Revision C78844-002
Processor Bus Error
Error Logging
PCI Bus Error
SMI Handler
Error Messages and Error Codes
157 C78844-002
Boot Bios Messages
Storage Device Bios Messages
No ROM Basic
158
159 C78844-002
160
Virus Related Bios Messages
System Configuration Bios Messages
Eprom
USB Bios Error Messages
Cmos Bios Messages
Miscellaneous Bios Messages
161 C78844-002
Error Codes and Messages
Post Error Codes
Smbios Bios Error Messages
Error Code Error Message Response
0146 Insufficient Memory to Shadow PCI ROM Pause
C78844-002 163
Error Codes Sent to the Management Module
Error code Error messages
164
Revision 165 C78844-002
Bios Generated Post Error Beep Codes
Bios Generated Beep Codes
Number of Beeps Description
Number of Beeps Troubleshooting Action
Boot Block Error Beep Codes
Boot Block Error Beep Codes
BMC Generated Beep Codes Professional/Advanced only
Checkpoints
System ROM Bios Post Task Test Point Port 80h Code
Diagnostic LEDs
Post Progress Code LED Example
Back edge of baseboard
Diagnostic LEDs
Post Code Checkpoints
Post Code Checkpoints
169 C78844-002
170 Revision C78844-002
Bootblock Initialization Code Checkpoints
Bootblock Initialization Code Checkpoints
Cmos
Bootblock Recovery Code Checkpoint
Bootblock Recovery Code Checkpoint
171 C78844-002
172 Revision C78844-002
DIM Code Checkpoints
DIM Code Checkpoints
Checkpoint Description
Memory Error Codes
Acpi Runtime Checkpoints
Post Progress Fifo Professional / Advanced only
Light Guided Diagnostics
174 Revision C78844-002
Power Connector Pin-out
Power Connectors
Intel Server Board SE7520JR2 Connectors and Jumper Blocks
12V Power Connector J4J1
Low Profile PCI-X Riser Slot
IDE Power Connector Pinout U2E1
Riser Slots
Low Profile Riser Slot Pinout
Pin PCI Spec Description Side Signal
Pin PCI Spec Description Side a Signal
Revision 177 C78844-002
Connectors and Jumper Blocks Intel Server Board SE7520JR2
178 Revision C78844-002
Revision 179 C78844-002
Pin connector length = 139.45mm=5.49
Full Height PCI-X Riser Slot
Prsntn
REFCLK2
Pin-Side PCI Spec Description Signal
180 Revision C78844-002
Perstn
Revision 181 C78844-002
182 Revision C78844-002
Revision 183 C78844-002
PAR64
Pxhrst
System Management Headers
Intel Management Module Connector
IMM Connector Pinout J1C1
184 Revision C78844-002
C78844-002 185
Description Pin
186 C78844-002
Ipmb Header
Pin Signal Name Type Description
Icmb Header
Icmb Header Pin-out J1D1
Pin Signal Name Description
188 Revision C78844-002
OEM RMC Connector Pinout J3B2
Control Panel Connectors
OEM RMC Connector J3B2
Pin Signal Name
Pin# Signal Name Pin #
190 Revision C78844-002
P5V P5VSTBY
Control Panel SSI Standard 34-Pin Header Pin-out
Revision 191 C78844-002
P5VSTBY Fpidledl FPSTATUSLED1R Fpidbtnl GND Fphddfltledr
VGA Connector Pin-out
I/O Connectors
VGA Connector
192
RJ-45 10/100/1000 NIC Connector Pin-out
NIC Connectors
Scsi Connectors
Internal/External 68-pin Vhdci Scsi Connector Pin-out
Pin# Signal Name
ATA-100 Connector
ATA-100 40-pin Connector Pin-out J3K1
Signal Name Pin#
Sata Connector Pin-out J1H1 and J1H5
Sata Connectors
Floppy Controller Connector
Revision 195 C78844-002
Internal 9-pin Serial a Header Pin-out J1A3
Serial Port Connectors
External RJ-45 Serial B Port Pin-out
196 Revision C78844-002
External USB Connector Pin-out
Keyboard and Mouse Connector
USB Connector
Stacked PS/2 Keyboard and Mouse Port Pin-out
Fan Headers
Internal 1x10 USB Connector Pin-out J1F1
Internal 2x5 USB Connector J1G1
198 Revision C78844-002
CPU1/CPU2 Fan Connector Pin-out J5F2, J7F1
Intel Server Chassis Fan Header Pin-out J3K6
Revision 199 C78844-002
Misc. Headers and Connectors
Chassis Intrusion Header
Hard Drive Activity LED Header
Jumper Block Definitions
Settings
Jumper Blocks
Revision 201 C78844-002
Output Connectors
Server Board SE7520JR2 Design Specification
Power Supply Requirements
Board Design Specifications
Power Harness Specification Drawing
Revision 203 C78844-002
P1 Main Power Connector
P1 Main Power Connector
P2 Processor Power Connector
P2 Processor Power Connector
P7 Hard Drive Back Plane Power Connector
P3 Power Signal Connector
P4 Peripheral Connectors
Grounding
Remote Sense
Standby Outputs
206 Revision C78844-002
Voltage Regulation Limits
Voltage Regulation
Dynamic Loading
Transient Load Requirements
Closed Loop Stability
Common Mode Noise
Capacitive Loading
Ripple / Noise
Timing Requirements
Soft Starting
Zero Load Stability Requirements
Output Voltage Timing
2500
210 Revision C78844-002
1500
100 1000
Residual Voltage Immunity in Standby Mode
Revision 211 C78844-002
Product EMC Compliance Class a Compliance
Product Safety Compliance
Product Regulatory Compliance
212 Revision C78844-002
Product Certification Markings
Certifications / Registrations / Declarations
Product Regulatory Compliance Markings
Revision 213 C78844-002
Industry Canada ICES-003
Electromagnetic Compatibility Notices
FCC USA
214 Revision C78844-002
Korean Compliance RRL
Europe CE Declaration of Conformity
Taiwan Declaration of Conformity Bsmi
Revision 215 C78844-002
Updating the System Software
Programming FRU and SDR Data
216 Revision C78844-002
Clearing Cmos
Cmos Clear Using J1H2 Jumper Block
Cmos Clear using Control Panel
Revision 217 C78844-002
Bios Recovery Operation
218 Revision C78844-002
Revision 219 C78844-002
Page
Appendix a Integration and Usage Tips
Revision 221 C78844-002
Glossary Intel Server Board SE7520JR2
222
Term Definition
Intel Server Board SE7520JR2 Glossary
C78844-002 223
224 Revision C78844-002
Intel Server Board SE7520JR2 Reference Documents
Revision 225 C78844-002