Introduction |
Thus, if local routing is disabled, any call coming into the system on a network side (i.e., local) D channel will be routed only to a user side D channel based on the called number. Even if the called number matches, such a call will never be routed to an HSU port or a network side D channel when local routing is disabled.
If local routing is enabled, then any call coming in on a D channel will be routed to the first matching phone number, regardless of whether or not the match is for a local device.
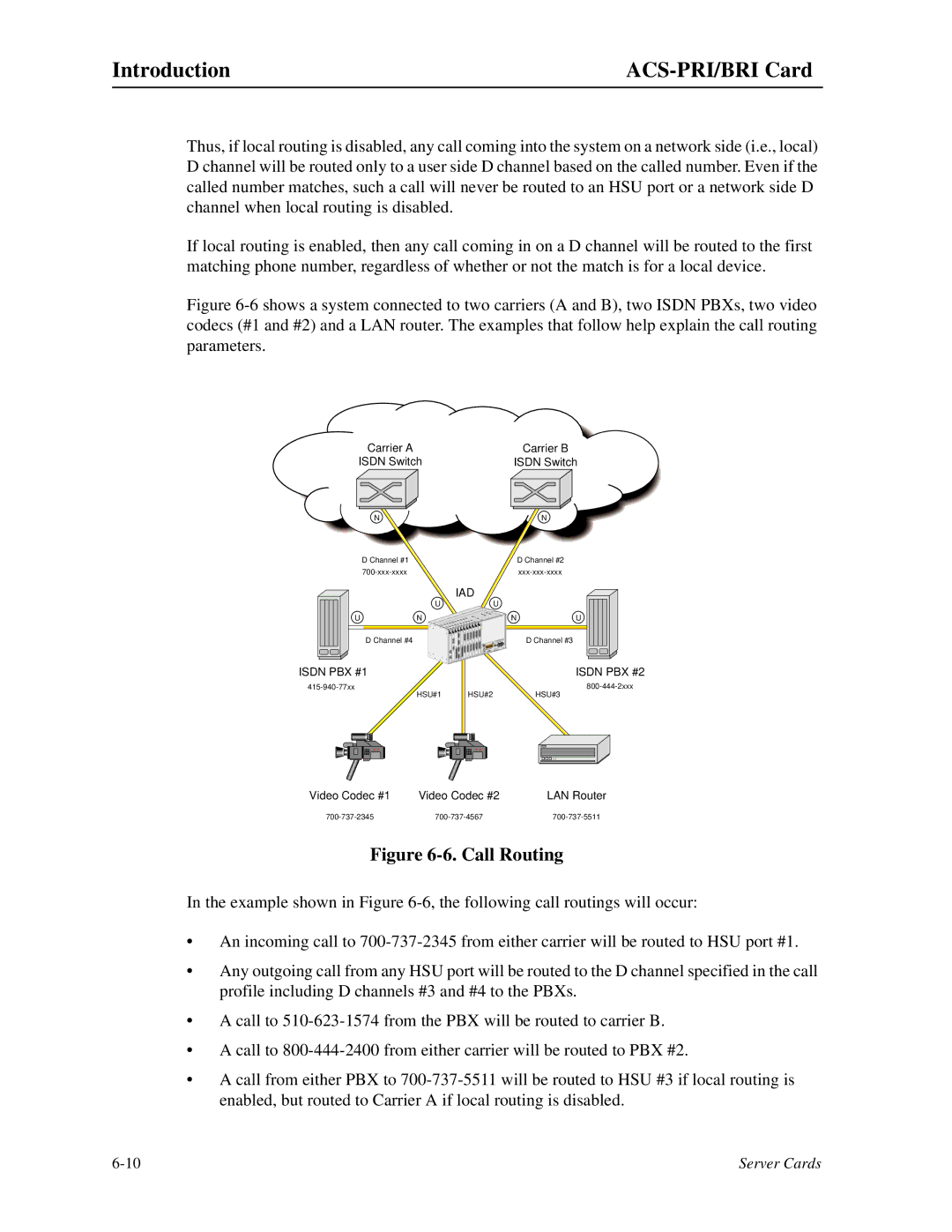
Figure 6-6 shows a system connected to two carriers (A and B), two ISDN PBXs, two video codecs (#1 and #2) and a LAN router. The examples that follow help explain the call routing parameters.
Carrier A | Carrier B |
ISDN Switch | ISDN Switch |
N
D Channel #1
N
D Channel #2
|
| IAD |
|
| U | U |
|
U | N | N | U |
| D Channel #4 |
| D Channel #3 |
ISDN PBX #1 |
|
|
|
| ISDN PBX #2 | ||||
|
|
|
| ||||||
|
|
| HSU#1 |
| HSU#2 | HSU#3 | |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Video Codec #1 | Video Codec #2 | LAN Router |
Figure 6-6. Call Routing
In the example shown in Figure
•An incoming call to
•Any outgoing call from any HSU port will be routed to the D channel specified in the call profile including D channels #3 and #4 to the PBXs.
•A call to
•A call to
•A call from either PBX to
Server Cards |