GE Fanuc Automation
Cimplicity 90-ADS
Cimplicity
Promacro
Cimstar
Preface
Preface
Related Publications
We Welcome Your Comments and Suggestions
Page
Contents
Contents
O Fault Table Explanations
Section Math Functions
Bit Operation Functions
Table Functions
Control Functions 107
137
Appendix a Instruction Timing
180
173
Table B-7
Introduction
Page
System Operation
PLC Sweep Summary
Standard Program Sweep
PLC Sweep
Sweep Description Time Contribution ms Element
Calculate sweep time
GCM
Sweep Time Calculation
Input Scan
Application Program Logic Scan or Solution
Programmer Communications Window
Output Scan
Programmer Communications Window Flow Chart
System Communications Window Models 331 and Higher
System Communications Window Flow Chart
PCM Communications with the PLC Models 331 and Higher
PCM Communications with the PLC
Constant Sweep Time Mode
Standard Program Sweep Variations
Page
OFF/STOP
ON/RUN
YES
Program Organization and User References/Data
Subroutine Blocks Series 90-30 PLC only
GFK-0467K System Operation
Examples of Using Subroutine Blocks
How Blocks Are Called
User References
Type Description
Transitions and Overrides
Retentiveness of Data
Page
Byte
Data Types
Type Name Description Data Format
Real
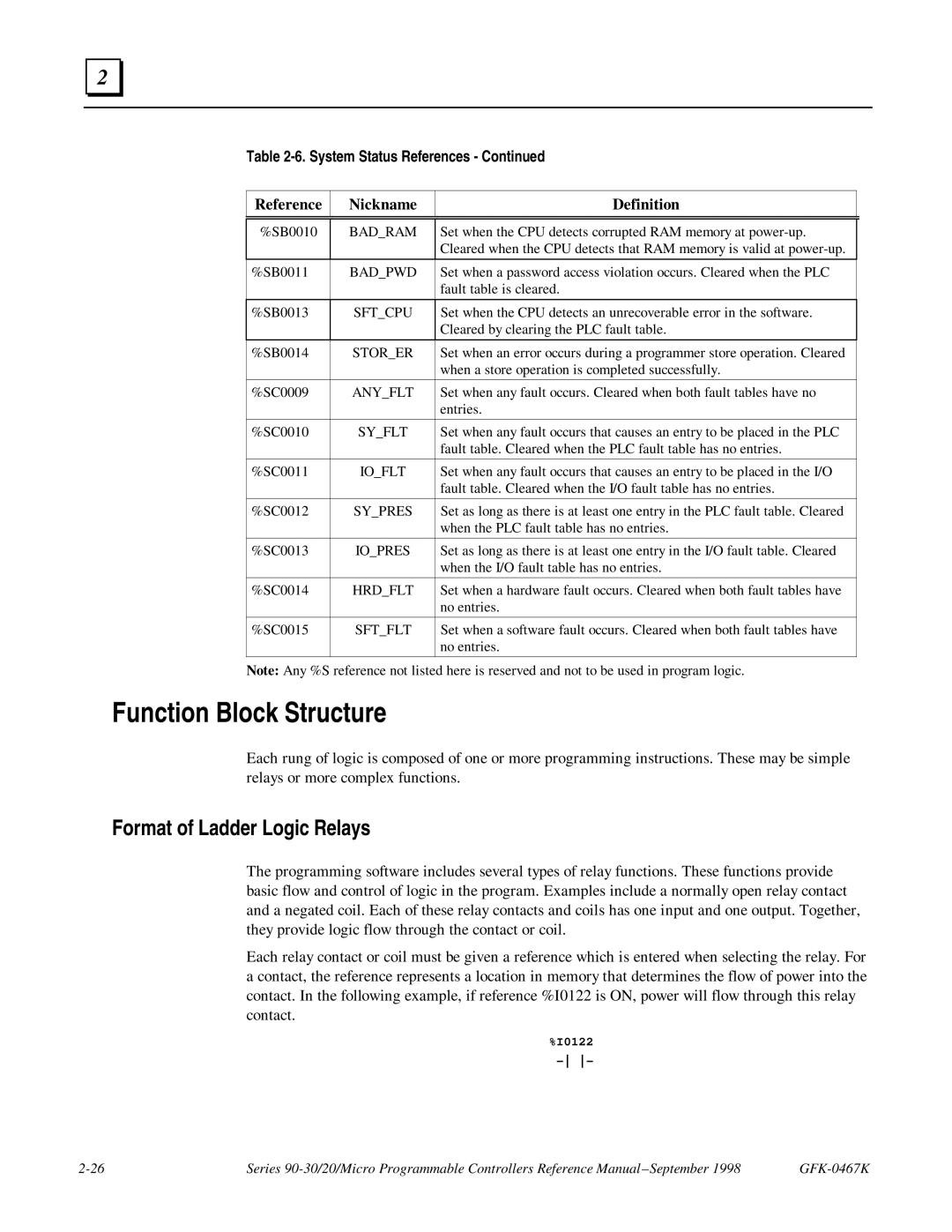
System Status References
Reference Nickname Definition
Reference Name Definition
Function Block Structure
Format of Program Function Blocks
Function Block Parameters
MUL
Power Flow In and Out of a Function
Power-Up and Power-Down Sequences
Power-Up
Power-Up Sequence
Flow Chart Terms
Power-Down
Elapsed Time Clock
Clocks and Timers
Time-of-Day Clock
Constant Sweep Timer
Watchdog Timer
Time-Tick Contacts
System Security
Passwords
Privilege Level Description
Locking/Unlocking Subroutines
Privilege Level Change Requests
Type of Lock Description
Series 90-30,90-20, and Micro I/O System
PLC I/O System
Model 30 I/O Modules
Catalog Pub Number Points Description
Input/Output Modules
Data Formats
Default Conditions for Model 30 Output Modules
Diagnostic Data
Catalog Pub Number Description
Model 20 I/O Modules
Global Data
Catalog Number Description Points
Micro PLCs
Fault Explanation and Correction
Section Title Description
Fault Handling
Fault Class Examples
Fault Summary
Fault Tables
Attribute Description
Fault Actions
Fault Action
Fault Action Response by CPU
Fault Reference Definitions
Side Effect Description
Accessing Additional Fault Information
PLC Fault Table Explanations
Fault Description
Fault Actions
Loss of, or Missing, Option Module
Reset of, Addition of, or Extra, Option Module
Daughterboard
System Configuration Mismatch
Option Module Software Failure
Low Battery Signal
Program Block Checksum Failure
Application Fault
Constant Sweep Time Exceeded
No User Program Present
Corrupted User Program on Power-Up
Password Access Failure
Informational
PLC CPU System Software Failure
Corrupted PLC Program Memory
Communications Failure During Store
O Fault Table Explanations
Diagnostic
Addition of I/O Module
Series 90-30/20/Micro Instructions Set
Relay Functions
Using Contacts
Type of Contact Display Contact Passes Power to Right
Function
Type of Coil Display Power to Coil Result
Using Coils
Types of Coils
Coil
Normally Open Contact
Normally Closed Contact
Negated Coil
Positive Transition Coil -−
Retentive Coil -M
Negated Retentive Coil -/M
Negative Transition Coil -↓
Reset Coil -R
SET Coil -S
Retentive SET Coil -SM
Retentive Reset Coil -RM
Links
Continuation Coils ---+ and Contacts +
Function Block Data Required for Timers and Counters
Timers and Counters
Abbreviation Function
Special Note on Certain Bit Operations
15 14 13 12 11 10 9 5 4 3 2 1
Ondtr
Parameter Description
Parameters
Valid Memory Types
Parameter Flow Const None
Const -PV
TMR
Parameters
Do DWL REL
Ofdt
EnableQ
Parameter flow %I %M %T %S %G %R AI %AQ const none
Upctr
Prtcnt
Dnctr
Countp
INT
Const
Math Functions
Abbreviation Function Description
Data Type Description
Standard Math Functions ADD, SUB, MUL, DIV
INT
I0001 Q0001
Math Functions and Data Types
Function Operation Displays as
Alwon
MOD INT, Dint
MOD
Sqrt INT, DINT, Real
I0001 Sqrt
Trig Functions SIN, COS, TAN, ASIN, ACOS, Atan
Acos in =
Enable
Logarithmic/Exponential Functions LOG, LN, EXP, Expt
Expt
Radian Conversion RAD, DEG
RAD
Relational Functions
Expanded Description
Function Description
BINFUL-I2
Range INT, DINT, Word
Word
Parameters
Range Truth Table Enable State L1 Value L2 Value
Constant
Bit Operation Functions
SHR
XOR
SHL
ROL
Or Word
WORD1 WORD2 Result
XOR Word
WORD3
Not Word
CAT -I1 Q-TAC
SHL and SHR Word
LEN
Length -N
ROL and ROR Word
R0001
Btst Word
PICKBIT-BIT
Bset and Bclr Word
SET
Bpos Word
POS
POS Word
If All Bits in I1 and I2 are the Same
Mskcmp WORD, Dword
If a Miscompare is Found
User logic to determine if a miscompare has occurred
I2 %M0017 = 606Fh = %M0033 = 000Fh =
I2 %M0017 = %M0033
Blkclr
Data Move Functions
Move
Shfr
Move BIT, INT, WORD, Real
Parameters
Before using the Move function
Blkmov INT, WORD, Real
Constant value -IN1 Q- output parameter Q
Enable IN1 IN7
Blkclr Word
BLK
Shfr BIT, Word
Parameters
Nxtcyc
Bitseq BIT
Memory Required for a Bit Sequencer
DIR
Step
Nxtseq
Command Block
Commreq
Command block has the following structure
Sysid
REQ
Table Functions
Arraymove INT, DINT, BIT, BYTE, Word
SNX
Const -SNX
00020
Input index -NX NX- output index
Contains the object of the search
I0001 Srch
Conversion Functions
BCD-4 INT
I0017-IN Q-%Q0033
INT BCD-4, Real
Total
Dint Real
R0017-IN Q-%R0001
Real INT, DINT, BCD-4, Word
Alwon INT Real
Word Real
I0002 REAL----------------RANGE
Trun INT, Dint
Real
Control Functions
Call
Doio
END
Input Example
Output Example
Enhanced do I/O Function for 331 and Later CPUs
Normal Doio Enhanced Doio Module Execution Time
Enable Control Block
SER
ParameterOffset Description
ParameterOffset Description
Status Extra Data
State Description
SER Notes
SER Data Block
Offset Parameter Description
GFK-0467K Series 90-30/20/Micro Instructions Set 119
Offset Register Parameter Description Value dec Value hex
GFK-0467K Series 90-30/20/Micro Instructions Set 121
Channel Number Channel Contents
Data Block
END
MCR
Differences Between MCRs and JUMPs
First + Endmcr
Endmcr
Jump
Non-nested Jump Nested Jump
Label
Example of a nested Label
Comment
Service Request Functions
Svcreq
GFK-0467K Series 90-30/20/Micro Instructions Set 133
Svcreq #1 Change/Read Constant Sweep Timer
∙ Disable Constant Sweep mode
Disable Constant Sweep mode Enable Constant Sweep mode
Ovswp
Mode Name Value Description
Svcreq #2 Read Window Values
Q0102
GFK-0467K Series 90-30/20/Micro Instructions Set 139
INT REQ Const -IN
Svcreq #4 Change System Comm. Window Mode and Timer Value
High Byte Low Byte
Word REQ
To Read the Current Word Count
Svcreq #6 Change/Read Number of Words to Checksum
To Set a New Word Count
Word INT
Svcreq #7 Change/Read Time-of-Day Clock
Const -+FNC
Parameter Block Contents
To Change/Read Date and Time Using BCD Format
Page
Svcreq #8 Reset Watchdog Timer
Svcreq #9 Read Sweep Time from Beginning of Sweep
Svcreq #10 Read Folder Name
Svcreq #11 Read PLC ID
Svcreq #12 Read PLC Run State
Svcreq #13 Shut Down Stop PLC
Svcreq #14 Clear Fault Tables
PLC Fault Table Output Format
Svcreq #15 Read Last-Logged Fault Table Entry
Fault Table Output Format
GFK-0467K Series 90-30/20/Micro Instructions Set 157
R0600
GFK-0467K Series 90-30/20/Micro Instructions Set 159
Svcreq #16 Read Elapsed Time Clock
Svcreq #18 Read I/O Override Status
Svcreq #23 Read Master Checksum
Svcreq #26/30 Interrogate I/O
Svcreq #29 Read Elapsed Power Down Time
Svcreq #46Fast Backplane Status Access
Read Extra Status Data Function #1
Location Field Meaning
Write Data Function #2
Read/Write Data Function #3
GFK-0467K Series 90-30/20/Micro Instructions Set 169
Word Const -IN
PID
IND
Parameters. Uses 40 %R words that cannot be shared
Register Parameter Low Bit Units Range of Values
PID Parameter Block
PID Parameters Overview
PLC
PID Parameters Overview
Operation of the PID Instruction
PID Parameters Details
Data Item Description
Bit
Internal Parameters in RefArray
PID Algorithm Selection Pidisa or Pidind and Gains
CV Amplitude and Rate Limits
Independent Term Algorithm Pidind
Sample Period and PID Block Scheduling
Determining the Process Characteristics
PVs/CVs = Gs = K * e **-Tp s/1 + Tc s
Setting User Parameters Including Tuning Loop Gains
Setting Loop Gains Ziegler and Nichols Tuning Approach
Sample PID Call
GFK-0467K Series 90-30/20/Micro Instructions Set 185
Instruction Timing
Execution Time Description
Table A-1. Instruction Timing
340/41 311
GFK-0467K Appendix a Instruction Timing
331 340/41
Function Enabled Disabled Increment
Group Function
Disabled
Table A-1 InstructionTiming
End Instruction Service Request #7 Read #7 Set #14
Table A-2. Instruction Sizes for 350 and 360 Series CPUs
Boolean Execution Speed
Instruction Sizes for 350 and 360 Series CPUs
Table A-3. Boolean Execution Speeds
Interpreting Fault Tables
PLC Fault Table
Rack
Long/Short Indicator
Spare
Slot
PLC Fault Group
Table B-1. PLC Fault Groups
Table B-2. PLC Fault Actions
Fault Action
Error Code
Table B-3. Alarm Error Codes for PLC CPU Software Faults
Plciscppcoverflow
Table B-4. Alarm Error Codes for PLC Faults
Comreq
Prgsyntaxerr
Table B-5. PLC Fault Data Illegal Boolean Opcode Detected
Fault Extra Data
PLC Fault Time Stamp
Table B-6. PLC Fault Time Stamp
Fault Table
Reference Address
Fault Address
Table B-7. I/O Fault Table Format Indicator Byte
Table B-8. I/O Reference Address
Table B-10. I/O Fault Groups
Fault Group
Point
Fault Actions for Specific Faults
Fault Specific Data
Symbolic Fault Specific Data
Table B-11. I/O Fault Actions
Fault Time Stamp
Table B-13. I/O Fault Time Stamp
Instruction Mnemonics
Function Instruction Mnemonic Group
GFK-0467K Appendix C Instruction Mnemonics
Key Sequence Description
Page
Print side 1 of GFJ-055C on this
Print side 2 of GFJ-055C on this
Floating-Point Numbers
Entered Displayed Description
Page
Internal Format of Floating-Point Numbers
Values of Floating-Point Numbers
Exponent e Mantissa f Value of Floating Point Number
Entered Displayed
Entering and Displaying Floating-Point Numbers
Invalid Entry Explanation
Neginf
Errors in Floating-Point Numbers and Operations
Posinf
Realindef
Operation Input Output Powerflow
General Case of Power Flow for Floating-Point Operations
Index
Editlock
Index
Commreq
EXP Exponential functions
Greater than function Greater than or equal function
Not equal function
Real
Signed integer
Sweep time calculation Sweep, PLC
Arraymove
Viewlock