Page
Page
PCL 5 Color Technical Reference Manual
Copyright License
Trademarks
Inside This Manual
What You Can Learn From This Manual
Manual Organization
Appendix C. Using Palettes Color LaserJet, 5, 5M, DeskJet
Color Vector Graphics HP-GL/2
Index
PCL 5 Comparison Guide
Related Documents
PCL 5 Printer Language Technical Reference Manual
Printer Job Language Technical Reference Manual
Contents
Modifying Output Color
Raster Graphics
Appendix B Using Color Modes Color LaserJet, 5, 5M, DeskJet
Index
Contents
Color Printing Overview
Introduction
Working with color documents
Color Specifications and Color Spaces
PCL 5 Color Concepts
Color
Page
HP’s ICC profiles are available through normal HP software
PCL 5 Color Mode
Palettes and Color Selection
PCL 5 Color Graphics Context
PCL 5 Raster Images
Pixels and Pixel Encoding
Row Plane Red
Well-Behaved Raster
Color Printing Overview
Black-and-White Mode Default
Simple Color Mode
PCL Imaging Mode
HP-GL/2 Imaging Mode
Default Range
Simple Color Mode
Simple Color Command
? *r#U
Plane CMY value =
Single Plane value =
Plane RGB value =
Index Color
PCL Imaging Mode
Configure Image Data CID Command
?*v6W b0 b1 b2 b3 b4 b5
Byte 0 Color Space
Byte Value Color Space
Byte 1 Pixel Encoding Mode
Value Pixel Encoding Restrictions Mode
Example
PEM 0 Indexed by Plane
PEM 1 Indexed by Pixel
Mode 2 Direct by Plane
Byte 2 Number of Bits per Index
R7-r0 G7-g0
Bytes 3, 4, and 5 No. of Bits for Components 1, 2,
Bits/Index Indices/Byte
HP-GL/2 Imaging Mode
Using Color Modes
Using Palettes
Page
Push/Pop Palette Command
Saving the Palette
? *p#P
Page
Palette Management by ID
Select Palette Command
?&p#S
Page
Palette Control ID
?&p#I
Palette Control
?&p#C
Page
Simple Color Palettes
Plane CMY value =
Bits/Index =
CID Color Palettes
Device RGB and sRGB Palettes
Bits/Index = 3 through
Bits/Index =
Device CMY Palettes
Bits/Index = Color
Bits/Index = 3 through
Four Pens
HP-GL/2 Palettes
Two Pens
Pen Number Color
Eight Pens
Foreground Color Command
Foreground Color
? *v#S
Color raster images
Color Component Two
Programming Color Palettes
Color Component One
? *v#A
?*v#C
Color Component Three
Assign Color Index
?*v#I
Modifying Output Color
Device Best Dither
Render Algorithm Command
Halftone Render Algorithms
? *t#J
Monochrome Print Mode Command
Monochrome Printing
?&b#M
Functionindex
Driver Configuration Command
Deviceid
Select Treatment
Treatment Command Other Color LaserJet
Screen Match
Finish Mode Command
Default =
?&b#F
PCL Print Model
PCL Print Model
Opaque and Transparency Modes
Page
Effect of Transparency Modes on Images
Command Sequence
Operation Comments
Source Transparency Mode Command
Default
? * v # N
Pattern Transparency Mode Command
? * v # O
Logical Operations
Definitions
Operators
Operands
Operation
Logical Operations and the Print Model
Logical Operations and Transparency Interactions
Logical Operation Command
?*l # O
Roprgb 252 Texture Source Destination
ROPs in the RGB Color Space
ROPs in the CMY Color Space
Using a ROP
CMY ROP Truth Tables
Example
Table of Logical Operations
Logical Operations ROP3 Boolean Input Value Function
Logical Operations ROP3 Boolean
Function Input Value
Logical Operations ROP3 Boolean
Logical Operations ROP3 Boolean
Logical Operations ROP3 Boolean
Pixel Placement
Pixel Placement
Pixel Placement Variations
Pixel Placement Command
?*l # R
Patterns for Rectangles
Filling with Patterns
Patterns for Text and Raster Images
HP-GL/2 Patterns
Pattern ID Area Fill ID Command
Selecting User-Defined patterns1
Shading Patterns
Cross-Hatch Patterns
Select Current Pattern Command
? * v # T
Using User-Defined Patterns
User-Defined Pattern Graphics
How the Printer Tiles a Pattern
10 Pattern Layout Across the Printable Area
Pattern Reference Point
11 Moving Pattern Reference Point for Pattern Filling
Download Pattern Command
Format Byte
Reserved Byte
Continuation Byte
Pixel Encoding Byte
Height in Pixels Bytes 4
User-defined Pattern Example
Page
Previous example, the raster data code is presented
Set Pattern Reference Point Command
? * p # R
Pattern Control Command
? * c # Q
Rectangular Area Fills Rules
? * c # a
Horizontal Rectangle Size PCL Units
Horizontal Rectangle Size Decipoints
? * c # H
? * c # B
Vertical Rectangle Size PCL Units
Vertical Rectangle Size Decipoints
? * c #
Fill Rectangular Area
? * c # P
Printer Language Technical Reference Manual for logical
Pattern Transparency for Rectangular Area Fill
12 Effect of Transparency Modes on Rectangular Areas
Rectangular Fill Examples
Solid Fill Black/White
13 Solid Fill Example
Shaded Fill
Page
PCL Print Model
Raster Graphics
Page
Image Type Number Bits per Components
PCL 5 Color Raster Graphics
Raster Area
Page
Raster Graphics Command Sequence
Well-Behaved Raster Command Sequence
Emphasis in the previous command sequence is that the Raster
Raster Graphics Resolution Command
? * t # R
Raster Graphics Expansion at 300 dpi
Raster Graphics Presentation Mode Command
Default = Range = 0
? * r # F
Raster Graphics Presentation Mode for Portrait Orientation
Raster Graphics Presentation Mode for Landscape Orientation
Source Raster Height Command
? * r # T
Maximum Raster Height
Source Raster Width Command
? * r # S
Maximum Raster Width
Start Raster Graphics Command
? * r # a
Page
Raster Y Offset Command
? * b # Y
Set Compression Method Command
Tagged Image File Format Encoding Method
Unencoded Method
Run-length Encoding Method
? * b # M
# of Bytes Binary value Decimal value 0000 127 0111
Examples Run-length and Tiff Compression
Unencoded
Run-length Encoding
Command byte1 to 8 Replacement bytes
Delta Row Compression Method
Tiff Encoding
Page
Seed Row
Example Delta Row Compression
Printing a Zeroed Row Setting the Seed Row to Zero
Repeating a Row
11111111
Adaptive Compression Method
Row 00001111 11111111 10101010
Value Compression Operation
Empty Row
Duplicate Row
Adaptive Compression Operation Hints
Comparison Guide for specifics
Transfer Raster Data Commands
Transfer Raster Data By Row/Block Command
Transfer Raster Data by Plane
Byte Counts and the Tiff v4.0 Compression Mode
?*b2m3W binary data
End Raster Graphics Command
? * r C
Resolution Scaling
Raster Scaling
Arbitrary Scaling
? * t # H
Destination Raster Width
Destination Raster Height
? * t #
Raster Graphics Example
Page
Page
Example of Raster Graphic Image Data
PCL Command Description Command Arguments
Color Raster Graphics Example
Raster Graphics
Raster Graphics
Color Vector Graphics HP-GL/2
Enter HP-GL/2 Mode
?%#B
Page
Default Settings when Entering HP-GL/2
Page
Default
MC Merge Control
Pixel Combinations Desired Destination Values
Page
Logical Operations ROP3 Boolean Input Value Function
Logical Operations ROP3 Boolean
Logical Operations ROP3 Boolean
Logical Operations ROP3 Boolean
Logical Operations ROP3 Boolean
Parameter Format Functional Range Default
PC Pen Color
Yellow
Shading Fill Type command FT10, the shading levels are
NP Number of Pens
Page
CR Color Range
PP Pixel Placement
Pixel Placement
PP, Pixel Placement Command
Mode Clamped integer Grid Intersection
Parameter Format Functional
Color Printing Overview Color LaserJet, 5, 5M DeskJet
Page
Palettes
Raster Mode
Color Concepts
Raster Color vs. Non-Raster Color
Device-Dependent vs. Device-Independent Color
Black and White References
Color Selection
Scenario White Reference Black Reference
Pixel Encoding
Encoding by Plane
C4 c3 c2 c1
Color Modes
Encoding by Pixel
Planar Encoding Pixel Encoding
Device-Dependent Color Spaces
Device-Independent Color Spaces
Page
Device-Independent Color
Device-Dependent Color
Device-Independent Color
Color Matching
Color Appearance Matching
Color Lookup Tables
Illumination Models
Color Raster Data
Processing Color Documents
Non-Raster Color vs. Raster Color
Marking Primitives
Color Processing Functions
Color Printing Overview Color LaserJet, 5, 5M, DeskJet
Using Color Modes Color LaserJet, 5, 5M DeskJet
Introduction
HP-GL/2 Imaging Mode
Simple Color Mode
Simple Color palettes are shown below
?*v#Wbinary data
Bits/index Bits/primary #1
Byte 15 MSB LSB Color space Ubyte Pixel encoding mode
Common 6-Byte Header
Bits/primary #2 Bits/primary #3
Byte Value Pixel Encoding Mode Restrictions
Mode 0 Indexed by Plane
Mode 1 Indexed by Pixel
Mode 2 Direct by Plane
Bytes are always 1 for this
Byte 3 Number of Bits for Primary #1
Byte 4 Number of Bits for Primary #2
Byte 5 Number of Bits for Primary #3
Short Form of CID Command Configure Image Data
Data Range Scaling
Long Form of CID Command Configure Image Data
Device RGB Long Form
Byte 15 msb Lsb
Device CMY Long Form
CIE L*a*b* Long Form
Byte 15 msb Lsb
Colorimetric RGB Long Form
Sign Exponent Fractional Portion
Byte 15 msb Lsb
Luminance-Chrominance Long Form
Byte 15 msb Lsb
Byte 15 msb Lsb
Examples Using the CID Command
Device RGB or Device CMY
CIE L*a*b
Non-Linear Smpte RGB, 2.2 Gamma, 1.0 Gain
Non-Linear Sony Trinitron
YUV Chrominance-Luminance Color Space
YUV Chrominance-Luminance with Sony Trinitron
HP-GL/2 Imaging Mode
Using Palettes Color LaserJet, 5, 5M DeskJet
Page
Saving the Palette
Page
Palette Management by ID
Select Palette Command
Page
Palette Control ID
Palette Control
Page
Using Palettes Color LaserJet, 5, 5M, DeskJet C-11
Plane CMY value =
Device RGB Palettes
Bits/Index = 3 through
Device CMY and Device-Independent Palettes
HP-GL/2 Palettes
Using Palettes Color LaserJet, 5, 5M, DeskJet C-17
Foreground Color Command
?*v#S
Color raster images
?*v#A
Color Component One
Color Component Two
?*v#B
Color Component Three
Assign Color Index
Using Palettes Color LaserJet, 5, 5M, DeskJet
Modifying Output Color Color LaserJet, 5, 5M DeskJet
Page
?*t#J
Error Diffusion
Snap to Primaries
Snap Black to White, Colors to Black
Ordered Dither and Clustered Ordered Dither
Monochrome Rendering
User-Defined Dithering
User-Defined Dithers
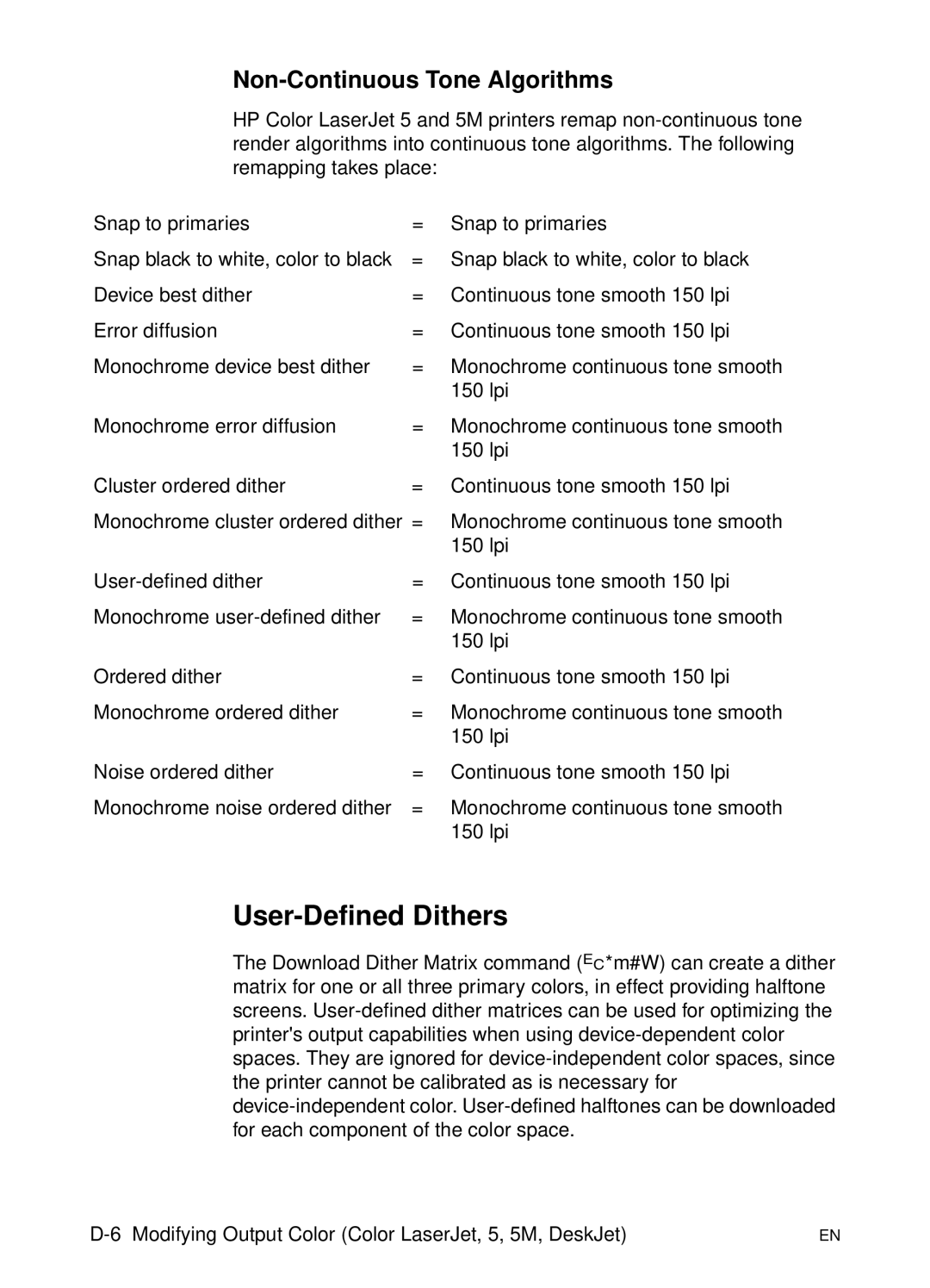
Non-Continuous Tone Algorithms
Download Dither Matrix Command
Byte 15 msb Lsb
Height and Width
Format
Number of Planes
Data Bytes
Multiple Dither Matrices
Example
Byte 15 msb Lsb
Color Lookup Tables Command
Color Lookup Tables
Figure D-1 Color Lookup Tables
Byte 15 msb Lsb
Value Color Space
Gamma Correction Command
Gamma Correction
?*t#I
Viewing Illuminant Command
Viewing Illuminant
Illuminant Chromaticity
Monochrome Print Mode Command
Value Printer Color LaserJet printer
Function Description Argument Range Index
Lightness
Saturation
Scaling
Transparency
No Adjustment
Process Blue
Out of Gamut
Setting Description MapID Device Dependent
Download Color Map
Setting Description MapID
Setting Description MapID Device-Independent
Index
Index-2
Index-3
Index-4
Index-5
Index-6