Using Filters for Security Purposes
Example 2: Blocking Access to Specific Stations
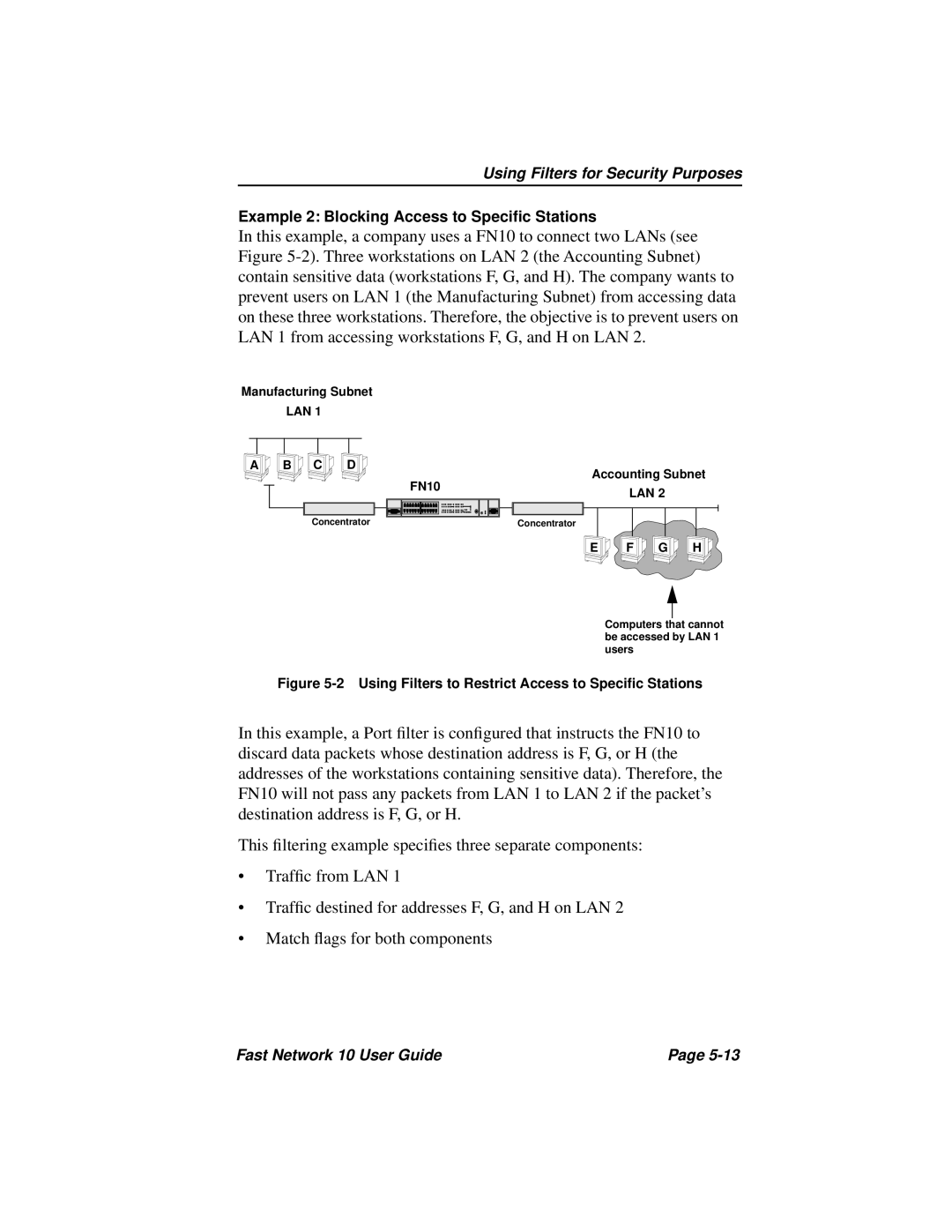
In this example, a company uses a FN10 to connect two LANs (see Figure
Manufacturing Subnet
LAN 1 |
|
|
A B C D | Accounting Subnet | |
| ||
| FN10 | LAN 2 |
|
| |
Concentrator | Concentrator |
|
| E | F G H |
Computers that cannot be accessed by LAN 1 users
Figure 5-2 Using Filters to Restrict Access to Specific Stations
In this example, a Port filter is configured that instructs the FN10 to discard data packets whose destination address is F, G, or H (the addresses of the workstations containing sensitive data). Therefore, the FN10 will not pass any packets from LAN 1 to LAN 2 if the packet’s destination address is F, G, or H.
This filtering example specifies three separate components:
•Traffic from LAN 1
•Traffic destined for addresses F, G, and H on LAN 2
•Match flags for both components
Fast Network 10 User Guide | Page |