C141-C013-01EN
For Safe Operation
Handling of This Manual
Revision History
This page is intentionally left blank
Overview of Manual
Glossary
Sense Data and Error Recovery Methods
Disk Media Management
Acronyms and Abbreviations
Conventions Used in this Manual
Conventions for Alert Messages
Manual Organization
Referenced Standards
Ansi
Contents
Contents
Command Processing 103
127
Command Specifications
Data Buffer Management
135
Parameter Data Format 281
Sense Data and Error Recovery Methods
359
382
Termination status analysis and error recovery methods
374
384
Glossary 417 Acronyms and Abbreviations 419 Index 421
Figures
Tables
100
107
226
311
Total unrecoverable verify errors posted to Init
SAS Interface
Topologies in SAS Interface
SAS Interface
SAS Layering
Topologies in SAS Interface
Physical links and phys
Ports narrow ports and wide ports
Ports narrow ports and wide ports
SAS devices
SAS devices
Pathways
Example of potential pathways
Connections
Names and identifiers
Names and identifiers
SAS addresses
SAS address format
Hashed SAS address
Hashed SAS address code parameter
Phy layer
Phy layer
1 8b10b coding
Usage of special characters
Link reset sequence
Reset-related terminology
OOB signal timing specifications
Start conditions of the link reset sequence
Out of band OOB signals
Comsas
OOB signal transmitter requirements
COMINIT/RESET
OOB signal receiver idle time detection requirements
OOB signal receiver burst time detection requirements
COMINIT/COMRESET
OOB signal receiver negation time detection requirements
SAS OOB sequency
3 4 n
Scenario 2 SAS phy a starts SAS OOB sequence
Scenario 3 SAS phy B misses SAS phy As Cominit
SAS speed negotiation sequence
∙ When the Cominit signal cannot be detected
∙ When the Comsas signal cannot be detected
Exception handling in the OOB sequence
SAS speed negotiation sequence timing specifications
11 SAS speed negotiation window
SAS Interface
12 SAS speed negotiation sequence Example
Phy reset sequence after devices are attached
14 Phy reset sequence Example
Exception handling in the speed negotiation sequence
When the speed negotiation sequence is successful
Phy layer dword synchronization DWS
10 Primitives not specific to type of connection 1/2
Link layer
Primitives
Link layer
10 Primitives not specific to type of connection 2/2
11 Primitives used only inside SSP and SMP connections
12 Primitive sequences
Primitive sequences
Primitives not specific to type of connections
AIP Arbitration in progress
Break
Broadcast
Close
Error
Hardreset
Eoaf End of address frame
Openreject
Notify
Openaccept
13 Openreject abandon primitives
Supported
14 Openreject retry primitives
No Destination
Soaf Start of address frame
Done
Primitives used only inside SSP and SMP connections
ACK acknowledge
15 Done primitives
Rrdy
EOF End of frame
NAK negative acknowledgement
SOF Start of frame
16 Clock skew management Align insertion requirement
Clock skew management
Idle physical link
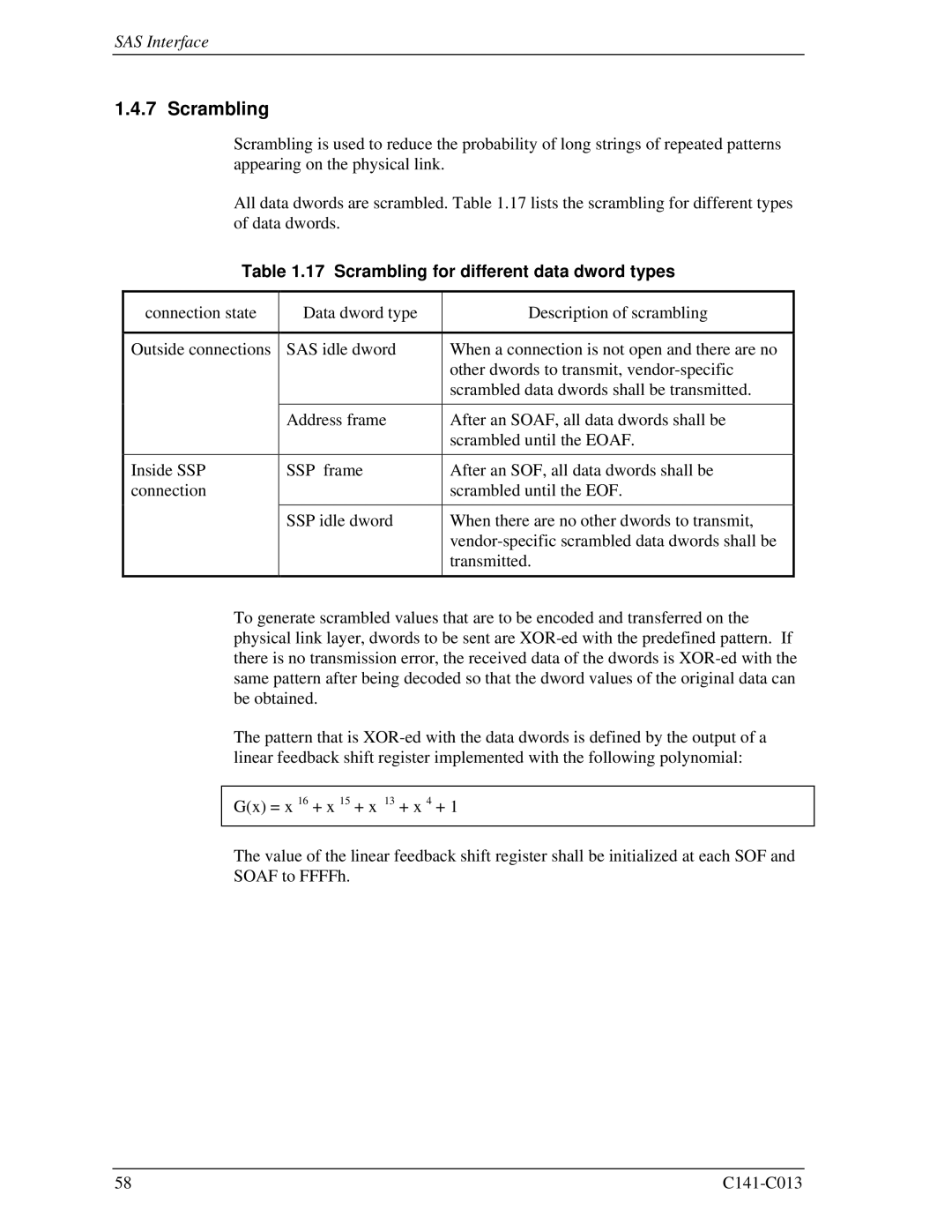
Scrambling
17 Scrambling for different data dword types
Address frames
Address frames
Address frames overview
18 Address frame format
20 Device Type field
Identify address frame
19 Identify address frame format
PHY Identifier
Device Type
SAS Address
22 Protocol field
Open address frame
21 Open address frame format
SMP
23 Connection Rate field
∙ Initiator Connection TAG
24 Arbitration Wait Time field
∙ Connection Rate
∙ Pathway Blocked Count
Identification and hard reset sequence
∙ Destination SAS Address
∙ Arbitration Wait Time
Connections overview
Connection request
Arbitration fairness
Connection responses
25 Connection responses
Bits 79-64 79 is MSB Bits 63-0 0 is LSB
Aborting a connection request
27 Abort connection responses
Close
Closing a connection
28 Close connection responses
Rate matching
Breaking a connection
29 Break connection responses
SSP link layer
30 Rate matching Align and/or Notify insertion requirements
Creditblocked
SSP frame transmission and reception
SSP flow control
Interlocked frames
31 SSP frame interlock requirements
17 Interlocked frames
18 Non-interlocked frames with the same tag
20 Closing an SSP connection example
32 SSP frame format
Transport layer
SSP frame format
Nodata
Transport layer
33 Frame Type field
Responsedata
SAS Interface
Information units
Command information unit
34 Command information unit
Head of Queue
35 Task Attribute field
Simple
Ordered
Transport layer
Task information unit
36 Task information unit
37 Task Management Function field
Abort Task SET
38 Xferrdy information unit
Response Data
Xferrdy information unit
39 An example of requested offset
Requested Offset Write Data
Length
21 Example of Xferrdy frames
Data information unit
40 Data information unit
SAS Interface
TOO Much Write Data
42 Datapres field
Response information unit
41 Response information unit
∙ Response information unit Nodata format
∙ Response information unit Responsedata format
∙ Response information unit Sensedata format
43 Response Data field
44 Response Code field
Transport layer
Sequences of SSP frames
22 Example of Task frame
23 Example of write command
Exceptional event processing of a drive
Transport layer
45 Exceptional event processing of a drive 1/2
Clear Task SET Management Function Complete
45 Exceptional event processing of a drive 2/2
102 C141-C013
Command Processing
Command Format
10-Byte CDB basic format
Command Processing
6-Byte CDB basic format
Operation code
Bit Byte Operation Code
Control Byte
Operation code
Logical block address
Transfer data length
Control byte
Command Format
Control byte
Handling an illegal CDB
Good status
Status Byte
Status
Check Condition status
Busy status
Command Terminated status
Condition MET Status
Intermediate status
Command Queuing Function
READ, Read EXTENDED, WRITE, Write Extended
Unit Attention Condition
When a Power On or Reset occurs
When I-T Nexus Loss occurs
Generation of the Unit Attention condition
Commands cleared by another Init
Logical Unit Reset
Report Luns command
Inquiry command
Request Sense command
Sense Data Hold State
Power Condition
∙ ActiveWait state
LED Display
∙ Commands that can be executed even in the Not Ready state
∙ Operation when formatting is not completed normally
LED Display
LED display
Command Processing Exceptions
Overlapped tag
Illegal LUN specification
Command Processing Exceptions
Outline of disk drive error recovery processing
Error recovery processing
Recovery procedures for disk drive errors
Reserved operation code
∙ Nexus
Abort processing
Comparison between SAS and Scsi about definition
Hard Reset
∙ Abort processing during write operation
10 Reset processing during write
Unrecoverable hardware errors
Fatal hardware errors
Self-diagnostic errors
Data Block Addressing
Data Block Addressing
Data space configuration
Logical block addressing
User space logical block addresses
Alternate area
Data buffer configuration and basic operation
Data Buffer
Data Buffer Management
Read operation
Data Buffer
Write operation
Caching operation
Look-Ahead Cache Feature
Caching object commands
Read Read Extended
− Write − Write Extended − Write and Verify
Look-Ahead Cache Feature
Disabling caching data
Data Buffer Management
Look-Ahead operation, Look-Ahead volume
Caching parameters
This page is intentionally left blank
Control/Sense Commands
Test Unit Ready
Command Specifications
Inquiry
Control/Sense Commands
Standard Inquiry data
Fujitsu
Version field
Command Specifications
Command queuing
SAM2
Version descriptor
Byte
OX0B, Oxfc SAS
Command support data
Support
VPD information
VPD information VPD identifier list
VPD information device serial No
MSB
10 VPD information device unique information 1/2
PIV
10 VPD information device unique information 2/2
MBS
Code SET
Command Specifications
Read Capacity
11 Read Capacity data
Mode Select
Command Specifications
Mode Select parameter structure
Command Specifications
12 Mode Select command Group 0 parameter configuration 1/2
12 Mode Select command Group 0 parameter configuration 2/2
SPF
Control/Sense Commands
Command Specifications
13 Mode Select parameters
Command Specifications
Mode Select Extended
Byte
Sub Page Descriptor Bit Byte
Mode Sense 1A
15 Mode
16 Mode Sense data type specifications
Control/Sense Commands
17 Mode Sense command group 0 parameter configuration 1/2
17 Mode Sense command group 0 parameter configuration 2/2
Header
Block descriptor
Descriptor
Control/Sense Commands
Mode Sense Extended 5A
Header Bit Byte
176 C141-C013
Rezero Unit
START/STOP Unit 1B
Control/Sense Commands
Reserve
Logical unit reserve function
Reserve right and third party reserve function
Reserve Extended
Release object and third party release function
Release
Release function
Release Extended
Request Sense
Command Specifications
LOG Select 4C
20 LOG Select command parameter configuration
19 PC page control
Length
Code
21 Page code
Parameter code
22 Log parameter
TSD ETC TMC
Byte
Lbin
LOG Sense 4D
23 Page Code assignment for the log pages
Log parameters
Persistent Reserve in 5E
Read Keys
Persistent Reserve in service actions
24 Persistent Reserve in service actions
Read Reservation
LSB MSB
Persistent Reserve in parameter data for Read Keys
25 Persistent Reserve in parameter data for Read Keys
Persistent Reserve in parameter data for Read Reservations
Format of the Reservation descriptors is defined in Table
∙ Persistent reservations type
∙ Persistent reservations scope
28 Persistent reservations scope
29 Persistent reservations type codes
Persistent Reserve OUT 5F
Command Specifications
Persistent Reserve OUT service actions
30 Persistent Reserve OUT service action codes
Aptpl
Persistent Reserve OUT parameter list
31 Persistent Reserve OUT parameter list
Control/Sense Commands
Command Specifications
Report Luns A0
Persistent Reserve
33 Report Luns parameter data
Report Device Identifier A3
34 Report Device Identifier parameter data
SET Device Identifier A4
35 SET Device Identifier parameter data
Read
Data Access Commands
Data Access Commands
Command Specifications
Read Extended
FUA
Write 0A
Data Access Commands
Write Extended 2A
Write and Verify 2E
Verify 2F
Seek 0B
Seek Extended 2B
Synchronize Cache
Format Commands
Format Unit
Format Commands
Defect list
Specifying the initialization method
36 Defect list format
FOV
37 Format Unit command parameter list configuration
Format parameters
Stpf
Command Specifications
Format Commands
38 Defect descriptor byte distance from index format
39 Defect descriptor physical sector address format
Command Specifications
40 Format Unit command defect processing 1/2
Defect processing during initialization
40 Format Unit command defect processing 2/2
Reassign Blocks
Bit Byte X07
41 Reassign Block command defect data list configuration
= Hardware Error
Correction of the defect descriptor
42 Defect data type
Bit Byte X37 PList GList
Transfer Byte Length MSB Transfer Byte Length LSB
44 Read Defect Data command defect data configuration
43 Defect data format
Defect descriptor list
45 Defect data conditions
Format Commands
Read Defect Data B7
46 Read Defect Data command B7 defect data configuration
Maintenance, Diagnostic Commands
Self-diagnosis test
47 Self-diagnosis test
Parameter specification
PER DTE
Maintenance, Diagnostic Commands
PHY Test
49 Send Diagnostic command parameter list configuration
50 Page code
51 Send Diagnostic parameters page code list
52 Send Diagnostic parameters PHY Test function
Maintenance, Diagnostic Commands
Command Specifications
54 Specifying address format
Logical unit Self-Test
55 SELF-TEST
Receive Diagnostic Results 1C
Parameters
Code list
57 Receive Diagnostic Results response data page code list
Logical/physical address conversion
59 Address format
Write Buffer 3B
60 Write Buffer transfer mode
61 Write Buffer command buffer data mode = 000
Mode = 0, 0, 0, 1 Header + data, with address specification
Mode = 0, 1, 0, 1 Microcode download, with saving
Mode = 0, 0, 1, 0 Data only, with address specification
Mode = 0, 1, 0, 0 Microcode download, without saving
Maintenance, Diagnostic Commands
Command Specifications
Mode = 1, 0, 1, 0 Echo buffer
62 Read Buffer transfer mode
Read Buffer 3C
63 Read Buffer command buffer data mode = 0000
Mode = 0, 0, 0, 1 Header + data, with address specification
Mode = 0, 0, 1, 1 Buffer descriptor
64 Read Buffer command buffer descriptor
Ebos
Mode = 1, 0, 1, 1 Echo buffer descriptor
65 Read Buffer command echo buffer descriptor
Read Long 3E
05 = Illegal Request
Write Long 3F
Command Specifications
Write Same
Command Specifications
Mode Parameters
Parameter Data Format
Parameter Data Format
Read/Write Error Recovery Parameters Page Code =
Mode Select parameters read/write error recovery parameters
Write Extended Write Long Write Same
Mode Parameters
Read Read Extended Read Long
Parameter Data Format
Mode Parameters
Combinations of error recovery flags
EER PER DTE DCR
Mode Select parameters disconnect/reconnect parameters
Disconnect/Reconnect Parameters Page Code =
Parameter Data Format
Mode Select parameters format parameters
Format Parameters Page Code =
Parameter Data Format
Mode Parameters
Parameter Data Format
C141-C013 293
Mode Select parameters drive parameters
Drive Parameters Page Code =
Mode Parameters
Verify
Verify Error Recovery Parameters Page Code =
Mode Select parameters verify error recovery parameters
Mode Parameters
Mode Select parameters caching parameters
Caching Parameters Page Code =
Mode Parameters
Parameter Data Format
Mode Parameters
Parameter Data Format
Mode Parameters
Control Mode Parameters Page Code = 0A
Mode Select parameters control mode parameters
Mode Parameters
TAS task aborted status not supported
Mode Parameters
10 Mode Select parameters notch parameters
Notch Parameters Page Code = 0C
Mode Parameters
Port Control Parameter Page Code =
11 Port control parameter Page 0 Format Short Page Format
Number of Phys
Code Description
12 Port control parameter Sub Page Format Long Format
13 SAS phy mode descriptor format
This page cannot be modified
Parameter Data Format
C141-C013 315
Power Condition Parameter Page Code = 1A
14 Power condition parameter Page 0 Format Short Page Format
15 Mode Select parameters informational exception control
Informational Exceptions Control Page Page Code = 1C
Parameter Data Format
Mode Parameters
16 Mrie 1/2
17 Interval timer
16 Mrie 2/2
Ffff
Background Control Mode Parameter Page Code = 1C/subpage =
18 Mode Select parameters background control mode parameter
Pre-Scan is disabled
Parameter Data Format
Additional Error Recovery Parameters Page Code =
Fujitsu unique parameter
20 Mode parameter default values
9A 0A 00 00 FF FF FF FF FF FF FF FF
21 Log parameter format
Log Parameters
Log Parameters
Parameter Data Format
Support Log
22 Support log
ETC TMC
Buffer Overrun/Underrun
23 Buffer overrun/underrun
Write Error Count
24 Write error count
Write errors recovered with possible delays page 02, code
Write errors recovered without delays page 02, code
25 Write errors recovered without delays page 02, code
Total recoverable write errors posted to Init page 02, code
Total write errors posted page 02, code
27 Total write errors posted page 02, code
TSD ETC
Total write bytes processed page 02, code
29 Total write bytes processed page 02, code
Read errors recovered without delays page 03, code
Read Error Count
31 Read error count
32 Read errors recovered without delays page 03, code
Total read errors posted page 03, code
Read errors recovered with possible delays page 03, code
33 Read errors recovered with possible delays page 03, code
34 Total read errors posted page 03, code
36 Total read bytes processed page 03, code
Total recoverable read errors posted to Init page 03, code
Total read bytes processed page 03, code
Verify Error Count
38 Verify error count
Verify errors recovered with possible delays page 05, code
Verify errors recovered without delays page 05, code
39 Verify errors recovered without delays page 05, code
TSD ETC TMC Lbin
Total verify errors posted page 05, code
41 Total verify errors posted page 05, code
Total verify bytes processed page 05, code
43 Total verify bytes processed page 05, code
45 Non-medium error count
Non-Medium Error Count
Temperature Page X0D
46 Temperature page X0D
Reference temperature page 0D, code
Temperature page 0D, code
47 Temperature page 0D, code
48 Reference temperature page 0D, code
Date of manufacture page 0E, code
Start-Stop Cycle Counter Page X0E
49 Start-stop cycle counter page X0E
50 Date of manufacture page 0E, code
Specified cycle count over device lifetime page 0E, code
Accounting date page 0E, code
51 Accounting date page 0E, code
52 Specified cycle count over device lifetime page 0E, code
Start-stop cycle counter page 0E, code
53 Start-stop cycle counter page 0E, code
Application Client Page X0F
54 Application client page X0F
Self-test result parameter data page 10, code
Self-Test Result
56 Self-test result
57 Self-test result parameter data page 10, code
58 Self-test results values
60 Background medium scan status parameter
Background Medium Scan
59 Background medium scan
61 BMS status
63 Reassign status
62 Background medium scan parameter
MSB LBA LSB
Protocol Specific Port Log
64 Protocol specific port log page format
ETC TMC Lbin
Details of the log parameter
65 Log parameter format
Init
Log Parameters
Parameter Data Format
66 Smart status page X2F
Smart Status Page X2F
Smart Data
67 Smart data
This page is intentionally left blank
Sense Data
Sense data format
ILI
Sense Data and Error Recovery Methods
Sense data format
Sksv
Sense data basic information
Additional Sense code, Additional Sense code Qualifier
Command inherent information
Additional sense data length
Sense key inherent information
Sksv MSB
Recovered Error
Sense key
Enable Spinup
Sense Data and Error Recovery Methods
Init
Sense Data and Error Recovery Methods
Sense Data
Sense Data and Error Recovery Methods
CDB operation code
Sense data additional information
Port
Detailed information
Init Error Recovery Methods Recommended
Termination status analysis and error recovery methods
Init Error Recovery Methods Recommended
Command completion wait time-out
Sense data analysis and error recovery methods
Sense data error classification 1/3
Sense data error classification 2/3
Sense data error classification 3/3
Error recovery processing procedures 1/4
Error recovery processing procedures 2/4
Spinup
Error recovery processing procedures 3/4
Error recovery processing procedures 4/4
Error states and retry processing procedures
Disk Drive Error Recovery Processing
Error logging
Seek error
Read error in uncorrectable data
Disk Drive Error Recovery Processing
Write error
Correctable data read error
Other internal HDD errors
Auto alternate block allocation processing
Disk Drive Error Recovery Processing
Error recovery processing control
Disk drive errors and number of retries
Sense Data and Error Recovery Methods
Defect Management
Defect lists
Disk Media Management
Alternate block allocation
Defect Management
Disk Media Initialization
Initialization during installation
Issuing the Mode Select command
Re-initialization
Issuing the Format Unit command
Mode Select command
Disk Media Initialization
Format Unit command
Alternate Block Allocation Processing
Alternate Block Allocation Processing
Background Media Scan BMS
Background Media Scan BMS mode
Pre-Scan mode
Overview
∙ PER
Write command operation during a Pre-Scan
Background Media Scan BMS
Conditions for operation
Mode Page 0x1C SubPage 0x01 Background Control Mode
Mode
Background Media Scan BMS
Background Media Scan Log
Background Media Scan Log Page format
BMS Status parameter format
Medium Scan parameter format
Background Media Scan BMS
Drive Self-Test DST
Drive Self-Test DST
Foreground mode
Self-test modes
Background mode
Extended self-test
Matters that are common to both modes
Short self-test
Test segments
Disk Media Management
Drive Self-Test DST
Smart Self-Monitoring Analysis and Reporting Technology
Data analysis
Smart Self-Monitoring Analysis and Reporting Technology
ASC Ascq
Failure prediction method
Smart ASC/ASCQ
Smart Self-Monitoring Analysis and Reporting Technology
Disk Media Management
Smart thresholds
Reporting function
Additional Sense Code
Command
Common Command Set CCS
Initiator Init
This page is intentionally left blank
ALT
ACK
AEN
Arre
Acronyms and Abbreviations
Index
Command Terminated
Index
Details of parameters on Mode
Intermediate Condition
Mode Sense Extended
Persistent Reserve OUT
Reservation Conflict
Receive Diagnostic
Report Device Identifier
SET Device Identifier
TB284
READER’S Comment Form
This page is intentionally left blank
C141-C013-01EN
Page