| Introduction |
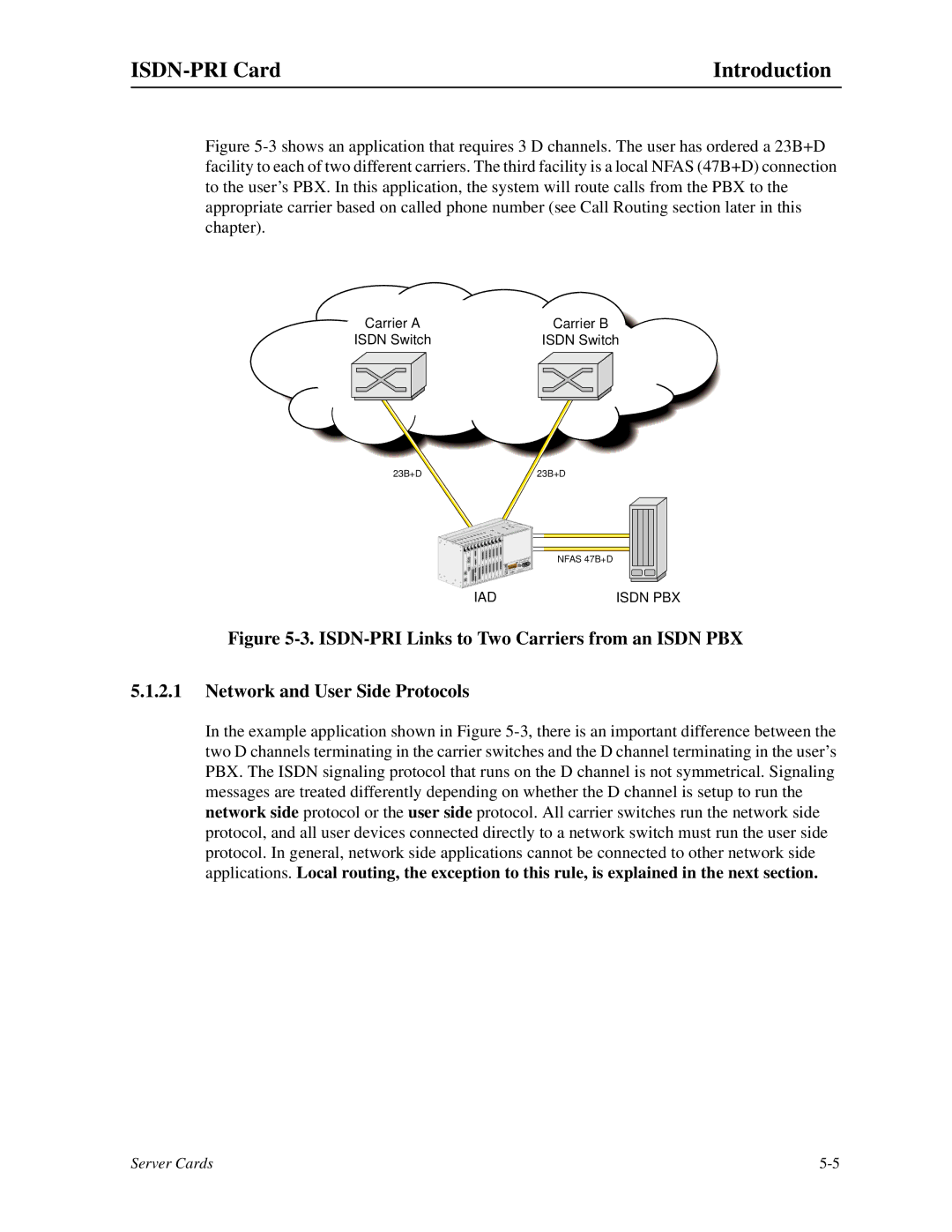
Figure 5-3 shows an application that requires 3 D channels. The user has ordered a 23B+D facility to each of two different carriers. The third facility is a local NFAS (47B+D) connection to the user’s PBX. In this application, the system will route calls from the PBX to the appropriate carrier based on called phone number (see Call Routing section later in this chapter).
Carrier A | Carrier B |
ISDN Switch | ISDN Switch |
23B+D | 23B+D |
| NFAS 47B+D |
IAD | ISDN PBX |
Figure 5-3. ISDN-PRI Links to Two Carriers from an ISDN PBX
5.1.2.1Network and User Side Protocols
In the example application shown in Figure
Server Cards |