Cross-Site Scripting Filter
You could do everything right with respect to security—such as always installing the latest security updates—yet still remain vulnerable to some types of security threats. For example, cross-site scripting attacks are a leading threat against Web sites and can be used to steal cookies or other data, deface pages, steal credentials, or launch more exotic attacks. Cross-scripting is not a browser vulnerability in itself, but Internet Explorer 8 includes a Cross-Site Scripting filter that runs silently in the background to help detect type-1 cross-site scripting attacks. If an attack is detected, the filter sanitizes the script to prevent it from doing harm.
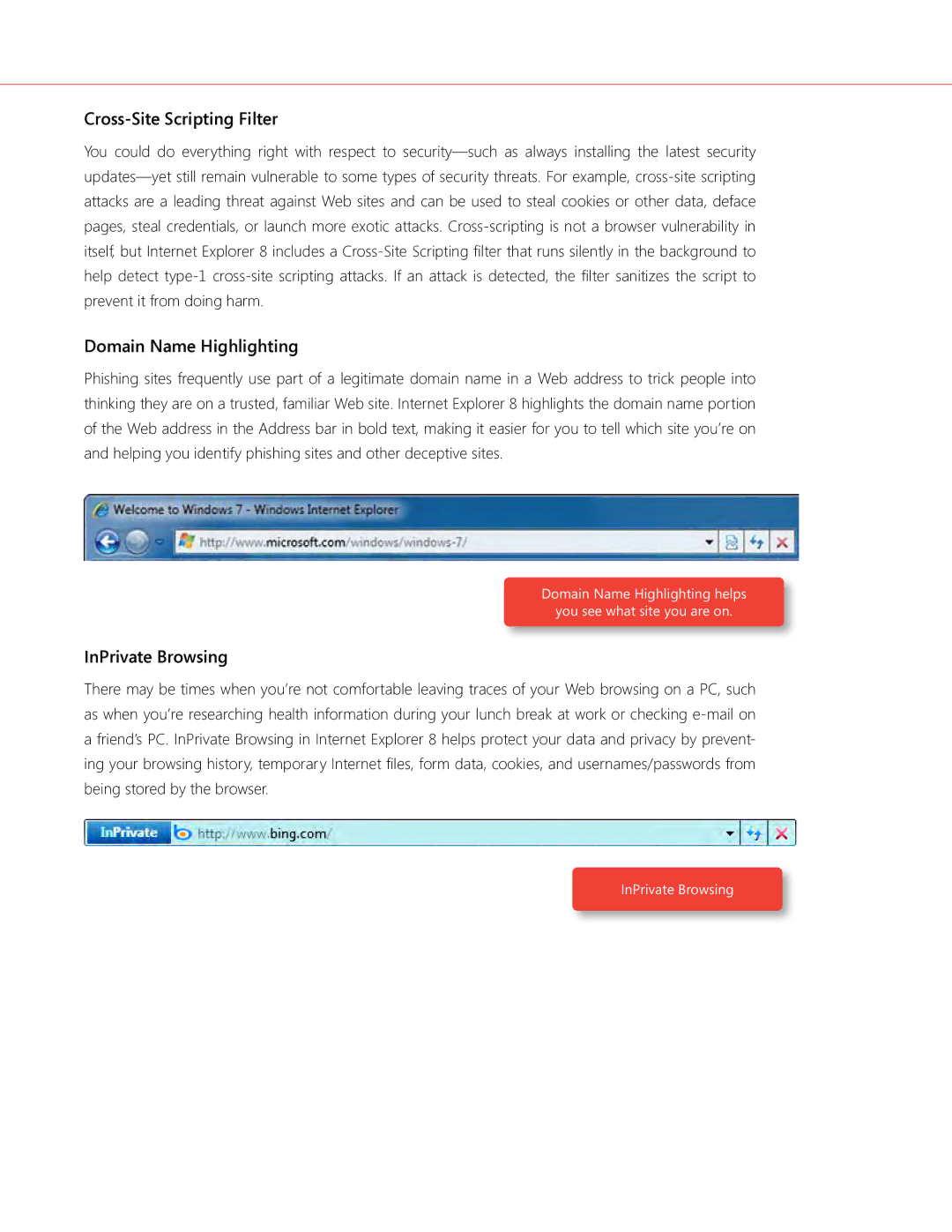
Domain Name Highlighting
Phishing sites frequently use part of a legitimate domain name in a Web address to trick people into thinking they are on a trusted, familiar Web site. Internet Explorer 8 highlights the domain name portion of the Web address in the Address bar in bold text, making it easier for you to tell which site you’re on and helping you identify phishing sites and other deceptive sites.
Domain Name Highlighting helps
you see what site you are on.
InPrivate Browsing
There may be times when you’re not comfortable leaving traces of your Web browsing on a PC, such as when you’re researching health information during your lunch break at work or checking e-mail on a friend’s PC. InPrivate Browsing in Internet Explorer 8 helps protect your data and privacy by prevent- ing your browsing history, temporary Internet files, form data, cookies, and usernames/passwords from being stored by the browser.
InPrivate Browsing