Configuration
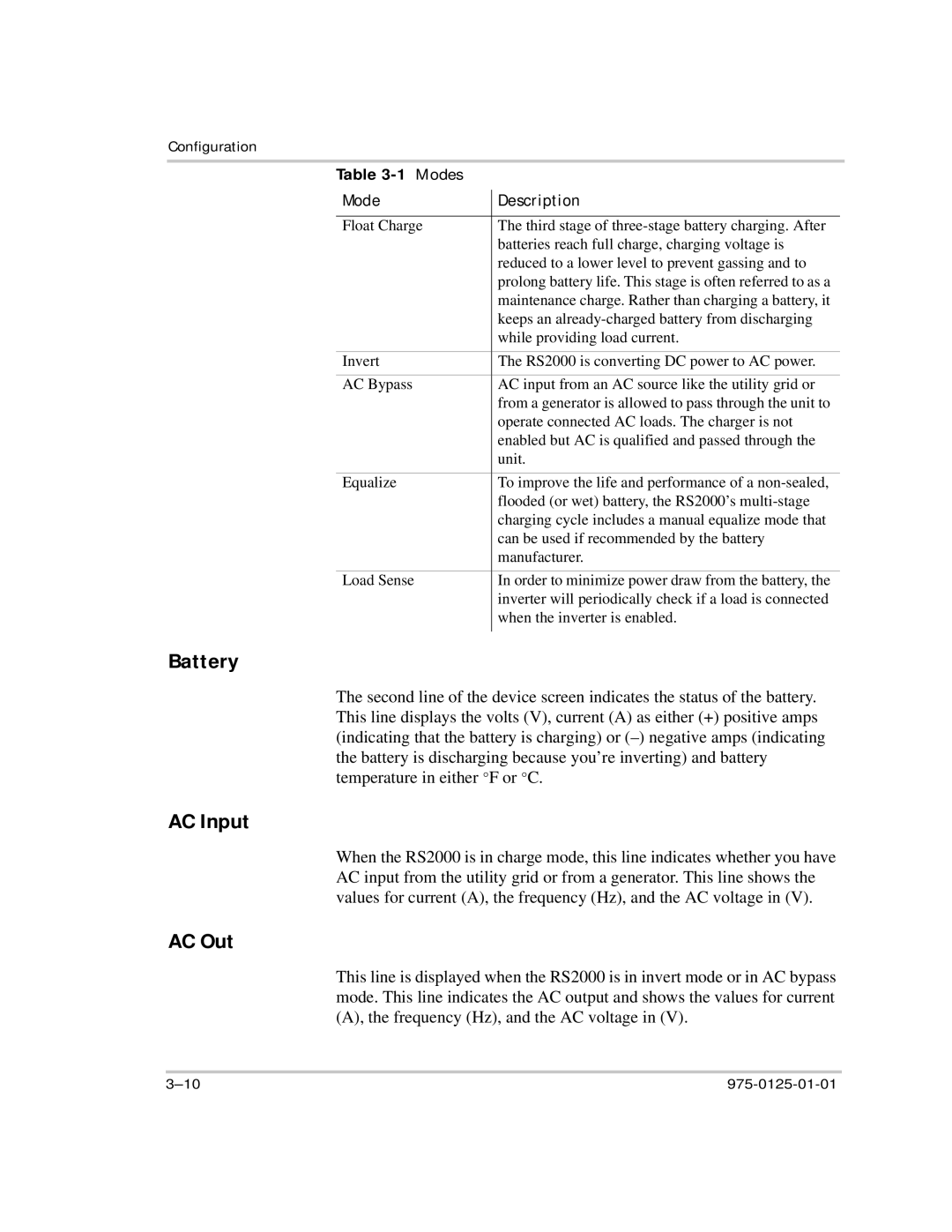
Table 3-1 Modes
Mode | Description |
|
|
Float Charge | The third stage of |
| batteries reach full charge, charging voltage is |
| reduced to a lower level to prevent gassing and to |
| prolong battery life. This stage is often referred to as a |
| maintenance charge. Rather than charging a battery, it |
| keeps an |
| while providing load current. |
Invert | The RS2000 is converting DC power to AC power. |
AC Bypass | AC input from an AC source like the utility grid or |
| from a generator is allowed to pass through the unit to |
| operate connected AC loads. The charger is not |
| enabled but AC is qualified and passed through the |
| unit. |
Equalize | To improve the life and performance of a |
| flooded (or wet) battery, the RS2000’s |
| charging cycle includes a manual equalize mode that |
| can be used if recommended by the battery |
| manufacturer. |
Load Sense | In order to minimize power draw from the battery, the |
| inverter will periodically check if a load is connected |
| when the inverter is enabled. |
|
|
Battery
The second line of the device screen indicates the status of the battery. This line displays the volts (V), current (A) as either (+) positive amps (indicating that the battery is charging) or
AC Input
When the RS2000 is in charge mode, this line indicates whether you have AC input from the utility grid or from a generator. This line shows the values for current (A), the frequency (Hz), and the AC voltage in (V).
AC Out
This line is displayed when the RS2000 is in invert mode or in AC bypass mode. This line indicates the AC output and shows the values for current (A), the frequency (Hz), and the AC voltage in (V).