AI296TM
Page
About this Document
Labels
Document Conventions
Convention Meaning
Tip
Iii
Electrostatic Discharge Caution
Ground Caution Proper Cooling Caution
FCC Warning
Email Support
Customer Assistance
Web Site Support
Phone Support
Table of Contents
AI296 Local Menu System
Exiting the Menu System
IP Over X.25 Subnet Configuration
AI296 Link Types Asynchronous Asynchronous PPP HDLC-Bridge
TOC-4
Diagnostics for TID Multiplexing
TID Multiplexing
AI296 Commands
Appendix a AI296 System Codes
Appendix B Standalone Mode and Switch Mode
AI296 Commands AI296 Menu Aliases FTP Sessions
Product Description
Features
Standalone Configuration
Performance Monitoring, Maintenance, Troubleshooting
Remote and Local Configuration
Link-to-Link Call Routing
System Diagnostics
TID Multiplexing
AI296 Hardware Components
Links 1-4 Connector
Links 5-8 Connector
Links 13-16 Connector
Links 9-12 Connector
Technical Specifications
Component Description
CAB257 Cable
Individual Port Access
Description Specification
DP196 Distribution Panel
DB-25 Connectors
Pin Signal Direction
RJ45 10BaseT Connectors
Displays the RJ45 10BaseT connector Pin
Typical Applications
Asynchronous to TCP/IP Application
IP Over X.25 Networks
Illustrates a common IP over X.25 application
AI296 Version 9.8x User’s Guide
Mixed Asynchronous and X.25 Networks
Mixed Asynchronous and X.25 Network
AI296 Version 9.8x User’s Guide
To TCP/IP Application
X.25 to TCP/IP Application
Trunking
Illustrates a common X.25 trunking application
AI296 Version 9.8x User’s Guide
Using the AI198TM Menu System
Accessing the Menu System
Types of Menu Items
Navigating the Menu System
Menu Numbering Structure
Following four types of menu items are available
Data
Submenus
Toggles
Menu re-appears with the entered IP address
Menu Item Description
Functions
Menu Item Descriptions
Exiting the Menu System
AI296 Local Menu System
TACACS+ Authentication
Multilevel User Name and Password Security
Radius Authentication
PPP Authentication Protocols PAP and Chap
Using a Telnet Connection for Login
Logging Into AI296
Using an Asynchronous Port for Login
Consecutive failed login attempts
Number of consecutive failed login attempts
Accessing the Local Menu System
Data Entry Items
Navigating the Local Menu System
Identifying Types of Menu Items
Direction Keys
Toggle Items
Accessing the Help Menu
Send
Exiting the Local Menu System
Save the changes
System Configuration
Description
General System Properties Configuration
Destination Menu Break Sequence
Format
Configuration in the AI198 Menu System
Menu Item Type
Toggle for both menu items
Ethernet Port Settings
Configuration in the AI296 Local Menu System
FTP Port
This menu item sets the FTP server port number
IP Settings
This example displays 16 FTP port number set to
Menu Item Types
Passive Link Settings
Access Menu
Minimum value is 25 seconds and the default is 60 seconds
Access the System Menu
Default is No
System Prompt
This item sets the system prompt value in the CLI
To on
TCP Settings
Toggle
Telnet Port
This item sets the Telnet port value for AI296
This example displays Telnet Port set to
Radius Configuration
Server Settings
Enabled
Shell/FTP Options
To configure the shell/FTP Radius option Access Menu
FALLBACK. The default is Disabled
Enabled
TACACS+ Configuration
Shell/FTP Options
00049
AI296 Local Menu Item Configuration
Snmp Configuration
Authentication Traps
Community Names
Data for all menu items
Following example displays
WriteComm Menu
Contact Persons
Node Information
Snmp Manager
10.65.32.4
Static Route Configuration
IP Address Settings
Following are available
TID to Modem Mux Configuration
Inactivity Timeout
This example displays Inactivity Timeout set to
Initialization String
Toggle for all menu items
Port Bit Settings
This example displays Init String set to conn23
TID to Route
AI296 Local Menu Item Configuration
Time Configuration
Daylight Savings Time
Sntp Settings
Settings
Access the Time Menu located under the System Menu
Time Zone
IP Over X.25 Subnet Configuration
Configuration Overview
Before Configuration
Local Settings
Local IP Address for this Subnet
Local IP Subnet Mask
This menu item configures the local IXE doorway link number
Local X.25 Link Number
Remote Settings
Remote IP Address for this Subnet
Remote X.121 Address
93.67.158.56
Link Configuration
Asynchronous
AI296 has six configurable link types
AI296 Link Types
Asynchronous PPP
HDLC-Bridge
Synchronous PPP
See Also
Default is Enabled
BX.25 Configuration
BX.25 Configuration Values Usage
BX.25 Modulo
BX.25 Support
BX.25 Timer Settings
This example displays BX.25 Support set to Enabled
00033
Alias
Connect Options Configuration
Access Menu For 02 Alias, enter 2, and the alias name
Link Type Availability
Call Retry Interval
This example displays 02 Alias set to async.4.1
Connect String
This example displays 03 Call retry interval set to
When
Default is OFF
Connection Settings
Connection settings are configured using three menu items
Is on
00030
Link Application
Destination AppAlias
Disconnect inactivity timer when the link receives a call
Disconnect Options Configuration
Disconnect Inactivity Timer Settings
Is Off
Select on or OFF. The default is on This example displays
Off. The default is On This example displays
Default is on
Disconnect Settings
Disconnect settings are configured using two menu items
Disconnect String
Disconnect
Async, AsyncPPP, HDLC-Bridge, MLT, SyncPPP,
General Link Properties Configuration
Auto Disable Error Limit
Flow Control
Async and AsyncPPP
This example displays SW Flow Control set to XonXoff
Access the Link Menu
Hardware Interface Interface Type
This example displays Interface Type set to
MLT
Interface Mode
Access menu 4.2.11.12.8 for MLT or menu 4.2.11.12.7 for
Link Description
This menu item defines a description for a link
Link Mode
This example displays Link Description set to New X.25 Link
This example displays 05*Link mode set to Passive
Link Number
This example displays 01 Link number set to
This menu item enables or disables a link
Link State
Link Type
This example displays Link state set to Down
Default is Disabled
Passive Link with Clocking
Port Data Bits
This menu item defines the number of databits in a data byte
Port Parity
This example displays Port data bits set to Seven
This menu item defines the baud rate for a port
Port Speed
This example displays Port parity set to Odd
Data in the AI296 local menu system
Menu 4.2.11.12.5 appears
Hdlc
Port Stop Bits
Sync Port Encoding
This menu item sets the binary encoding on a port
Xon Repeat Interval
Aysnc and AsyncPPP
This example displays 10 Xon Repeat interval set to
Following menu items are available for PPP configuration
General PPP Properties Configuration
Ipcp Address Settings
AsyncPPP and SyncPPP
Ipcp Address Parameters
Maximum Unit Settings
Set to
Network Control Protocol
For an Ipcp network control protocol
Ipcp
Lapb Parameters Configuration
Frame Settings
For Frame Window Size, enter the window size. The default is
Size set to
Lapb Timer Settings
N2 Retry Counter
150
Modem Option Configuration
Modem String
Dialing Time-out Interval
Number of Dial Attempts
This example displays Dialing time-outset to
Modem Setup Menu
This example displays Number of dial attempts set to
PPP Authentication Configuration
Local Authentication Settings
PAP
RAS Option
Radius
Remote Authentication Settings
Chap
Quick X.25 Configuration
Active
Number of PVCs
Toggle for max packet size Data for packet window size
Packet Settings
This example displays Number of PVCs set to
128 256 512
Normal Passive Extended
SVC Settings
Local Address
This example displays SVC Low set to 250 and SVC High set to
This example displays X121 Local Address set to
Async and AsyncPPP and SyncPPP
RTS/DTR Lead Control Configuration
DTR State Configuration
RTS State Configuration
Flow Control
DTR connect state Off DTR disconnect state
Parameters Configuration
Maximum Packet Size
Packet Window Size
This example displays Max Packet Size set to
Protocol Version
This example displays Packet Window Size set to
Counter Settings
Default is This example displays
Facilities Negotiation
Timer Settings
12,90000
Parameters Menu
43729
Virtual Circuit Configuration
PVC Configuration Settings
PVCs are configured using four menu items
Menu PVC Type LCN Range CallTmr ResetTmr
PVC Type Timer Type Range Default
Passive Reset Timer This example displays
For Timer Value, select the timer interval value
SVC Configuration Settings
Menu Item Type
0005
TID Multiplexing
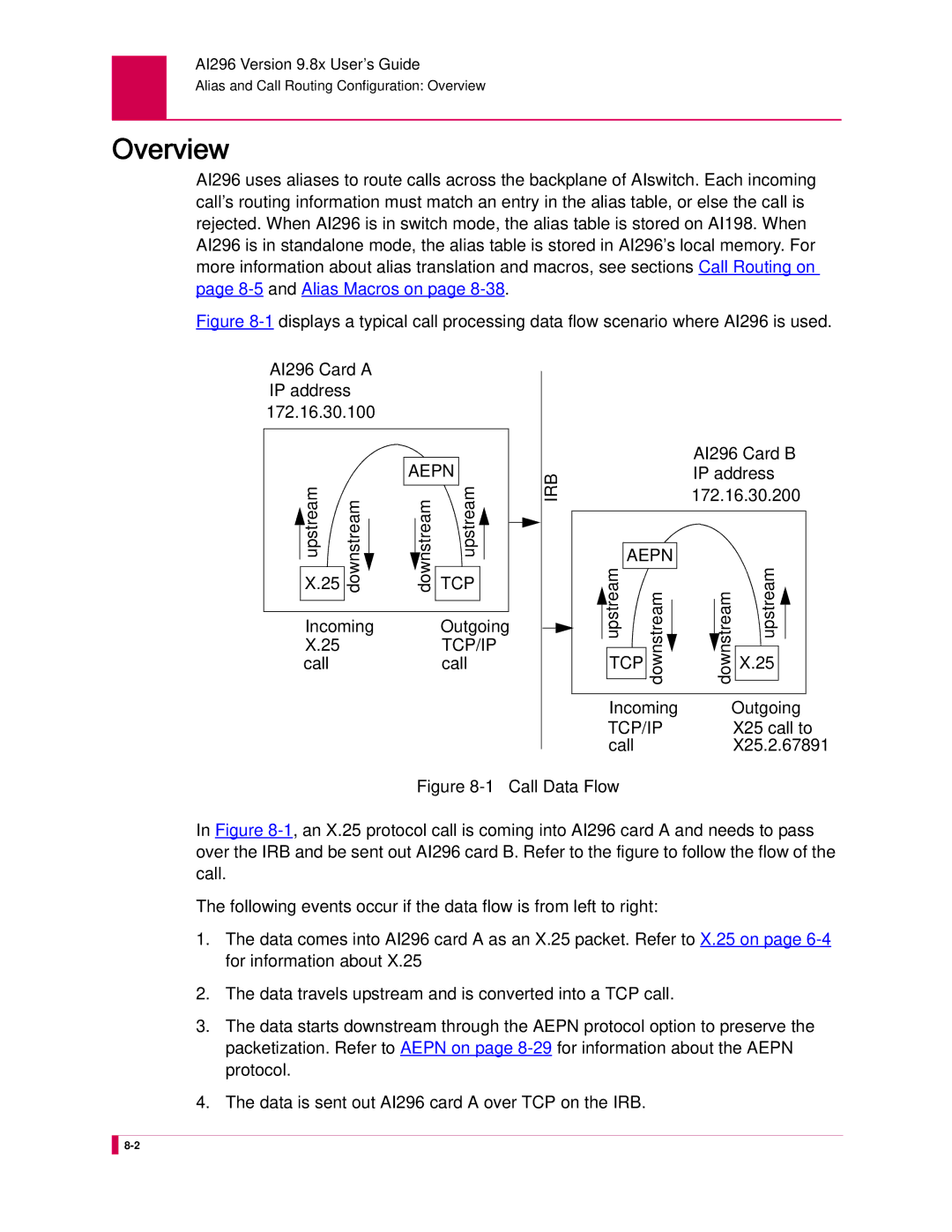
Overview
AI296 Version 9.8x User’s Guide
Menu appears
TID Multiplexing Configuration
Configuring the Parent Alias
Values are 1 to
Destination
Configuring the Children Aliases
TidforAI296 Defines the terminal identifier for AI296
During the parent alias configuration
TIDtid
Example Configurations
For Alias name, enter
YES
Alias Edit Menu Alias Name 172.16.1.23#1000
TL1DM.1
Alias Edit Menu Alias Name
Normal Response Format
TID Multiplexing Troubleshooting
Parameters
Response Item Description
Error Response Format
Normal Response Example
Errcde
Diagnostics for TID Multiplexing
Error Response Example
AI296 Version 9.8x User’s Guide
Alias and Call Routing Configuration
Call
Downstream
Incoming Outgoing
AI296 Card B IP address
Tocardb
X25.2.67891
Configuring an Alias in the AI198 Menu System
Call Routing
AI296 Version 9.8x User’s Guide
Configuring an Alias in the AI296 Menu System
Alias Edit Menu
Arranging Aliases in the Alias Table
Configuring an Alias with X.25 Keep-Alive
Notifies the 296 that this is the X-25 keep-alive feature
Where
Source/Destination Protocol Tables
Async 25 SVC
Asynchronous Source Without Breaks AI198
Source Destination Menu Item Information
Following options are available
Packetized
Asynchronous Source With Breaks AI198
Async With Following options are available TL1 Break
On a CR
X.25 SVC Source Without Breaks AI198
Option
Packetizing With async Break Address Async Call data
X.25 SVC Source With Breaks AI198
Called
Time
Called Following options are available Address
X.25 PVC Source Without Breaks AI198
25 PVC 25 SVC Alias name
25 PVC Alias name
25 PVC TL1 PAD TL1
25 PVC Async with Alias name
25 PVC Async break Called
TCP/IP Source Without Telnet Breaks AI198
With Called Following options are available Break Address
Async Alias name
TCP/IP Source With Telnet Breaks AI198
With Called
Asynchronous Source Without Breaks AI296
Async with Alias name
Async break Called
Async 25 SVC Alias name
Async 25 PVC Alias name
Async With Called
10 Asynchronous Source With Breaks AI296
Protocol Async 25 PVC Alias name
TL1 Break Async Address Packetized Call data
11 X.25 SVC Source Without Breaks AI296
12 X.25 SVC Source With Breaks AI296
Break Address Caller’s
13 X.25 PVC Source Without Breaks AI296
14 X.25 PVC Source With Breaks AI296
15 TCP/IP Source Without Telnet Breaks AI296
16 TCP/IP Source With Telnet Breaks AI296
Async with Alias name
Protocol Processing Modules
Module Types
Aepx
Prevents the PAD protocol from passing breaks downstream
Enables Macstar compatibility
Prevents the PAD protocol from passing breaks upstream
Causes the PAD protocol to reply to X.25 breaks
To zero, the option is turned off
An X.25 when X.3 parameter 3 is set to
Provides packetizing and sets the packetizing timer to
Specify up to 16 characters
Provides packetizing but prevents breaks from being
Carriage return and semi-colon
Feed and delete
Propagated upstream
To zero, this option is turned off
Feed and delete
Provides TL1 packetizing and sets the packetizing timer to
Seconds
Provides TL1 packetizing and prevents breaks from passing
Module Properties
Module Arguments
Entry Description
Alias Macro Components
Start Symbols
Alias Macros
Comments
Variables
Wildcard Symbols
Constants
Variable Value
Operators
Operator Description
Returns the Ascii integer value of the first
20 Alias Macro Functions
Alias Macro Function Description of Operation
Character in a string
Returns characters from string starting with
Match any of the expressions, then default is
20 Alias Macro Functions
Xth character and continuing to the right-most end
Alias Macro Configuration
Configuration Examples
=LA,PA,’#’,1-1=MYIP1
Examples are given for the following connections
Alias Configuration Examples
SVC to SVC Connection
TL1
SVC to PVC Connection Diagram
SVC to PVC Connection
PVC
PVC to SVC Connection
Called address
16.X25.2.3
MLT Route
MLT Call Routing Example
MLT6
Link-to-Link Routing Example
Menu F1 Help F2 Send F4 Close Ctrl-R Return to Main Menu
AI296 Commands
Shell Connections
Commands Overview
Shell Commands
Establishing a Local Shell Connection
Establishing a Remote Shell Connection
Using winslc Commands
Winslc Commands
Displaying winslc Command Logging
Log/Alarm Message Header
Header Element Description
Formats
Command Type
Aaa
Shell
Disable-Disables TACACS+ authentication
All-Enables or disables TACACS+ authentication on all
Async-Enables or disables TACACS+ authentication on
Enable-Enables TACACS+ authentication
AI296 Version 9.8x User’s Guide
AI296 Version 9.8x User’s Guide
Command Defaults
Examples
AAA
Following parameters is accepted
Alarm
Hyphens
Caused the alarm is resolved
Alarm group
Self-clearing alarms clear themselves when the problem that
Unmask. Valid values are existing alarm groups
This example displays all alarms by severity level
This example displays all system alarms in group links
This example displays alarms for links 5-8in group links
This example displays the unmasking of alarm group links
Command Types
Arp
Column Description
296arp -d Mapping for 10.40.53.2 deleted
Break
296break 10.40.5.11#1821 Breaking connection 10.40.5.11#1821
Bridge
This example displays the dumping of the bridge table
Reset error counters for links 1
Creset
To reset error counters for links 1, 2,
Example, 1,2-3 to reset error counters for links 1, 2,
Date
Debug
This example displays the enabling of all debug data logging
Filename Defines the name of the file to delete
This command deletes a specified file that resides on AI296
Delete
This example displays the deletion of file log.txt
Diag-conn
Display Item Description
Pattern 1, Logic 2, and Pattern 3 are evaluated before
This option prompts for the ID of the connection to view
Displays details for that connection
Logic 4 and Pattern 5 are considered
Using Interpretation Mode
Diag-eth
Using the Help Option
Deletes a filter
Following formats apply to filters
Adds a filter
Defines the source address MAC, IP, or TCP/UDP
Adds or deletes a specific protocol filter. Available
MAC/IP address settings
Defines the TCP/UDP port number regardless
Protocol filters are
This example displays Ethernet diagnostic help information
Ijkl
FF FC
This example displays the deletion of filter protocol tcp
This example displays the deletion of all filters
Diag-info
Means the X.25 frame level is established
Displays the link number
Means the X.25 frame level is not established
Buffers were available
Displays the name of the Streams resource
Last rebooted
Rebooted
Displays the number of free or available Streams resources
Specifies that the link is not established
Connection to be enabled
Displays the state of the driver. Two states are available
Displays the number of bytes coming into the link
Received packets
Had CRC errors
Displays the number of frame length violations
Displays the number of short received frames
Displays the number of bytes received on
Displays the number of frames received on
Connection
Displays the number of times transmitted frames
Displays the number of frames received on the connection
Does not indicate an error
Displays the number of transmit errors that have occurred
Displays the number of bytes received on the connection
Excessive deferral timer is exceeded. An excessive deferral
Errors
Displays the number of alignment errors
Error is recorded when the following events occur
Following values may appear
Ethernet interface needs to be reset
Displays the current state of the Ethernet interface.
Ethernet interface is uninitialized
Diag-line
Option Function
Diag-line
Only present in data packets, then the data byte count is
Displayed as Ascii String
Diag-tconn
Baseport Defines the baseport number for AI296
Dir
This example displays all available files
Exit
This example displays an exit from the current shell session
Head
This command displays the first few lines of a file
Defines the number of lines to display. The default is
Defines the name of the file to display
This example displays a list of all available commands
Help
This example displays help information for command show
This example displays the current user name and profile
This command displays the current user name and profile
Formats Examples
This example displays the configured IP address information
Ip init
Enter IP Address Range default 1 Setting range to 296
Link
This example displays the starting of links 1 through 4
This example displays the stopping of links 6
Linkstat
This command displays link statistic information
For the AI296 system command
Baseport Indicates the baseport number of AI296
C D
9600 RS-232 @AI198154041 072204 Sev=F Base=064 Msg
This command turns the display of log messages on or off
Log
This example displays the closing of a shell session
This command closes a shell session
Logout
This command displays a list of available files
This example displays the AI296 Main Menu
This command accesses the AI296 main menu system
Menu
More
Pad
This example displays the setting of the PAD profile
Resets the current call
Enables the transparent mode of operation
Sets page wait to n lines
Winslc
This command forces AI296 to crash dump and halt
Panic
Baseport Defines the AI296 baseport number
This command changes an existing user’s password
Passwd
Ping
Pppstatus
Displays one of the following
IP address of AI296 if the link status is Running
Profilename-Defines the name of a user profile
Command Type shell Formats
Profile
Have write permission
Removes a user profile. The following parameter is accepted
Newprofile-Defines the name of a new user profile
Lists all user profile names
Pvcedit
Forces the PVC to become passive
Pvclist
This example displays PVC information for link
Column Description
This example displays the resetting of AI296
Reset
This command resets AI296
This example displays AI296 receiving two files from a PC
Cnf extension
Configuration file
Selcnf
PDisplays the content of the file one page at a time
Sholog
Displays all active connections
Show
Displays comments
Displays crash dump information
Displays WAN diagnostic information
MAC address when in standalone mode
Displays the default and backup gateway IP address
Displays link data. The following parameters are accepted
This example displays the AI296 version number
This example displays the serial link performance for links
Lead is negated
This command displays the status of the EIA leads
Staeia
CTS
This example displays the current standalone mode status
Standalone
Staslc
Displays the number of framing errors
Is asserted and means the signal is negated
Displays the number of parity errors
Displays the number of overrun errors
Syncflash
Sz filename
Tacacs
Displays the number of failed connection attempts that were
This example displays a TACACS+ debug log file
TACACS+ server
Made to the TACACS+ server
Were received when AI296 attempted to read them from
Displays the number of errors that occurred when AI296
When AI296 attempted to read a packet from the TACACS+
Configuring the time out value, refer to command aaa on
Tacacs server
All-Enables or disables all AAA phases for the specified
Configures the AAA phases that are allowed for specified
Account-Enables or disables the accounting phase for
Authen-Enables or disables the authentication phase for
Displays the server numbers. The +/ signs indicate if
Disabled
Associated servers are enabled + or disabled
Displays the TACACS+ shared secrets passwords for specified
Servers
Specifies that a line number value will be entered
This command displays the last few lines of a file
Tail
This example displays the last 10 lines of file userlog.txt
Tcpoutconn
Tftp
Tftp
106
File Downloaded successfully 296
Tftpboot
109
Timezone
111
Priority Level
Default
Trace
This example displays the configuration of trace
Traceroute
This example displays the traceroute to IP address
Displays text from the file one page at a time
Defines the file for which you want to view the contents
Type
Update
Defines the source file to copy
Uptime
Useradd
Profilename Permission
Specifies a user who can only execute the following commands
Description of Permissions Profilename
Userdel
Users
Who
Xvc
124
AI296 System Codes
This appendix provides information about AI296 system codes
Cause Code Description
Cause Codes and Diagnostic Codes
Standard Reset Indication Cause Codes
0x9B Remote DTE originated reset
Kentrox-Specific Reset Indication Cause Codes
0X1D Reset due to network out of order
Standard Clear Indication Cause Codes
0x39 Ship absent 0x7F Registration/cancellation confirmed
Standard ISO Diagnostic Codes
Ccitt Diagnostic Codes
Cause Code Description
Cause Code Description
Kentrox-Specific Diagnostic Codes
Common Crash Codes
Error Code Description Hexadecimal Decimal
Crash Codes
AI296 Crash Codes
System Failure Crash Reports
Kentrox Technical Support
AI296 Version 9.8x User’s Guide
Standalone Mode and Switch Mode
At the FTP prompt, open AI296
Standalone Mode
Downloading Software for a Standalone AI296
Transfer the software image to AI296
Configuring BOOTP/TFTP
At the FTP prompt, open AI198
Switch Mode
Downloading Software for AI296 in Switch Mode
Transfer the software image to AI198
Defines the software image file name
AI296 Version 9.8x User’s Guide
Commands for AI296 TACACS+ Server Enhancements
AI296 Commands
Following keyword lets users access destinations
AI296 Menu Aliases
Menu Menualias
FTP Sessions
Following AI296 keywords apply to FTP access
Provides FTP read access

![]()
![]()