MX240 Ethernet Services Router Hardware Guide
Midplane
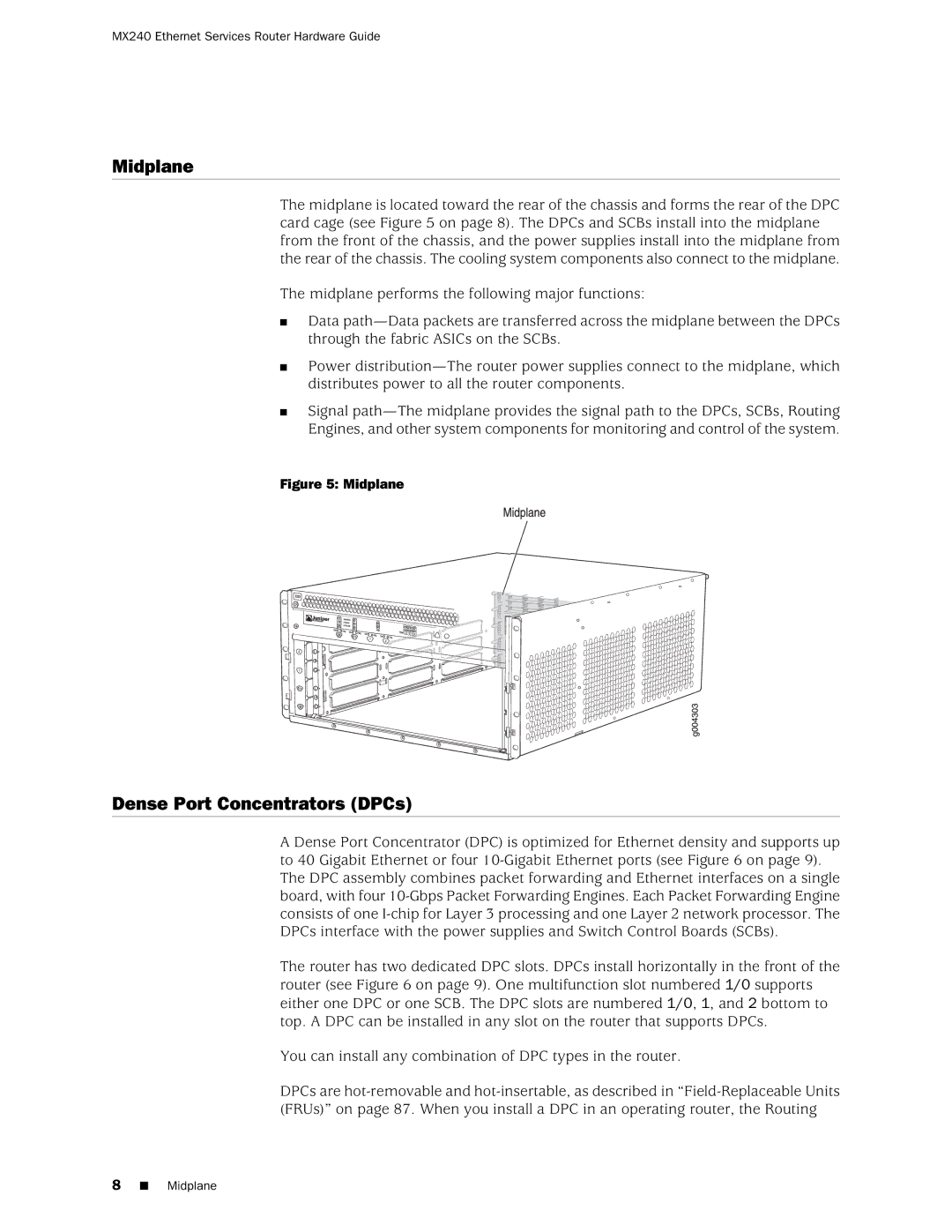
The midplane is located toward the rear of the chassis and forms the rear of the DPC card cage (see Figure 5 on page 8). The DPCs and SCBs install into the midplane from the front of the chassis, and the power supplies install into the midplane from the rear of the chassis. The cooling system components also connect to the midplane.
The midplane performs the following major functions:
■Data
■Power
■Signal
Figure 5: Midplane
Dense Port Concentrators (DPCs)
A Dense Port Concentrator (DPC) is optimized for Ethernet density and supports up to 40 Gigabit Ethernet or four
The router has two dedicated DPC slots. DPCs install horizontally in the front of the router (see Figure 6 on page 9). One multifunction slot numbered 1/0 supports either one DPC or one SCB. The DPC slots are numbered 1/0, 1, and 2 bottom to top. A DPC can be installed in any slot on the router that supports DPCs.
You can install any combination of DPC types in the router.
DPCs are
8 ■ Midplane