National Semiconductor Corporation
Block Diagram
General Description
MAY
Table of Contents
Features
Device Overview
Advanced Audio Interface
Bluetooth LLC
Can Interface
Quad Uart
Versatile Timer Unit
MICROWIRE/SPI
ACCESS.BUS Interface
MULTI-FUNCTION Timer
Development Support
Power Management
DMA Controller
Serial Debug Interface
LQFP-144
Signal Descriptions
CP3BT26
LQFP-128
X1CKO
Reset
X1CKI
Bbclk
Name Pins Primary Function Alternate Alternate Function
PG6
PG4
Sdat
PG5
X1CKI
CTS PE4
Selio
WR0
WR1
SLE
CPU Architecture
GENERAL-PURPOSE Registers
Dedicated Address Registers
No carry or borrow occurred Carry or borrow occurred
Processor Status Register PSR
Interrupt Base Register Intbase
12 11 Reserved
Is held in the Intbase register, which is not
Configuration Register CFG
When the IDT has 16-bit entries, and all ex
Mode for the CR16B large model.
Addressing Modes
Addb R1, R2
Loadw 12R5, R6
Instruction SET
Stacks
Instruction Set Summary Mnemonic Operands Description
LPR
Ashud
Lshd
Tbit
Popret
Retx
Push
POP
Wait
Stormp
Eiwait
NOP
Memory
Operating Environment
IN/A
Empty
BUS Interface Unit BIU
BUS Cycles
BIU Control Registers
Static Zone 0 Configuration Register SZCFG0
2 I/O Zone Configuration Register Iocfg
Static Zone 1 Configuration Register SZCFG1
Static Zone 2 Configuration Register SZCFG2
WBR RBE Hold Wait Ipst
RAM Memory
Access to Peripherals
Wait and Hold States
Flash Program/Data Memory
System Configuration Registers
Module Configuration Register Mcfg
System Configuration Registers Name Address Description
Module Status Register Mstat
Software Reset Register Swreset
Flash Memory
Flash Memory Protection
Flash Memory Organization
Flash Memory Operations
Main Block Write
Main Block Page Erase
Main Block Module Erase
Information Block Module Erase
Boot
Information Block Words
Area
Empty Ispe
CPU Reset Behavior
Boot Area Start-Up Operation
Flash Memory Interface Registers
FMIBDR/FSMIBDR
Flash Memory 0 Write Enable Register FM0WER/FSM0WER
Flash Memory 1 Write Enable Register FM1WER
Flash Memory Information Block Data Register
Flash Data Memory 0 Write Enable Register FSM0WER
Flash Memory Control Register Fmctrl
Fsmctrl
Fsmstat
Fsmpsr
FMSTART/FSMSTART
Flash Memory End Time Reload Register FMEND/FSMEND
FMRCV/FSMRCV FSMAR1
Flash Memory Auto-Read Register 0 FMAR0/ FSMAR0
Flash Memory Auto-Read Register 2 FMAR2/ FSMAR2
DMA Channel Assignment Peripheral Trans Register Action
DMA Controller
Channel Assignment
Transfer Types
Operation Modes
Debug Mode
Software DMA Request
DMA Controller Register SET
Device B Address Register ADRBn
Device a Address Counter Register ADCAn
Device a Address Register ADRAn
Device B Address Counter Register ADCBn
DMA Control Register DMACNTLn
Block Length Register BLTRn
DMA Status Register Dmastat
VLD Chac OVR
VLD
Interrupt Controller Registers
Interrupts
NON-MASKABLE Interrupts
Maskable Interrupts
Interrupt Vector Register Ivct
External NMI Trap Control and Status Register Exnmi
Non-Maskable Interrupt Status Register Nmistat
Interrupt Status Register 2 ISTAT2
Interrupt Enable and Mask Register 1 IENAM1
Interrupt Enable and Mask Register 2 IENAM2
Interrupt Status Register 1 ISTAT1
IRQ Number Description
Maskable Interrupt Sources
Nested Interrupts
Maskable Interrupts Assignment IRQ Number Description
Triple Clock and Reset Module
Triple Clock and Reset
Capacitor C1, C2 Capacitance
External Crystal Network
Crystal Resonance Frequency
Type
Min. Q factor
Main Clock
Slow Clock
PLL Clock
System Clock
POWER-ON Reset
External Reset
Clock and Reset Registers
MODE20
Module Activity Summary Power Mode Clock
Power Management
Active Mode
Power Save Mode
Power Management Control Register Pmmcr
Idle Mode Power Management Registers
Halt Mode
Power Management Registers Name Address Description
DHC
Hccm
Hcch
Active Mode to Power Save Mode
OHC OMC OLC
OHC
Wake-Up Transition to Active Mode
Entering Idle Mode
Entering Halt Mode
Software-Controlled Transition to Active Mode
Multi-Input Wake-Up
Multi-Input Wake-Up Module Block Diagram
Multi-Input Wake-Up Registers Name Address Description
MULTI-INPUT WAKE-UP Registers
Miwu Sources
Miwu Channel
Wake-Up 1 Edge Detection Register WK1EDG
Wake-Up Interrupt Enable Register WK0IENA
Wake-Up 1 Interrupt Enable Register WK1IENA
Wake-Up Enable Register WK0ENA
WK1ICTL1 WK1ICTL2
Wake-Up Interrupt Control Register
WK0ICTL1 WK0ICTL2
Wake-Up 1 Interrupt Control Register
Wake-Up 1 Pending Clear Register WK1PCL
Wake-Up Pending Register WK0PND
Wake-Up Pending Clear Register WK0PCL
Wake-Up 1 Pending Register WK1PND
Programming Procedures
Port Registers
Input/Output Ports
Address Description
Port Registers
Port Direction Register PxDIR
Port Alternate Function Register PxALT
Port Data Input Register PxDIN
Port Data Output Register PxDOUT
Port Pin PxALTS =
Port High Drive Strength Register PxHDRV
Port Alternate Function Select Register PxALTS
Alternate Function Select
OPEN-DRAIN Operation
Rfdata
Bluetooth Controller
RF Interface
X1CKI/BBCLK
Sdat
Serial Interface
Rfce
Sclk
Serial Interface Write Timing Read Operation
Write Operation
First part of read cycle driven by CP3BT26. Address is 0Ah
Bit, and register address for a read cycle. In the second
15.4 LMX5252 POWER-UP Sequence
15.3 LMX5251 POWER-UP Sequence
Bluetooth Sleep Mode
Bluetooth Global Registers
Bluetooth Sequencer RAM
Bluetooth Shared Data RAM
16.0 12-Bit Analog to Digital Converter
Functional Description
Data Path
Pen-Down Detector
Operation
ADC Clock Generation
ADC Voltage References
Touchscreen Interface
Touchscreen Driver Configuration
RYP
Measuring Pen Force
RX2
RY2
ADC Registers Name Address Description
ADC Operation in POWER-SAVING Modes
Freeze
ADC Register SET
Touchcfg ADC0/TSX+ ADC1/TSY+ ADC2/TSX ADC3/TSY
Muxcfg
Prefcfg
Nrefcfg
Clkdiv
ADC Start Conversion Delay Register Adcscdly
ADC Conversion Control Register Adccntrl
ADC Start Conversion Register Adcstart
Sign
ADC Result Register Adcreslt
Adcresult
Adcoflw
Random Number Generator RNG
RNG Module Block Diagram
Random Number Generator Register SET
Functional States
USB Controller
TX Fifo RX Fifo
Endpoint Operation
Transmit Endpoint Fifo Operation TXFIFO1, TXFIFO2, TXFIFO3
Bidirectional Control Endpoint FIFO0 Operation
USB Controller Registers
Receive Endpoint Fifo Operation RXFIFO1, RXFIFO2, RXFIFO3
USB Controller Registers Name Address Description
Main Control Register Mcntrl
NFS
Node Functional State Register Nfsr
NFS
USB Functional States
Main Event Register Maev
Main Mask Register Mamsk
Alternate Event Register Altev
Alternate Mask Register Altmsk
Transmit Event Register Txev
Transmit Mask Register Txmsk
Receive Event Register Rxev NAK Event Register Nakev
Receive Mask Register Rxmsk
NAK Mask Register Nakmsk
Fifo Warning Event Register Fwev
Frame Number High Byte Register FNH
Fifo Warning Mask Register Fwmsk
Dsrc
DMA Event Register Dmaev
DMA Count Register Dmacnt
DMA Error Register Dmaerr
DMA Mask Register Dmamsk
Mirror Register MIR
Transmit Command 0 Register TXC0
Endpoint Control 0 Register EPC0
Transmit Status 0 Register TXS0
Receive Command 0 Register RXC0
Transmit Data 0 Register TXD0
Receive Status 0 Register RXS0
Receive Data 0 Register RXD0
Endpoint Control Register n EPCn
Transmit Status Register n TXSn
RFF
Transmit Command Register n TXCn
Tfwl
Last
Bytes Remaining in Fifo
Transmit Fifo Warning Limit
Receive Status Register n RXSn
Tfwl
Rfwl
Receive Command Register n RXCn Receive Data Register n RXD
Transceiver Interface
Receive Fifo Warning Limit
Can Module
Basic can Concepts
Can Block Diagram
Arbitration Field
Can Frame Types
Can Frame Fields
Start of Frame SOF
ACK Field
Data Length Code DLC
Data Field
Cyclic Redundancy Check CRC
Remote Frame
Data Field
Cyclic Redundancy Check Field CRC
Error Frame Overload Frame
Error Frame
Acknowledgment Error
Stuff Error
Form Error
Bit CRC Error
Error Counters
Error Active
Error Warning
Error Passive
Bit Timing
Bit Time Logic
Can Bit Time
Synchronization
CKI
Message Transfer
From the can bus Gmask and BMASK. shows
Acceptance Filtering
Example 1 Acceptance of a Single Identifier
Two 32-bit masks are used to filter unwanted messages
120
Receive Structure
Rxbusy
Receive Procedure
Receive Timing
Writing to Buffer Status Code During
122
Buffer Read Routine Bufflock Enabled
Transmit Structure
Transmit Scheduling
Transmit Priority
PRI
Txpri
TX Buffer States
Interrupts
IRQ IST3 IST2 IST1 IST0
Time Stamp Counter
Message Buffer Map Address Register
CPU Access to can Registers/Memory
Memory Organization
Message Buffer Organization
Can Controller Registers
Can Controller Registers Name Address Description
Buffer Status/Control Register Cnstat
Buffer Status Section of the Cnstat Register
ST3 DIR ST2 ST1 ST0 Busy
Buffer Status
Standard Frame with 8 Data Bytes Address Buffer Register
Data Length Coding
DLC
Storage of Standard Messages
Extended Messages with 8 Data Bytes Address Buffer Register
Cnstat DLC
PRI SRR
Extended Remote Frame Address Buffer Register
Frame is received, the contents of these registers will be
Contents of these registers are ignored. If a remote
Storage of Remote Messages
Can Global Configuration Register Cgcr
Dress, as shown in Figure
Listen Only bit can be used to configure
When the Ignore Acknowledge bit is set,
When the Loopback bit is set, all messages
SJW
Xrtr
TSEG1
TSEG2
RTR IDE
BM170
Can Interrupt Enable Register Cien
Basic Mask Register BMSKB/BMSKX
Basic Mask BM2818
IRQ
EFID30
Can Error Counter Register Canec
Can Error Diagnostic Register Cediag
Error Field Identifier
External Connection
Can Timer Register Ctmr
External can Pins Signal Name Type Description
System START-UP and MULTI-INPUT WAKE-UP
Remote Frames
Minimum Clock Frequency Requirements Baud Rate
Bit Time Logic Calculation Examples
Acceptance Filter Considerations
Usage Hint
Audio Interface Signals
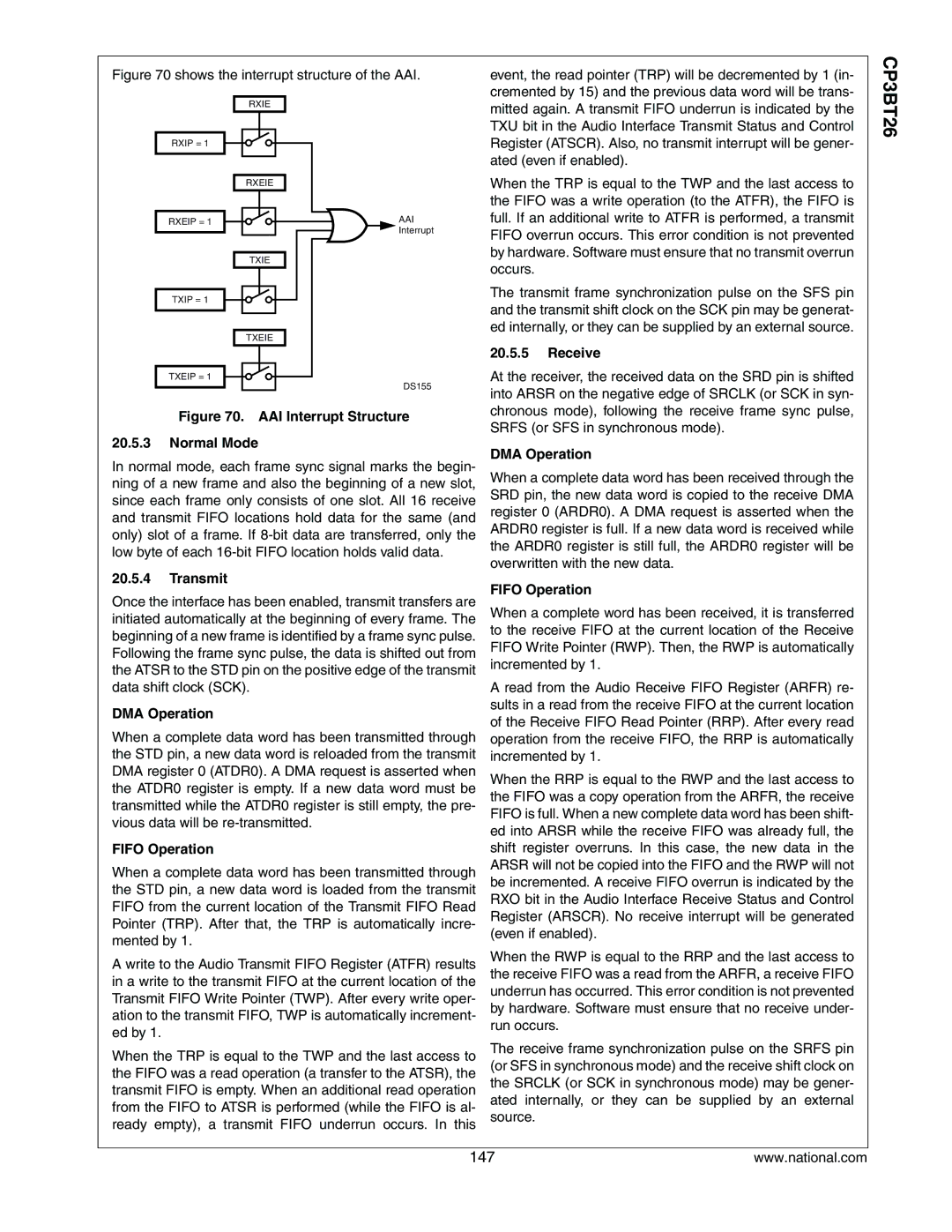
Advanced Audio Interface
Audio Interface Modes
Synchronous Mode
Normal Mode
DMA Support
145
Audio Interface Operation
Clock Configuration
Frame Clock Generation
BIT Clock Generation
Receive
Transmit
DMA Operation
Fifo Operation
Frame Sync Signal
Communication Options
Data Word Length
Short and Long Frame Sync Pulses
Audio Control Data
IOM-2 Mode
Loopback Mode
150
Freeze Mode
Audio Interface Registers
Audio Interface Registers Name Address Description
Audio Transmit DMA Register n ATDRn
Audio Receive Fifo Register Arfr
Audio Transmit Fifo Register Atfr
Audio Receive DMA Register n ARDRn
FSL
Audio Global Configuration Register Agcr
Slots per Mode Frame
SCS
Txeip
Audio Interrupt Status and Control Register Aiscr
Txeip Txip Rxeip Rxip Txeie Txie Rxeie Rxie
Txeic Txic Rxeic Rxic Rxie
Rxsa Bit Slots Enabled
Rxdsa Bit Slots Enabled For DMA
Audio Receive Status and Control Register Arscr
Txsa Bit Slots Enabled
Txdsa Bit Slots Enabled For DMA
Audio Transmit Status and Control Register Atscr
DMA Request Condition
Audio Clock Control Register Accr
Audio DMA Control Register Admacr
RMD
CVSD/PCM Conversion Module
Operation
PCM Conversions
Interrupt Generation
Cvsd Conversion
PCM to Cvsd Conversion
Cvsd to PCM Conversion
CVSD/PCM Converter Registers
Linearout
Cvsd Status Register Cvstat
Uart Modules
Functional Overview
Uart Operation
Uart Asynchronous Communication
Uart Block Diagram
Frame Format Selection
Diagnostic Mode
Prescaler Factor
Prescaler Factors
Parity Generation and Detection
Break Generation and Detection
Uart Registers Name Address Description
Uart Registers
Uart Frame Select Register UnFRS
Uart Baud Rate Divisor UnBAUD
Uart Receive Data Buffer UnRBUF
Uart Transmit Data Buffer UnTBUF
Uart Status Register UnSTAT
Uart Mode Select Register 1 UnMDSL1
Oversampling Rate
Uart Interrupt Control Register UnICTRL
Uart Oversample Rate Register UnOVR
UOVSR30
Oversampling Rate Sample Position
Uart Mode Select Register 2 UnMDSL2
Baud Rate Calculations
Uart Sample Position Register UnSPOS
173
174
Shifting
Microwire/SPI Interface
Microwire Operation
Microwire Interface
Clocking Modes
Writing
Normal Mode Scidl =
Master Mode
Slave Mode
Microwire Interrupt Trigger Condition Status Enable Bit
MWCTRL1
Mwen
Microwire Interface Registers
OVR RBF BSY
Microwire Status Register Mwstat
SCM
Scdv
Start and Stop
ACCESS.bus Interface
ACB Protocol Overview
Data Transactions
Acknowledge Cycle
Addressing Transfer Formats
Arbitration on the Bus
ACB Functional Description
Slave Error Detections
Master Error Detections
Bus Idle Error Recovery
Slave Mode
ACCESS.BUS Interface Registers
ACB Control Status Register Acbcst
Stop
Tgscl
ACB Control Register 1 ACBCTL1
Start
ACB Control Register 3 ACBCTL3
ACB Control Register 2 ACBCTL2
Saen
Usage Hints
ACB Own Address Register 1 ACBADDR1
Saen Addr
190
Avoiding Bus Error During Write Transaction
191
Timer T0 Operation
Timing and Watchdog Module
TWM Structure
Register Locking
Power Save Mode Operation
Watchdog Operation
TWM Registers
T0IN
Mdiv
Watchdog Count Register Wdcnt
Watchdog Programming Procedure
Watchdog Service Data Match Register Wdsdm
TWMT0 Control and Status Register T0CSR
196
Multi-Function Timer
Timer Structure
Clock Source Block
Counter Clock Source Select
Timer Operating Modes
Pulse Accumulate Mode
Limitations in Low-Power Modes
198
Mode 1 Processor-Independent PWM
Dual-Input Capture Mode
Mode 2 Dual Input Capture
200
Mode 3 Dual Independent Timer/Counter
Input Capture Plus Timer Mode
Mode 4 Input Capture Plus Timer
Tben
Timer Interrupts
Timer I/O Functions
Taen
Timer Registers
Timer Mode Control Register Tctrl
Reload/Capture a Register Tcra
Reload/Capture B Register Tcrb
Timer Interrupt Clear Register Ticlr
Timer Interrupt Control Register Tictl
Versatile Timer Unit VTU
VTU Functional Description
206
VTU PWM Generation
Dual 8-bit PWM Mode
208
VTU 16-bit PWM Mode Dual 16-Bit Capture Mode
ISE Mode operation
VTU Dual 16-bit Capture Mode Low Power Mode
Mode Control Register Mode
VTU Registers
VTU Registers Name Address Description
Interrupt Control Register Intctl
CxEDG Capture Counter Reset
Clock Prescaler Register 1 CLK1PS
Interrupt Pending Register Intpnd
Clock Prescaler Register 2 CLK2PS
Period/Capture Register n PERCAPx
Counter Register n COUNTx
CNTx
Duty Cycle/Capture Register n DTYCAPx
Register Map
Bluetooth LLC Registers
USB Node Registers
Register Name Size Address Access Value After Comments Type
EPC4
EPC1
TXC1
EPC2
Can Module Message Buffers
DMA Controller
Can Registers
Bus Interface Unit
System Configuration
Flash Program Memory Interface
Flash Data Memory Interface
CVSD/PCM Converter
Triple Clock + Reset
General-Purpose I/O Ports
Multi-Input Wake-Up
Comments Type
Register Name Size Address
Interrupt Control Unit
Advanced Audio Interface
UART1
UART0
UART3
UART2
ACCESS.bus
Multi-Function Timer
Timing and Watchdog
ADC
Versatile Timer Unit
Word FF F284h
RNG
Rngcst
Rngd
Register Bit Fields
USB
Fwmsk RXWARN31
Setup Toggle Rxlast Rcount RXC0
IGN Ignout Rxen Setup EPC1
Nakev OUT Nakmsk Fwev RXWARN31
Control Status
Can
Dmac
Memory Registers
Flash
System Configuration Registers
BIU
TBI Register
Flash Data Memory
CLK3RES
CVSD/PCM
AAI
PMM Register
MIWU16
Gpio Registers
Uart
ICU Registers
MWSPI16
ACB Registers
MFT16
VTU
Rngdivh
Rngcst
Imsk
Rngd
TBD
Electrical Characteristics
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Max Units
Absolute Maximum Ratings
IOOff
DNL
Symbol Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Units
INL
LSB
Flash Memory ON-CHIP Programming
TRI-STATE
Output Signal Levels
Clock and Reset Timing
Reset and NMI Input Signals
Clock Timing
NMI Signal Timing
Uart Timing
Uart Output Signals
30.9 I/O Port Timing
Port Output Signals
Advanced Audio Interface AAI Timing
AAI Output Signals
Receive Timing, Long Frame Sync
Transmit Timing, Short Frame Sync
Microwire/SPI Output Signals
MICROWIRE/SPI Timing
Microwire/SPI Signals Symbol Description Reference Min ns
Microwire/SPI Input Signals
254
Normal Mode After FE on
Microwire Data Out Valid
Alternate Mode After RE On MSK Propagation Time
255
256
Microwire Transaction Timing, Alternate Mode, Scidl =
257
ACCESS.bus Output Signals
ACCESS.BUS Timing
259
260
ACB Data Timing
MULTI-FUNCTION Timer MFT Timing
USB Port AC Characteristics
262
Versatile Timing Unit VTU Timing
TIOx Input High Time Rising Edge RE on CLK
TIOx Input Low Time RE on CLK
External BUS Timing
External Bus Output Signals
264
Early Write Between Normal Read Cycles No Wait States
265
266
Consecutive Normal Read Cycles Burst, No Wait States
267
268
Early Write Between Fast Read Cycles
X1CKO X1CKI
Pin Assignments
LQFP-128 Package
PWR
SDA ADC0 TSX+
Reset TMS
Avcc PWR Adgnd Advcc Uvcc
X2CKI X2CKO ENV2
PF1 MDIDO/TIO2
PE0 RXD0 Gpio PE1 TXD0 PE2 RTS PE3 CTS PE4 CKX/TB PE5
SRFS/NMI
PF0 MSK/TIO1
272
LQFP-144 Package
ADC7 Adcin
SCL SDA ADC0 TSX+
ADC4 MUXOUT0
ADC5 MUXOUT1
Pin Name Alternate Functions Pin Number Type
A10
A22 A21 A20 A19 A18 A17 A16 A15 A14 A13
A12
A11
Revision History
Revision History
Date Major Changes From Previous Version
LQFP-128 Package LQFP-144 Package
Physical Dimensions millimeters unless otherwise noted
Form when properly used in accordance with instructions
Life Support Policy
Banned Substance Compliance