Sundance Technology
ST201
PRELIMINARY draft 2
are independent of each other in general. A special case is when a transmit under run occurs. In this case the current frame being transmitted is the only frame in the TxFIFO. When a transmit under run occurs, the ST201 stops TxDMA operation and generates an interrupt with a TxUnderrun error flagged in TxStatus. The host system can deter- mine which is the under run error frame by examin- ing the current value of TxDMAListPtr. The host system can assume that all frames in the TxDMAL- ist ahead of the under run error frame have been transmitted successfully. To recover from an under run, the host system should halt the TxDMA Logic by setting the TxDMAHalt bit, wait until TxDMAIn- Prog and TxInProg are cleared, then issue a TxRe- set to reset the under run (TxFIFO and Transmit MAC). Transmission needs to be enabled (by TxEnable) again and all
FRAME RECEPTION AND RXDMA
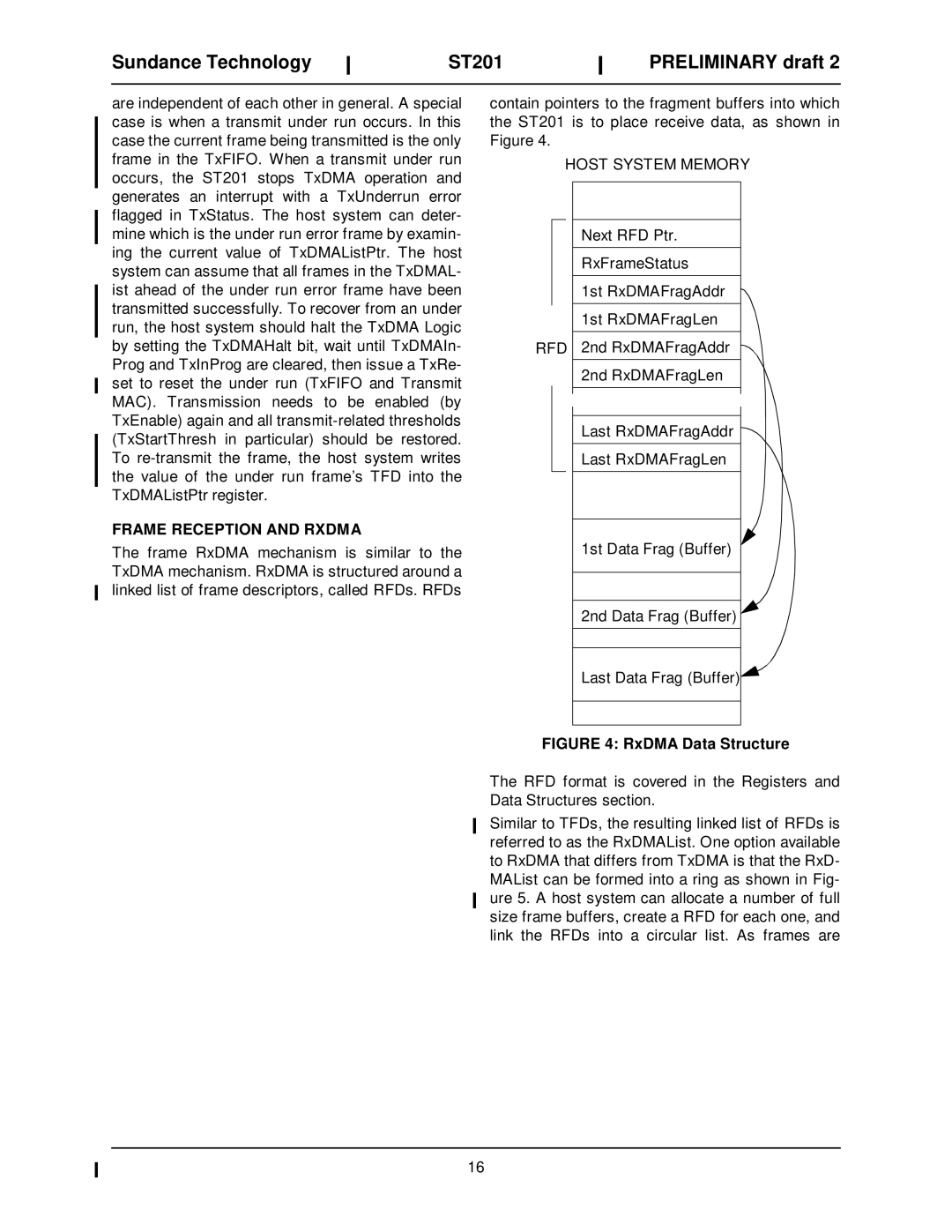
The frame RxDMA mechanism is similar to the TxDMA mechanism. RxDMA is structured around a linked list of frame descriptors, called RFDs. RFDs
contain pointers to the fragment buffers into which the ST201 is to place receive data, as shown in Figure 4.
HOST SYSTEM MEMORY
Next RFD Ptr.
RxFrameStatus
1st RxDMAFragAddr
1st RxDMAFragLen
RFD 2nd RxDMAFragAddr
2nd RxDMAFragLen
Last RxDMAFragAddr
Last RxDMAFragLen
1st Data Frag (Buffer)
2nd Data Frag (Buffer)
Last Data Frag (Buffer)![]()
FIGURE 4: RxDMA Data Structure
The RFD format is covered in the Registers and Data Structures section.
Similar to TFDs, the resulting linked list of RFDs is referred to as the RxDMAList. One option available to RxDMA that differs from TxDMA is that the RxD- MAList can be formed into a ring as shown in Fig- ure 5. A host system can allocate a number of full size frame buffers, create a RFD for each one, and link the RFDs into a circular list. As frames are
16