For the HP ProCurve Series 3400cl Switches
Release Notes Version M.10.72 Software
Publication Number
Contents
Known Issues
Page
Release M.10.26
Software Fixes in Release M.08.51 M.10.72
Viii
Page
Page
Downloading Software to the Switch
Software Updates
Download Switch Documentation and Software from the Web
View or Download the Software Manual Set
Downloading Software to the Switch
T e
Tftp Download from a Server
Xmodem Download From a PC or Unix Workstation
ProCurve config# console baud-rate
Syntax copy xmodem flash primary secondary
Saving Configurations While Using the CLI
Do you want to save current configuration y/n ?
Install Recommendations for I.08.12 Boot ROM Update
Boot Rom Version Current Boot Primary
ProCurve Switch, Routing Switch, and Router Software Keys
Software ProCurve Networking Products Letter
Software Management
OS/Web/Java Compatibility Table
Minimum Software Versions for Series 3400cl Switch Features
For Switch 3400cl Hardware Accessories
Switch Management Access Security
Default Settings Affecting Security
Secure File Transfers
Local Manager Password
Inbound Telnet Access and Web Browser Access
Snmp Access Simple Network Management Protocol
Snmp-server mib hpswitchauthmib excluded
Physical Access to the Switch
Other Provisions for Management Access Security
Web and MAC Authentication
Network Access Security
Access Control Lists ACLs
Traffic/Security Filters
Secure Shell SSH
Secure Socket Layer SSLv3/TLSv1
802.1X Access Control
Port Security, MAC Lockdown, MAC Lockout, and IP Lockdown
Key Management System KMS
Identity-Driven Management IDM
Non-Genuine Mini-GBIC Detection and Protection Initiative
Publication Updates
Operating Notes for Jumbo Traffic-Handling
Igmp Command Update
General Switch Traffic Security Guideline
Igmp Operating Notes
Rate-Limiting
Management Vlan IP Address
Interoperating with 802.1s Multiple Spanning-Tree
Known Issues
Release M.10.17
Release M.08.73 Enhancements
Release M.08.69 Enhancements
Release M.08.70 through M.08.72 Enhancements
Release M.08.74 through M.08.77 Enhancements
Release M.08.78 Enhancements
Using Fastboot To Reduce Boot Time
ProCurveconfig# show fastboot Fast Boot Disabled
Release M.08.79 Enhancements
Release M.08.80 through M.08.83 Enhancements
Operating Notes
Release M.08.89 Enhancements
Release M.08.84 Enhancements
Release M.08.85 through M.08.88 Enhancements
DNS Resolver
ProCurve# Ping leader
Basic Operation
Ping accounts015 traceroute sales021
10.28.229.220 Alive, time =
ProCurve# traceroute Remote-01.common.group.net
10.22.240.73
Configuring a DNS Entry
Example Using DNS Names with Ping and Traceroute
Example Network Domain
Viewing the Current DNS Configuration
10.28.192.2 10.28.229.219
Server 10.28.229.10
IP Config IP Address Subnet Mask
Arp Age Domain Suffix Pubs.outdoors.com
Manual 10.28.192.1 255.255.255.0
Event Log Messages
Message Meaning
Changing and Viewing the Snmp Access Configuration
Security Notes
ProCurveconfig# Snmp-server mib hpswitchauthmib excluded
Snmp Communities
Mstp Default Path Cost Controls
Releases M.08.90 and M.08.91 Enhancements
QoS Pass-Through Mode
Description
Configuring QoS Pass-Through Mode
Example Showing QoS Pass-Through Mode Set Using the CLI
Displaying the Current QoS Pass-Through Mode on the Switch
Release M.08.94 Enhancements
ProCurveconfig# dhcp-relay option 82 append mgmt-vlan
Example
UDP Broadcast Forwarding
Dhcp Operation for the Topology in Figure
Release M.08.96 Enhancements
RADIUS-Assigned Access Control Lists ACLs
Releases M.08.95 through M.10.01 Enhancements
Releases M.08.97 through M.10.01 Enhancements
Release M.10.02 Enhancements
Operates on the 3400cl switches
Terminology
General Operation
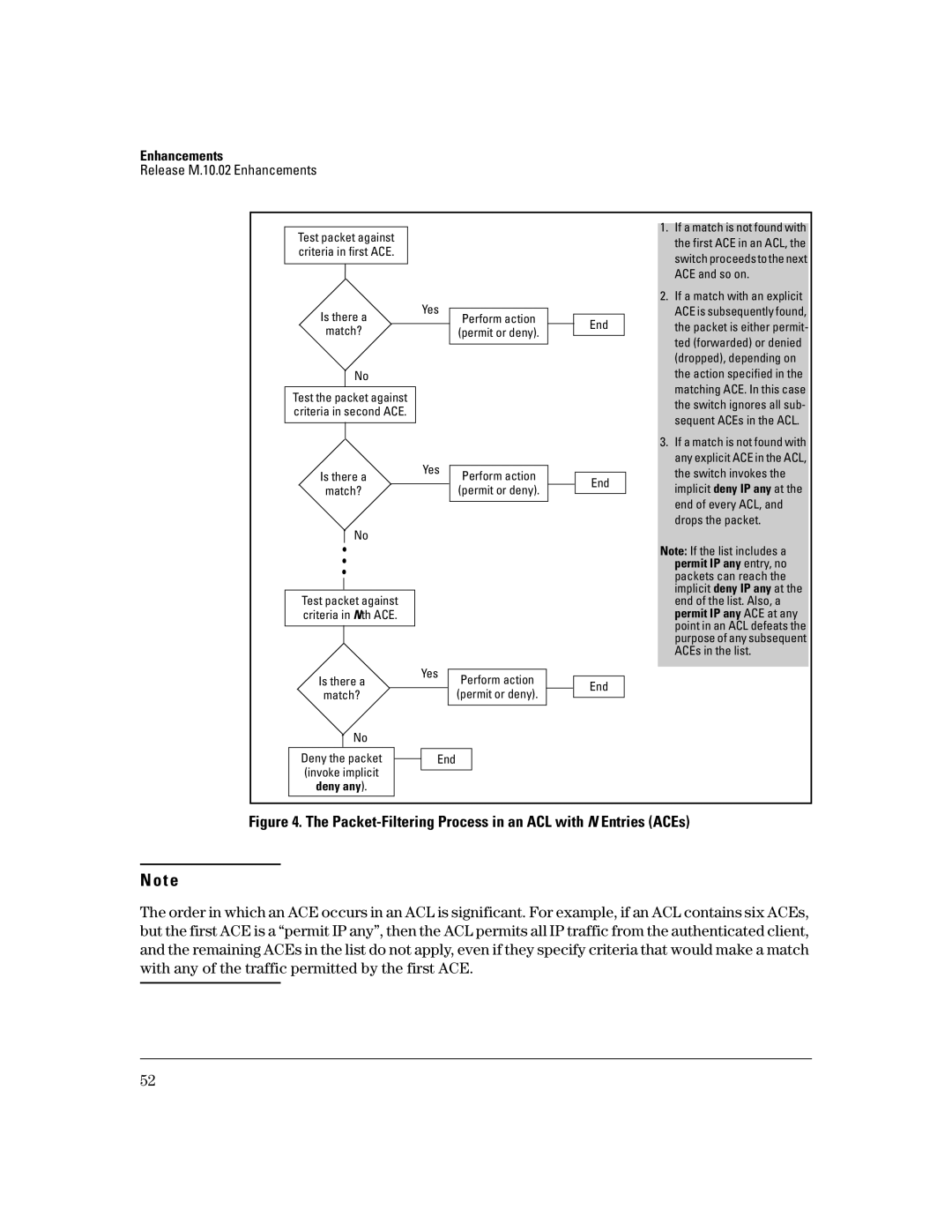
Packet-filtering Process
T e s
Example of Sequential Comparison
Packet-Filtering Process in an ACL with N Entries ACEs
Example of How a RADIUS-Based ACL Filters Packets
General Steps
Determining Traffic Policies
Planning the ACLs Needed To Enforce Traffic Policies
Guidelines for Structuring a RADIUS-Based ACL
Operating Rules for RADIUS-Based ACLs
Limits for RADIUS-Based ACLs, Associated ACEs, and Counters
Limits Affecting RADIUS-Based ACL Applications
Configuring an ACL in a Radius Server
Limit Notes
END-VENDOR
Client 10.10.10.125 nastype = other secret =
Format Details for ACEs Configured in a RADIUS-Based ACL
Deny in udp from any to any 135, 137-139
Configuring the Switch To Support RADIUS-Based ACLs
802.1X Option
MAC Authentication Option
Web Authentication Option
Port port-#, No Radius ACLs applied on this port
Syntax show port-access authenticator port-list
Event Log Messages
Port port-# , No Radius ACLs applied on this port
ACE parsing error, destination IP
ACE parsing error, tcp/udp ports
Exceeded counter per port limit
SFlow Show Commands
Viewing SFlow Configuration
Viewing sFlow Agent Information
Release M.10.04 Enhancements
Instrumentation Monitor
Ip-address-count
Known Limitations
Configuring Instrumentation Monitor
Viewing the Current Instrumentation Monitor Configuration
Examples
ProCurve# show instrumentation Monitor configuration
TCP/UDP Port Closure
Enabling/Disabling RIP
Enabling/Disabling Tftp
Enabling/Disabling Snmp
Spanning Tree Show Commands
Enabling/Disabling Stacking
Operating Notes
BPDUs Tx BPDUs Rx 256654
Release M.10.05 Enhancements
Release M.10.06 Enhancements
Release M.10.09 Enhancements
Release M.10.07 Enhancements
Release M.10.08 Enhancements
Uni-Directional Link Detection Udld
Udld Example
Configuration Considerations
Configuring Udld
ProCurveconfig# link-keepalive interval
ProCurveconfig#interface al link-keepalive
ProCurveconfig#interface al-a4 link-keepalive
ProCurveconfig# link-keepalive retries
Viewing Udld Information
Udld
ProCurve# clear link-keepalive statistics
Configuration Warnings and Event Log Messages
CLI Command Example Warning Message Possible Problem
Release M.10.10 Enhancements
Configuring STP Bpdu Filters
ProCurveconfig# spanning-tree a9 bpdu-filter
Spanning Tree Per-Port Bpdu Filtering
Viewing Status of Bpdu Filtering
Viewing Configuration of Bpdu Filtering
Bpdu
Releases M.10.14 through M.10.16 Enhancements
Releases M.10.11 through M.10.12 Enhancements
Release M.10.13 Enhancements
Release M.10.17 Enhancements
Terminology
Release M.10.17 Enhancements
Configuring STP Bpdu Protection
ProCurveconfig# spanning-tree 1-10 bpdu protection
Viewing Bpdu Protection Status
Release M.10.21 Enhancements
Configuring Loop Protection
ProCurveconfig# loop-protect port-list
Release M.10.22 Enhancements
Example of Show Loop Protect Display
Release M.10.25 Enhancements
Release M.10.23 Enhancements
Release M.10.24 Enhancements
Release M.10.26 Enhancements
Release M.10.27 Enhancements
Enhancements
Release M.10.30 Enhancements
Release M.10.28 Enhancements
Release M.10.29 Enhancements
Release M.10.31 Enhancements
Release M.10.32 Enhancements
Scheduled Reload
Vlan Assignment on a ProCurve Port
How RADIUS-Based Authentication Affects Vlan Operation
Release M.10.33 Enhancements
103
104
Example of an Active Vlan Configuration
106
107
Release M.10.34 Enhancements
Concurrent TACAS+ and Sftp
Introduction
Release M.10.35 Enhancements
Dynamic ARP Protection
ProCurveconfig# arp protect vlan
Enabling Dynamic ARP Protection
Configuring Trusted Ports
Configuring Trusted Ports for Dynamic ARP Protection
ProCurveconfig# arp protect trust b1-b4, d1
Adding an IP-to-MAC Binding to the Dhcp Database
Configuring Additional Validation Checks on ARP Packets
ProCurveconfig# arp protect validate src-mac dst-mac
Verifying the Configuration of Dynamic ARP Protection
Displaying ARP Packet Statistics
Monitoring Dynamic ARP Protection
Release M.10.36 Enhancements
Release M.10.37 Enhancements
Configuring Mstp Port Connectivity Parameters
117
Release M.10.38 Enhancements
Spanning-tree B2 priority
Enabling and Configuring Snmp Informs
Send Snmp v2c Informs
Release M.10.39 Enhancements
Community
Overview
Configuring Radius Authentication
Radius Server Unavailable
122
Specifying the MAC Address Format
SSH
ARP Age Timer Increase
Example of Setting the ARP Age Timeout to 1000 Minutes
IP Config
125
Release M.10.42 Enhancements
Release M.10.40 Enhancements
Release M.10.41 Enhancements
Release M.10.43 Enhancements
Differences Between Switch Platforms
Protection Against IP Source Address Spoofing
Prerequisite Dhcp Snooping
Filtering IP and MAC Addresses Per-Port and Per-VLAN
An Example of a Static Configuration Entry
10.0.10.1 001122-110011
Enabling Dynamic IP Lockdown
Potential Issues with Bindings
Adding an IP-to-MAC Binding to the Dhcp Binding Database
Verifying the Dynamic IP Lockdown Configuration
Adding a Static Binding
Example of show ip source-lockdown status Command Output
Displaying the Static Configuration of IP-to-MAC Bindings
Example of show ip source-lockdown bindings Command Output
Debugging Dynamic IP Lockdown
Example of debug dynamic-ip-lockdown Command Output
Release M.10.44 through M.10.64 Enhancements
Mstp Vlan Configuration Enhancement
Release M.10.65 Enhancements
ProCurveconfig# spanning-tree protocol-version mstp
Enabling Mstp on the Switch
PreConfiguring VLANs in an MST Instance
ProCurveconfig# write mem
Configuring Mstp Instances with the Vlan Range Option
ProCurveconfig# spanning-tree instance 1 vlan
Operating Notes
Configure Logging via Snmp
Release M.10.66 Enhancements
Adding a Description for a Syslog Server
Adding a Priority Description
Example of the Logging Command with a Priority Description
Release M.10.68 Enhancements
Lacp and Link Traps Global Disable
Release M.10.67 Enhancements
Release M.10.71 Enhancements
Release M.10.69 Enhancements
Release M.10.70 Enhancements
Release M.10.72 Enhancements
Release M.08.54
Release M.08.52
Release M.08.53 Never Released
Release M.08.55 Release M.08.60
Show CDP the Yes is changed to Yes,Receive Only
Release M.08.62
Problems Resolved in Release M.08.62
Problems Resolved in Release M.08.63 Not a general release
Release M.08.63
Release M.08.66
Release M.08.64
Release M.08.65
Release M.08.67
Release M.08.68
Problems Resolved in Release M.08.68 Not a general release
Problems Resolved in Release M.08.69
Release M.08.69
Problems Resolved in Release M.08.71 Never released
Problems Resolved in Release M.08.70 Not a general release
Duplicate access control entry
Release M.08.70
Release M.08.74
Release M.08.72
Release M.08.73
Release M.08.77
Release M.08.75
Release M.08.76
Release M.08.80
Release M.08.78
Release M.08.79
Release M.08.81
Release M.08.85
Release M.08.83
Release M.08.84
Release M.08.86
Release M.08.87
Problems Resolved in Release M.08.87 Not a general release
Problems Resolved in Release M.08.88 Not a general release
Release M.08.88
Release M.08.90
Problems Resolved in Release M.08.90 Not a general release
Problems Resolved in Release M.08.92 Not a general release
Release M.08.91
Release M.08.95
Release M.08.93
Release M.08.94
Release M.08.96
Release M.10.02
Release M.08.97
Release M.10.01
Release M.10.03
Release M.10.06
Release M.10.04
Release M.10.05
Release M.10.07
Problems Resolved in Release M.10.07
Problems Resolved in Release M.10.08
Release M.10.08
Release M.10.09
Problems Resolved in Release M.10.09
Problems Resolved in Release M.10.10
Release M.10.10
Release M.10.13
Release M.10.11
Release M.10.12
Release M.10.16
Release M.10.14
Release M.10.15
Release M.10.17
Problems Resolved in Release M.10.17
Problems Resolved in Release M.10.20
Release M.10.18 Release M.10.19
Release M.10.21
Problems Resolved in Release M.10.21 Not a general release
Problems Resolved in Release M.10.22 Not a general release
Release M.10.22
Release M.10.23
Problems Resolved in Release M.10.23 Never released
Problems Resolved in Release M.10.24 Never released
Release M.10.24
Release M.10.26
Problems Resolved in Release M.10.26 Not a general release
Problems Resolved in Release M.10.27 Never released
Release M.10.27
CCCCCline 10007 Error setting configuration
Problems Resolved in Release M.10.28 Not a general release
Problems Resolved in Release M.10.29 Never released
Release M.10.28
Problems Resolved in Release M.10.31
Transceiver hotswap PR1000390888 Transceiver hotswap issues
Problems Resolved in Release M.10.30
Release M.10.30
Release M.10.32
Problems Resolved in Release M.10.32
Problems Resolved in Release M.10.33
Release M.10.33
Release M.10.34
Problems Resolved in Release M.10.34
Problems Resolved in Release M.10.35
Release M.10.35
Release M.10.38
Release M.10.36
Release M.10.37
Release M.10.41
Release M.10.39
Release M.10.40
Release M.10.44
Release M.10.42
Release M.10.43
Release M.10.47
Release M.10.45
Release M.10.46
Problems Resolved in Release M.10.49 Not a Public Release
Fatal error Server unexpectedly closed connection
Problems Resolved in Release M.10.48 Not a Public Release
Release M.10.48
Problems Resolved in Release M.10.65 Not a Public Release
Software exception at ConfigTree.cc508 -- in mChassCtrl
Problems Resolved in Release M.10.50 M.10.64 Never Built
Release M.10.50 through M.10.64
Software exception at dsnoopctrl.c109 -- in mDsnoop002
Problems Resolved in Release M.10.66 Not a Public Release
Release M.10.66
Problems Resolved in Release M.10.67 Never Released
Release M.10.67
Release M.10.68
Problems Resolved in Release M.10.68
Problems Resolved in Release M.10.69 Not a Public Release
Release M.10.69
Problems Resolved in Release M.10.70 Not a Public Release
Release M.10.70
Software exception at aaa8021xproto.c255 -- in m8021xCtrl
Software exception at ldbalutil.c2525 -- in mLdBalCtrl
Release M.10.71
Problems Resolved in Release M.10.71 Not a Public Release
Problems Resolved in Release M.10.72
Release M.10.72
184
185
Message
October